

31st May 2025 (11 Topics)
Context
The United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA) has issued a grave warning that the entire population of Gaza is at risk of famine due to severe shortages of humanitarian aid. Despite Israel authorizing some aid trucks, bureaucratic and security barriers have restricted adequate supplies from entering Gaza, exacerbating an already dire humanitarian crisis.
Gaza Strip:
Geographical Location:
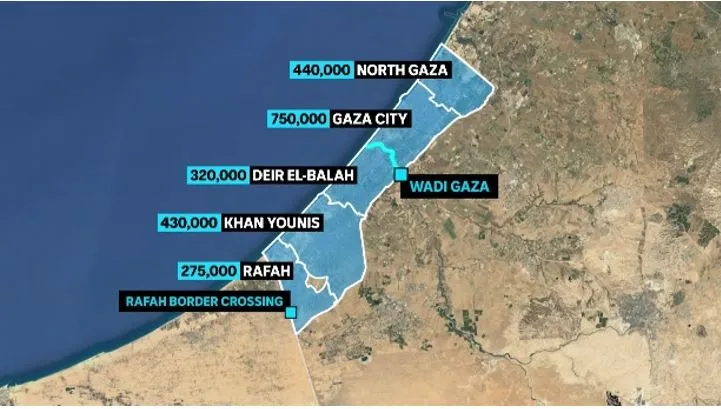
- The Gaza Strip lies in the eastern Mediterranean basin, bordered by Egypt (southwest), Israel (north and east), and the Mediterranean Sea (west).
- It is one of the world’s most densely populated areas, with over 2 million people residing in a very small territory.
Characterization:
- Often described as an “open-air prison” due to severe restrictions on movement, limited access to resources, and harsh living conditions imposed by surrounding borders.
Historical Background:
- 1967 Six-Day War: Israel captured Gaza from Egypt and began military occupation.
- 2005 Disengagement: Israel withdrew settlements from Gaza but maintained control over borders, airspace, and maritime access.
- 2007 Hamas Takeover: Following Hamas’s rise to power, Israel and Egypt imposed a strict blockade citing security concerns.
Border and Access Points:
- Gaza is surrounded by walls on three sides; the Mediterranean Sea forms the fourth side.
- Three key border crossings:
- Karem Abu Salem Crossing (Israel-controlled): Primarily for goods.
- Erez Crossing (Israel-controlled): Mainly for people.
- Rafah Crossing (Egypt-controlled): Main entry/exit point with Egypt.
United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (UN OCHA)Establishment:
Historical Context:
Key Tools and Mechanisms:
Funding Mechanisms:
|
More Articles

