24th June 2024 (12 Topics)
Mains Issues
Context
The election of a new Speaker for the 18th Lok Sabha highlights the crucial role this position plays in India's parliamentary system. Understanding the duties and responsibilities of the Speaker is essential for comprehending the functioning of the lower house of Parliament.
Constitutional Provisions
- Presiding Officer: The Speaker serves as the presiding officer of the Lok Sabha, as stipulated in Article 93 of the Constitution, and is responsible for maintaining order during proceedings.
- Constitutional Functions: The Speaker certifies Money Bills under Article 110 and decides on disqualification of members under the Anti-Defection Law (Tenth Schedule).
- Rule Interpretation: The Speaker interprets and enforces the Rules of Procedure and Conduct of Business in Lok Sabha, making rulings on points of order and parliamentary procedures.
Administrative Responsibilities
- House Management: The Speaker oversees the functioning of the Lok Sabha secretariat and determines the agenda of the House in consultation with the Business Advisory Committee.
- Committee Appointments: The Speaker nominates members to various parliamentary committees and serves as the ex-officio Chairman of certain committees.
- Inter-Parliamentary Relations: The Speaker represents the Lok Sabha in international parliamentary forums and hosts visiting delegations from foreign parliaments.
Judicial and Quasi-Judicial Functions
- Privilege Matters: The Speaker adjudicates on matters of privilege and contempt of the House, issuing warrants for breach when necessary.
- Disqualification Proceedings: As the sole arbiter in cases of disqualification under the Anti-Defection Law, the Speaker conducts hearings and passes orders.
- Notice Admissibility: The Speaker decides on the admissibility of notices for various parliamentary devices like adjournment motions and calling attention notices.
Guardian of Parliamentary Privileges
- Rights Protection: The Speaker protects the rights and privileges of members and the House as a whole, ensuring equal opportunities for participation.
- Minority Rights: The Speaker safeguards the rights of the minority and opposition in the House, maintaining a balance of power.
- Impartiality: Despite being elected on a party ticket, the Speaker is expected to conduct proceedings in a fair and unbiased manner.
Mains Practice Question
Q: “Discuss the significance of the Speaker's role in maintaining parliamentary democracy and the challenges faced in ensuring impartiality.”
PYQQ. ‘Once a Speaker always a speaker’! Do you think this practice should be adopted to impart objectivity to the office of the speaker of Lok Sabha? What could be its implication for the robust functioning of parliamentary business in India? (150 Words) (2020) |


Mains Issues
Context
Indian industry is urging the government to reconsider restrictions on Chinese Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and high import tariffs on electronics components, arguing that these measures hinder India's competitiveness in the global electronics market.
How India’s trade policy affect ‘competitiveness’?
- India’s trade policy has focused on relatively high tariff and low non-tariff measures compared to comparator economies.
- Both tariffs and non-tariff measures in India have become more restrictive in recent years.
- These restrictive trade policies introduce inefficiency in domestic production, thus affecting competitiveness, which in turn, adversely affects exports and imports.
- The 2020 measure has outlived its utility and needs review with adequate safeguards.
- Current restrictions send a message of non-friendly investment climate, hurting component ecosystem development.
- Global Competitiveness: High import duties make Indian electronic goods uncompetitive compared to Vietnam and China.
- Localization Impact: Tariffs haven't boosted local production of critical inputs as intended.
- Tariff Rationalization: Industry suggests bringing majority of tariff lines to 5% or lower to enhance competitiveness.
Role of government policies is fostering competitiveness
- Production-Linked Incentive (PLI): Government policies, especially the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI), have played a significant role in fostering competitiveness and attracting investments.
- While the PLI wasn’t explicitly designed for exports, its impact on domestic industries has indirectly contributed to enhanced global competitiveness.
- Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) play a pivotal role in facilitating exports, going beyond the reduction of tariff barriers.
- India has FTA with Sri Lanka, Bhutan, Thailand, Singapore, Malaysia, Korea, Japan, Australia, UAE, Mauritius and ASEAN (Association of Southeast Asian Nations).
- Foreign direct investment (FDI) plays a vital role in enhancing a country’s integration into Global Value Chains (GVC).
- National Policy on Electronics (NPE) 2019: This policy envisions India as the global epicenter for Electronic System Design and Manufacturing (ESDM).
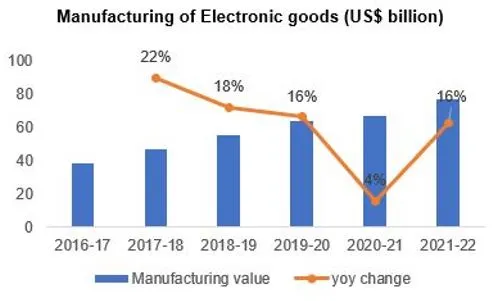
Electronic Systems Sector in India
|
Mains Practice Question
Q. "Discuss the implications of high import tariffs and FDI restrictions on India's electronics manufacturing sector. What measures can be taken to enhance the sector's global competitiveness?"


