22nd April 2025 (9 Topics)
Context
The International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) reported that seasonal snowfall in the Hindu Kush-Himalayan (HKH) region is 23.6% below normal, the lowest in 23 years. This threatens water security for nearly two billion people dependent on snowmelt for freshwater.
Key Findings of the ICIMOD Report
- Snow persistence has dropped 6% below normal, continuing a three-year declining trend.
- Delayed and reduced snowfall observed across winter months (especially late start in January).
- Drought warnings issued across several countries.
- Snow loss in Mekong and Salween basins reached around 50%, affecting China and Myanmar.
- Impacts include:
- Reduced river flows
- Increased reliance on groundwater
- Greater risk of agricultural droughts and food insecurity
- Countries Affected: Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, China, India, Myanmar, Nepal, and Pakistan
- These nations are members of ICIMOD and depend heavily on glacial and snowmelt-fed rivers.
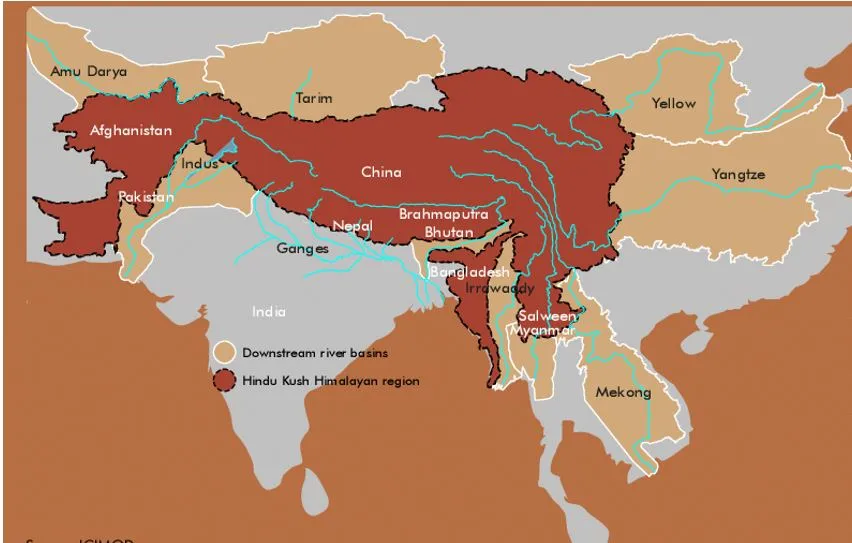
- The Hindu Kush-Himalayan (HKH) region spans Afghanistan to Myanmar, encompassing 12 major river basins including the Ganga, Brahmaputra, Indus, Salween, and Mekong.
- It is home to the third-largest ice and snow reserves in the world, after the Arctic and Antarctica.
- The region is often referred to as the "Third Pole" due to its vast cryospheric extent.
- Major rivers:It is the source of ten large Asian river systems – the Amu Darya, Indus, Ganges, Brahmaputra (Yarlungtsanpo), Irrawaddy, Salween (Nu), Mekong (Lancang), Yangtse (Jinsha), Yellow River (Huanghe), and Tarim (Dayan)
- India’s area: Entire territory of 11 mountain states (Assam, Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh, Manipur, Jammu & Kashmir (Indian administered area), Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim, Tripura, Arunachal Pradesh), & Darjeeling district of West Bengal state.
Implications
- Water Security: Melting snow contributes significantly to pre-monsoon river flows. Lower snowfall disrupts agriculture, hydropower, and drinking water supply in Himalayan foothill regions. Greater reliance on groundwater raises concerns of aquifer depletion.
- Food Security: Upcoming harvests at risk, especially rabi crops like wheat. Drought and water stress may lead to crop failures, impacting food supply and rural livelihoods.
- Climate Change: Declining snowfall reflects climate-induced anomalies. ICIMOD warns of "locked-in carbon emissions" making such anomalies recurrent.
Required Measures
- Regional Cooperation: Rivers in the HKH region are transboundary, needing joint water governance mechanisms. ICIMOD calls for:
- Improved water management
- Drought preparedness
- Early warning systems
- Regional collaboration
|
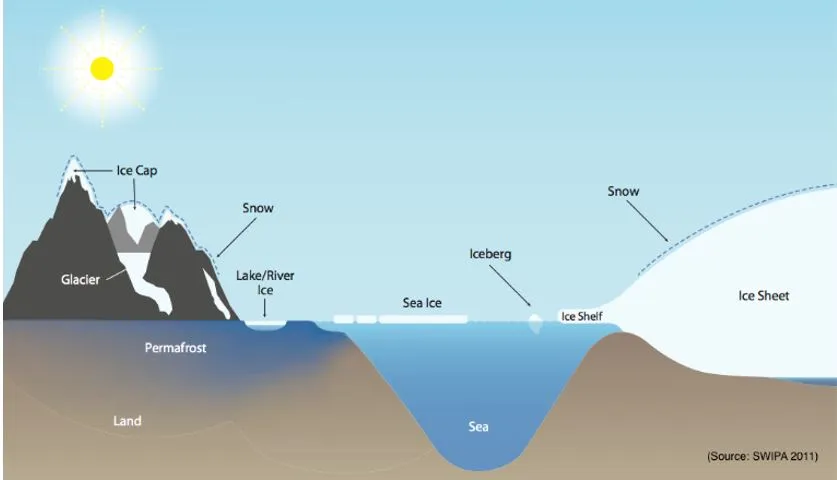
Fact-Box Cryosphere:
|