

21st March 2022 (6 Topics)
Context
India’s ‘Arctic Policy’ document was unveiled recently
About
About India's Arctic Policy:
- India's Arctic Policy aims to combat climate change and protect the environment.
- The document is titled 'India and the Arctic: building a partnership for sustainable development'.
- India’s Arctic Policy also aims to enhance the country’s cooperation with the resource-rich and rapidly transforming region.
- The policy is built on six central pillars-
- science and research
- climate and environmental protection
- economic and human development
- transportation and connectivity
- governance and international cooperation,
- National capacity building
- It was unveiled by Ministry of Earth Sciences.
|
Article Circle:
|
India’s engagement to Arctic Region:
- India's engagement with the Arctic began when it signed the Svalbard Treaty in February 1920 in Paris between Norway, the US, Denmark, France, Italy, Japan, the Netherlands, Great Britain, and Ireland, and the British overseas Dominions and Sweden concerning Spitsbergen.
- Ever since then, India has been closely monitoring all the developments in the Arctic region.
- India initiated its Arctic research program in 2007 with a focus on climate change in the region.
- The objectives included studying teleconnections between Arctic climate and Indian monsoon, to characterize sea ice in the Arctic using satellite data, to estimate the effect on global warming.
- India already has a research station in the Arctic, Himadri, for the research work.
- India received the ‘Observer’ country status in the Arctic Council in 2013.
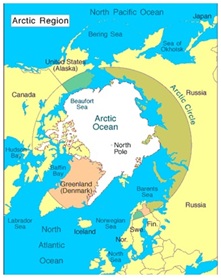
About Arctic Council:
- The Arctic Council is a high-level intergovernmental forum that addresses issues faced by the Arctic governments and the indigenous people of the Arctic.
- It was established through the Ottawa Declaration of 1996.
- Only states with territory in the Arctic can be members of the Council.
- It has eight member countries: Canada, the Kingdom of Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, Russia, Sweden, and the United States.
- India is one of the observer states along with China, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, South Korea, Netherlands, Poland, Singapore, Spain, and the United Kingdom.
- India was first granted the Observer status in 2013.
- As an Observer, India will not be allowed to take part in the active meetings but will participate in side events.