Mains Issues
Context
The European Union's proposed 'chat control' law, aimed at combating child sexual abuse online, has sparked controversy due to concerns over privacy and potential undermining of encryption.
Key-highlights of the Proposal
- Report Title: Regulation on combating child sexual abuse online
- Proposed by European Commissioner for Home Affairs Ylva Johansson in May 2022
- Allows for mass scanning of private messages by breaking end-to-end encryption
- France, Germany, and Poland have opposed the clause on encryption breaking
- Spain and Ireland's Interior Ministers have supported the proposal
- A network of children's rights advocates criticize EU leaders for inaction on child sexual abuse
Privacy Concerns
- End-to-end Encryption: Breaking encryption could create vulnerabilities exploitable by third parties, compromising user privacy.
- Mass Surveillance: The law could potentially be misused by governments for bulk surveillance of citizens.
- Precedent Setting: Implementation of such measures in the EU could encourage similar laws in less democratic countries.
Technical Challenges
- Feasibility Issues: Scanning encrypted messages without compromising security remains a technical challenge.
- False Positives: Mass scanning could lead to a high rate of false positives, causing unnecessary intrusions.
- Operational Costs: Implementing and maintaining such systems could be expensive for tech companies.
Impact on Tech Industry
- Company Resistance: Major tech firms and messaging apps threaten to leave markets if forced to implement such measures.
- Innovation Hindrance: Stringent regulations could stifle innovation in privacy-preserving technologies.
- Market Fragmentation: Differing regulations across regions could lead to fragmentation of digital services.
Who are Data Fiduciaries?
|
|
Mains Practice Question
Q. “Discuss the balance between ensuring online child safety and maintaining user privacy in the context of the European Union’s proposed 'chat control' law.”


Mains Issues
After years of delay, Russia has approved the draft of a mutual logistics agreement to be signed with India, marking a significant step in military-to-military cooperation between the two nations.
What is RELOS?
- The Reciprocal Exchange of Logistics Agreement(RELOS)is a long-awaited administrative agreement that would enable the militaries of both the countries(India and Russia) to access logistics and support facilities at each other’s bases and ports.
- It would facilitate the replenishment of fuel, rations, spare parts and berthing for troops, warships and aircrafts while operating away from home ports and bases during the war and peacetime missions.
- RELOS would further ensure smooth use of the host nation’s existing logistics networkswhich would reduce the overall costs of the mission and provide a strategic edge to each other’s military operations.
Scope of the Agreement
- Military Exchanges: Simplifies logistics for exercises, training, and port calls between the two militaries.
- Humanitarian Assistance: Facilitates cooperation in Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR) efforts.
- Operational Efficiency: Aims to improve operational turnaround and increase interoperability, especially for the Indian Navy.
Global Context
- Similar Agreements: India has signed comparable logistics agreements with several countries, starting with the U.S. in 2016.
- Mutual Benefits: These agreements have been advantageous for both parties involved.
- Maritime Focus: Indian Navy has been the biggest beneficiary of such administrative arrangements globally.
Significance for India:
Economic and Geo-Strategic significance:
Strategic Counterweight:
|
Mains Practice Question
Q: "Discuss the significance of the Reciprocal Exchange of Logistics Agreement (RELOS) between India and Russia. How does this agreement enhance bilateral defense cooperation and what measures are required for its effective implementation?"


