24th June 2024 (12 Topics)
Context
Indian industry is urging the government to reconsider restrictions on Chinese Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and high import tariffs on electronics components, arguing that these measures hinder India's competitiveness in the global electronics market.
How India’s trade policy affect ‘competitiveness’?
- India’s trade policy has focused on relatively high tariff and low non-tariff measures compared to comparator economies.
- Both tariffs and non-tariff measures in India have become more restrictive in recent years.
- These restrictive trade policies introduce inefficiency in domestic production, thus affecting competitiveness, which in turn, adversely affects exports and imports.
- The 2020 measure has outlived its utility and needs review with adequate safeguards.
- Current restrictions send a message of non-friendly investment climate, hurting component ecosystem development.
- Global Competitiveness: High import duties make Indian electronic goods uncompetitive compared to Vietnam and China.
- Localization Impact: Tariffs haven't boosted local production of critical inputs as intended.
- Tariff Rationalization: Industry suggests bringing majority of tariff lines to 5% or lower to enhance competitiveness.
Role of government policies is fostering competitiveness
- Production-Linked Incentive (PLI): Government policies, especially the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI), have played a significant role in fostering competitiveness and attracting investments.
- While the PLI wasn’t explicitly designed for exports, its impact on domestic industries has indirectly contributed to enhanced global competitiveness.
- Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) play a pivotal role in facilitating exports, going beyond the reduction of tariff barriers.
- India has FTA with Sri Lanka, Bhutan, Thailand, Singapore, Malaysia, Korea, Japan, Australia, UAE, Mauritius and ASEAN (Association of Southeast Asian Nations).
- Foreign direct investment (FDI) plays a vital role in enhancing a country’s integration into Global Value Chains (GVC).
- National Policy on Electronics (NPE) 2019: This policy envisions India as the global epicenter for Electronic System Design and Manufacturing (ESDM).
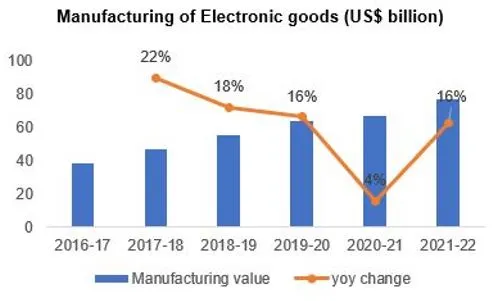
Electronic Systems Sector in India
|
Mains Practice Question
Q. "Discuss the implications of high import tariffs and FDI restrictions on India's electronics manufacturing sector. What measures can be taken to enhance the sector's global competitiveness?"