

20th October 2023 (9 Topics)
Context:
A new study reveals the emergence of an "extreme heat belt" in USA which is likely to spread in other regions of the world by 2030.
What are Heat belts?
- “Extreme heat belt" -- with at least one day per year in which the heat index hits 125 Fahrenheit (52C).
- The developing "Extreme Heat Belt" forms a region of vulnerability for most of the states in US.
|
It was estimated that the extreme heat belt will expand from 50 counties in 2023 to more than 1,000 by 2053. |
Calculation of Heat Index:
- The Heat Index is a parameter that considers both temperature and humidity to calculate the apparent temperature or "feel like" temperature for human beings.
- It helps in understanding the impact of humidity on high temperatures and how it contributes to human discomfort during hot weather.
- The Heat Index has been launched on an experimental basis by the Indian Meteorological Department (IMD).
- It aims to provide general guidance for regions experiencing higher apparent temperatures causing discomfort to people.
Temperature belts of world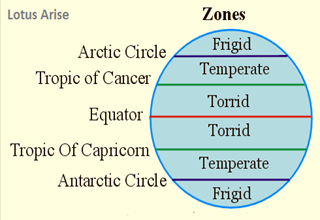
- The three major heat zones of the Earth are:
- Temperate Zone: This is the habitable heat zone of the Earth. There are two temperate zones lie in between in both 23½° to 66½° the hemisphere. These regions have moderate, tolerable temperatures.
- Torrid Zone: This is the hottest zone of the Earth. The region that lies from the Tropic of Cancer (23.5°N), across Equator (0°) to the Tropic of Capricorn (23.5°S) is considered the torrid zone (Tropical Zone). The Sun’s ray falls directly at least once a year.
- Frigid Zone: This is the coldest zone of the Earth. This area lies to the north of the Arctic circle (66.6°N) and to the south of the Antarctic circle (66.5°S) and is permanently frozen. There is no sunlight for most of the months is of the year in this zone.
- These are based on the distance they have from Equator. Frigid Zone
Importance of the Heat Zones
- This division of the Earth into different heat zones helps in understanding the climate changes and to study weather conditions across the world.
|
Mean Annual Temperature Distribution:
|
More Articles