Mains Issues
Context
The Indian government is considering the establishment of a global trade promotion body aimed at boosting exports from Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs).
Key-Highlights of the Proposal
- Proposal Title: Global Trade Promotion Organization (GTPO)
- Objective: To enhance MSME exports and address India’s rising trade deficit.
- Inspiration: Modeled after the Japan External Trade Organization and the Australian Trade and Investment Commission.
- Structure: The GTPO will have branch offices in major global economies.
- Functionality: It will assist MSMEs with registration, licensing, and certification for exports, and facilitate business opportunities in collaboration with Indian consulates abroad.
Reasons Behind the Initiative
- Trade Deficit: India's increasing trade deficit necessitates a strategic approach to boost exports, particularly from the MSME sector.
- Lack of Global Presence: Existing trade promotion bodies lack a robust international presence, which limits their effectiveness in promoting MSME exports.
- Economic Muscle: MSMEs often lack the resources to market their products internationally, and a dedicated trade promotion body can bridge this gap.
Expected Benefits for MSMEs
- One-Stop Solution: The GTPO will provide comprehensive support to MSMEs, from export documentation to market access.
- Increased Exports: By facilitating participation in global exhibitions, trade shows, and buyer-seller meets, the GTPO aims to increase MSME exports significantly.
- Economic Impact: Enhanced exports will contribute to reducing the trade deficit and boosting India's GDP, given that MSMEs contribute about 45% to the country’s total exports.
Challenges and Considerations
- Coordination: Effective coordination between the GTPO and various government ministries is crucial for the success of the initiative.
- Global Competition: Indian MSMEs will need to compete with well-established global players, necessitating high-quality products and competitive pricing.
- Sustainability: The GTPO must ensure sustainable growth for MSMEs without compromising on quality and ethical standards.
Broader Implications
- Employment: Enhanced MSME exports can lead to increased employment opportunities, supporting over 110 million people currently employed by the sector.
- Sectoral Growth: Specific sectors like handicrafts, textiles, ayurveda, leather goods, and imitation jewelry, which have significant global markets, can see substantial growth.
- Economic Diversification: Diversifying export markets will reduce reliance on a few countries and spread economic risk.
Required Measures for Effective Implementation
- Policy Support: The government must provide continuous policy support, including financial incentives and simplified regulatory processes.
- Capacity Building: Training and capacity-building programs for MSMEs will be essential to enhance their competitiveness in global markets.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Regular monitoring and evaluation of the GTPO’s performance will ensure that it meets its objectives and adapts to changing market conditions.
Fact Box: Schemes for MSMEs
|


Prelims Articles
Context
At least 1,301 people died during Hajj, Saudi Arabia says, mostly unauthorised pilgrims who walked long distances in intense heat.
About:
- The Hajj is a religious pilgrimmage to the holy city of Mecca in Saudi Arabia that is mandatory for all able-bodied Muslimswho can afford it. It is one of the Five Pillars of Islam and is considered a central part of Muslim religious life.
Five Pillars:
- Shahada (Faith): The declaration of faith in the oneness of God and the acceptance of Muhammad as God's prophet.
- Zakat (Charity):Giving a portion of one's wealth to those in need
- Salah (Prayer):Performing the five daily prayers facing the Kaaba in Mecca.
- Sawm (Fasting):Fasting during the month of Ramadan.
- Hajj (Pilgrimage):Making a pilgrimage to the holy city of Mecca at least once in a lifetime if one is physically and financially able.
Rituals:
- Ihram: State of spiritual purity marked by simple white garments.
- Tawaf and Sa’i: Circumambulation of the Kaaba and walking between Safa and Marwah.
- Day of Arafat: Standing in prayer and reflection.
- Muzdalifah and Mina: Collecting pebbles and symbolic stoning of the devil.
- Eid al-Adha: Festival of Sacrifice, animal sacrifice, and charity.
- Final Tawaf: Conclusion with a final circumambulation of the Kaaba.



