

24th April 2025 (12 Topics)
Context
Prime Minister Narendra Modi visited Saudi Arabia to co-chair the second meeting of the India-Saudi Arabia Strategic Partnership Council. Modi also visited Jeddah (the first Indian Prime Minister in over 4 decades). The visit led to the signing of several Memoranda of Understanding (MoUs) and expansion of strategic cooperation, but was cut short due to a terror attack in Jammu and Kashmir’s Pahalgam.
Key-highlights of the visit:
- Strategic Partnership Council (SPC)
- The second meeting of the India–Saudi Arabia Strategic Partnership Council was co-chaired by Prime Minister Narendra Modi and Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman in Jeddah.
- The Council reviewed progress in key sectors such as defence, energy, trade, and cultural cooperation.
- The structure of the SPC was expanded from two to four ministerial committees, with the inclusion of new committees on Defence Cooperation and Tourism and Cultural Cooperation.
- MoUs and Agreements Signed
- Space Cooperation: A Memorandum of Understanding was signed between the Saudi Space Agency and the Department of Space, Government of India.
- Health Cooperation: An MoU was signed between the Ministry of Health of Saudi Arabia and the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India to strengthen health systems and managing public health risks.
- Anti-Doping Cooperation: A bilateral agreement was signed between the Saudi Anti-Doping Committee and India’s National Anti-Doping Agency.
- Postal Services: An MoU was signed between the Saudi Post Corporation and India Post.
- Defence and Security Cooperation
- A dedicated Ministerial Committee on Defence Cooperation was established under the Strategic Partnership Council framework.
- India and Saudi Arabia reaffirmed growing collaboration through joint military exercises such as SADA TANSEEQ and AL MOHED AL HINDI.
- A trilateral staff-level dialogue mechanism among the three armed services was initiated.
- Energy and Climate Cooperation
- Both countries agreed to work together to ensure the stability of global oil markets and improve mutual energy security.
- Joint collaboration was initiated in the areas of green hydrogen development, renewable energy technologies, and strategic petroleum reserves.
- Saudi Arabia reiterated its support for regional environmental initiatives such as the Saudi Green Initiative and the Middle East Green Initiative.
- Investment and Economic Engagement
- India and Saudi Arabia are collaborating on setting up two major refinery projects and resolving bilateral tax-related challenges.
- An “India Desk” was officially launched at the Saudi Public Investment Fund (PIF) to facilitate investor engagement.
- Both sides reaffirmed their commitment to finalizing the Bilateral Investment Treaty and initiating negotiations on the India-GCC Free Trade Agreement.
- The GCC bloc—comprising Saudi Arabia, UAE, Qatar, Kuwait, Bahrain, and Oman—represents a strategic economic zone for India.
Why Saudi Arabia is important for India?
- IMEC: Saudi Arabia sits at the heart of the IMEC corridor’s proposed land and maritime routes.
- The IMEC is a planned economic corridor that aims to bolster economic development by fostering connectivity and economic integration between Asia, the Persian Gulf and Europe.
- The corridor is a proposed route from India to Europe through the United Arab Emirates (UAE), Saudi Arabia, Israel and Greece.
- Energy: India and Saudi Arabia’s energy ties are foundational to the broader economic relationship. Saudi Arabia is a major oil supplier for India and is increasingly collaborating with India in areas like green hydrogen, refining, and petrochemicals.
- Saudi Arabia’s geographical position, investment capacity, and strategic importance give it a central role in India’s foreign policy. For India, engaging with Saudi Arabia strengthens its westward connectivity, elevates its global economic role, and helps craft a multipolar regional order.
What is the current state of India-Saudi Arabia relations?
- Diplomatic ties between India and Saudi Arabia were established in 1947.
- The relationship was elevated to a Strategic Partnership with the Delhi Declaration (2006) and Riyadh Declaration (2010) during PM Manmohan Singh’s visit.
- In 2019, PM Narendra Modi's second visit led to the formation of the Strategic Partnership Council (SPC) to institutionalize high-level engagement.
- Trade: India is Saudi Arabia’s second-largest trading partner, while Saudi Arabia is India’s fifth-largest. In FY 2023–24, bilateral trade reached USD 42.98 billion, with:
- Indian exports: USD 11.56 billion
- Indian imports: USD 31.42 billion
- Investment: Indian companies have invested approximately USD 3 billion in Saudi Arabia across IT, telecom, pharma, and construction. Saudi investments in India are led by the Public Investment Fund (PIF), with a total of USD 10 billion
- Saudi Arabia ranks 20th in FDI equity inflows into India (cumulative FDI: USD 3.22 billion, 2000–2024).
- Energy Partnership: In FY 2023–24, Saudi Arabia was:
- India’s 3rd largest source of crude oil (14.3% of total imports)
- 3rd largest supplier of LPG (18.2% of total LPG imports)
- Defence and Security Cooperation: The first joint land military exercise, EX-SADA TANSEEQ, was held in 2024.
- The bilateral naval exercise ‘Al Mohed Al Hindi’ has become a regular feature.
- The Indian community in Saudi Arabia (approx. 6 million) is the largest expatriate group, widely respected and preferred.
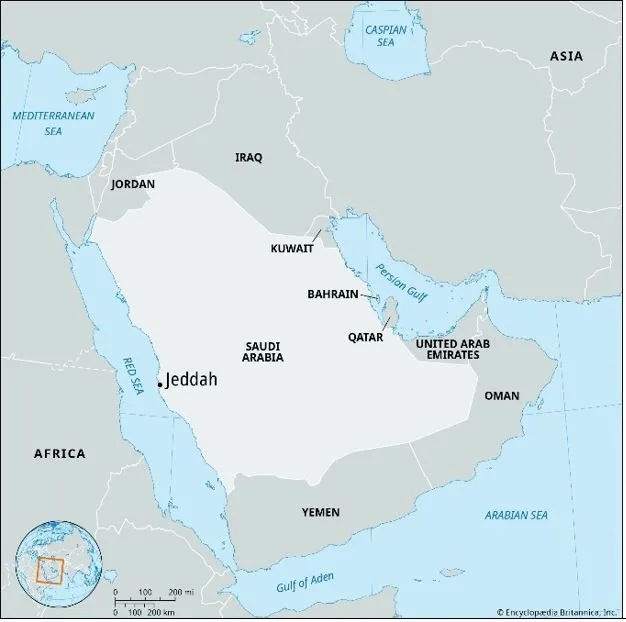
Fact Box: Jeddah
 |
PYQQ. Which of the following is not a member of ‘Gulf Cooperation Council’? (2016)
Solution: (a) Q. The question of India’s Energy Security constitutes the most important part of India’s economic progress. Analyse India’s energy policy cooperation with West Asian countries. (2017) |
More Articles