Prelims Articles
Context
IUCN changes Iberian lynx’s status to ‘vulnerable’ from ‘endangered’ in conservation success story.
About
- The Iberian lynx (Lynx pardinus) is one of the four extant species within Lynx, a genus of medium-sized wild cats.
- Habitat: The Iberian lynx is endemic to the Iberian Peninsula in southwestern Europe.
- It inhabits Mediterranean scrubland, oak and cork oak forests, and grasslands.
- IUCN Status: Vulnerable
- CITES:Appendix II
- Threats: Habitat loss, hunting, and a decline in prey populations—particularly the European rabbit

Fact Box: About Mediterranean scrubland
|


Prelims Articles
Context
Researchers have reported the results of the rst attempt to measure the PFNS of induced ssion in Pu-240 with neutrons of energy greater than 0.85 MeV.
About
- 240Pu is a radioactive isotope with a half-life of 6,561 years. It decays primarily through alpha emission, with a small fraction undergoing spontaneous fission.
- 240Pu is produced as a byproduct in nuclear reactors through the neutron capture of 239Pu. In typical reactor-grade plutonium, 240Pu constitutes about 20-30% of the total plutonium content.
- In civilian nuclear power, the presence of 240Pu in reactor-grade plutonium affects fuel performance and reactor design. Its tendency for spontaneous fission increases neutron emission, which can complicate reactor control and fuel handling procedures.
- The presence of 240Pu is a crucial factor in weapons-grade plutonium. Its high rate of spontaneous fission can lead to premature detonation in nuclear weapons, reducing yield and reliability. For this reason, weapons-grade plutonium typically contains less than 7% 240Pu.


Editorials
Context
The recent collision involving the GFCJ container train and the Agartala-Sealdah Kanchanjunga Express, resulting in 11 fatalities and around 40 injuries, has raised critical questions about railway safety. Despite improvements, the Indian Railways faces significant challenges in achieving zero fatalities, and the need for a thorough examination of safety measures is pressing.
Safety Record and Financial Investments:
- Improvements in Safety: Efforts like closing unmanned level crossings and enhancing track maintenance have improved the safety record of Indian Railways. However, the goal of zero fatalities remains unmet.
- Government Investment: The Union government allocates nearly 25% of its total capital expenditure to railways, ensuring ample funding for safety works.
- Resource Availability: With substantial financial investments, the lack of resources can no longer be an excuse for safety lapses.
Issues with Blame and Communication:
- Pattern of Blame: Typically, lower-level functionaries such as train crews and station masters are held responsible for accidents, as seen in the current investigation by the Commissioner of Railway Safety (CRS).
- Premature Statements: The premature declaration by the Chairperson of the Railway Board about the causes of the accident and the status of the crew highlights issues in information management and communication.
- Insensitive and Erroneous Information: Incorrect statements, such as the erroneous announcement of the crew members' deaths, undermine credibility and sensitivity in crisis communication.
Technological and Managerial Challenges:
- Slow Implementation of Kavach: The slow rollout of Kavach, an indigenous signalling system designed to prevent collisions, is attributed to limited industrial capacity. However, it reflects a lack of focus on safety projects.
- Alternative Systems: The Indian Railways' decision to adopt Kavach over the European ETCS Level II system and the delays in its implementation suggest a need for re-evaluation of safety priorities.
- Safety-Critical Staffing: Overstaffing in non-critical areas contrasts with vacancies in safety-critical positions like loco pilots and signal maintainers, leading to overwork and stress among existing staff.
UPSC Mains Questions:
Q. Critically analyze the safety challenges faced by Indian Railways. Discuss the role of technological advancements like Kavach in mitigating these challenges.


Editorials
Context
India faces significant challenges in climate adaptation despite recent innovations in Digital Public Infrastructure and food security. Erratic climate patterns, extreme weather, and natural disasters threaten the country's progress. The need for effective climate adaptation strategies is critical to mitigate these risks and ensure sustainable development.
Challenges in Climate Adaptation:
- Diverse Climate Impacts: India experiences various climate impacts such as erratic monsoons, extreme heatwaves, rising sea levels, and increased frequency of natural disasters like floods and cyclones, affecting millions.
- Agricultural Dependency: With a large portion of the population relying on agriculture, climate change threatens food security and employment, making adaptation crucial for economic stability.
- Reactive Efforts: Existing initiatives like the National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC) are slow, fragmented, and underfunded, focusing more on prevention than adaptation, leaving communities vulnerable.
Implementation and Coordination Issues:
- Infrequent Meetings: The Prime Minister’s Council on Climate Change (PMCCC) meets infrequently and lacks adequate staffing, leading to ineffective implementation of climate strategies.
- State-Level Challenges: Local and state-level adaptation plans often lack coordination and resources, hindering their effectiveness in addressing climate change impacts.
- Economic Impact: Extreme weather affects economic productivity, especially for outdoor workers, with insufficient action on a cohesive framework to cope with extreme heatwaves and related health issues.
Strategic Recommendations for Effective Climate Adaptation:
- Aggressive Water Conservation: Implementing measures like strategic water reservoirs, inter-basin water transfers, and groundwater replenishment are essential to manage inconsistent rainfall.
- Climate-Resistant Agriculture: Developing climate change-resistant crops tailored to regional conditions can ensure agricultural resilience and food security.
- National Awareness and Action Plan: Engaging experts, incentivizing the private sector, and fostering innovation are crucial to developing frugal and local solutions for climate adaptation.
Policy and Governance Considerations:
Missing Institutional Design:
- Lack of Climate Legislation: India lacks formal climate legislation at both federal and state levels, impeding coordinated and effective climate action.
- Fiscal Constraints: Sub-national units often lack the capacity and fiscal resources to implement climate initiatives, despite being tasked with executing India’s international pledges.
- State Action Plans: Most state-level plans, including those for net-zero carbon emissions by 2070, lack committed leadership and adequate resources, resulting in minimal progress.
Role of Cooperative Federalism:
- Heat Action Plans (HAPs): While more states are adopting HAPs, only a few conduct vulnerability assessments and develop monitoring systems to ensure compliance and support affected communities.
- Long-Term Investments: Investing in reforestation, urban green cover enhancement, and long-term climate programmes is essential for sustainable urbanization and climate resilience.
- Finance Commission Priority: Making climate adaptation an agenda priority for the 16th Finance Commission can demonstrate a national commitment and drive cooperative federalism for effective climate action.
UPSC Mains Questions:
Q. Discuss the challenges faced by India in implementing effective climate adaptation


Editorials
Context
The push for ethanol as a green alternative to fossil fuels raises concerns about its true environmental impact. While it appears renewable and cleaner, several underlying issues challenge its sustainability and efficacy as an eco-friendly fuel.
Concerns Surrounding Ethanol Production:
- Energy Inefficiency: Ethanol production from sugarcane demands 4.99 megajoules per litre, with an energy return on investment (EROI) of only 4.26. This low EROI indicates that ethanol production is not as energy-efficient as other biofuels.
- Carbon Footprint: Despite a lower carbon footprint of 0.295 kg CO2 equivalent per litre compared to fossil fuels, the production and transportation of ethanol involve significant emissions, undermining its eco-friendly claims.
- Water Footprint: Ethanol production has a high water footprint of 1,344 litres per litre. In India, heavy reliance on groundwater for sugarcane irrigation exacerbates water scarcity, threatening both water and food security.
Impact on Agricultural Policy and Soil Health:
- Agricultural Policy Contradictions: The push for ethanol production conflicts with the crop diversification programme under the RKVY-Raftaar scheme, which aims to shift from water-intensive paddy to more sustainable crops. Increased ethanol production may lure farmers back to cultivating water-intensive crops, undermining these conservation efforts.
- Soil Degradation: Intensive sugarcane farming practices, such as monoculture, frequent tilling, and heavy use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides, degrade soil health. This leads to reduced agricultural productivity, waterlogging, soil compaction, and erosion.
- Biodiversity Loss: Monoculture reduces biodiversity, essential for maintaining soil structure and health, further exacerbating environmental degradation.
Food Security and Economic Implications:
- Competition for Land: Diverting agricultural land for biofuel production reduces the area available for food crops, leading to higher food prices and potential food shortages. This competition can result in decreased food crop production and increased food insecurity.
- Price Volatility: The World Bank reported that rapid biofuel expansion can cause food price spikes, making basic necessities less affordable for low-income households. Biofuel crop prices are influenced by both food and energy markets, making them susceptible to fluctuations in oil prices and energy policies.
UPSC Mains Questions:
Q. Analyze the potential risks of biofuel production on food security in India. Suggest policy interventions to ensure food security while supporting biofuel initiatives.