

27th August 2025 (18 Topics)
Context:
India has crossed 56.75 lakh registered EVs by February 2025, marking record adoption under flagship schemes like FAME-II, PM E-Drive, PLI, and PM e-Bus Sewa.
Policy Push for Electric Mobility
- National Electric Mobility Mission Plan (NEMMP 2020): Laid the foundation for EV adoption.
- FAME-I (2015–2019): Supported 2.55 lakh EVs and approved 520 charging stations.
- FAME-II (2019 onwards): With ?11,500 crore budget, supported over 16.29 lakh EVs and sanctioned 9,332 charging stations (8,885 installed by June 2025).
Major Flagship Schemes
- PLI-Auto (2021): ?25,938 crore outlay; attracted ?29,576 crore investment; created 44,987 jobs; requires 50% domestic value addition.
- PLI-ACC Battery Storage (2021): ?18,100 crore outlay; awarded 40 GWh capacity; 25–60% domestic value addition mandate.
- PM E-Drive (2024–28): ?10,900 crore outlay; subsidised 24.79 lakh e-2Ws, 3.15 lakh e-3Ws, 5,643 e-trucks, 14,028 e-buses, and e-ambulances.
Electric Buses and Public Transport
- PM e-Bus Sewa (2023): ?20,000 crore budget; target 10,000 e-buses; 7,293 approved by Aug 2025.
- PM e-Bus PSM (2024): ?3,435 crore outlay; supports 38,000 buses over 12 years with payment security mechanism.
Industrial Transformation
- Made in India EVs: Launch of Suzuki’s e-VITARA and localized hybrid battery electrode production.
- Global Hub Vision: India positioned as Suzuki’s export base for over 100 countries.
- SPMEPCI (2024): Incentivizes global automakers; requires ?4,150 crore investment and phased domestic value addition (25–50%).
Milestones and Targets
- EV Registration:75 lakh EVs (Feb 2025).
- Sales:49 lakh e-2Ws sold in FY 2024–25 (21% increase over previous year).
- Targets: 30% EV penetration by 2030; reduce carbon emissions by 1 billion tonnes; cut carbon intensity by 45% by 2030; net-zero by 2070.
- India Electric Mobility Index (IEMI, 2025): Assesses progress across states; Delhi, Maharashtra, Chandigarh lead as frontrunners.
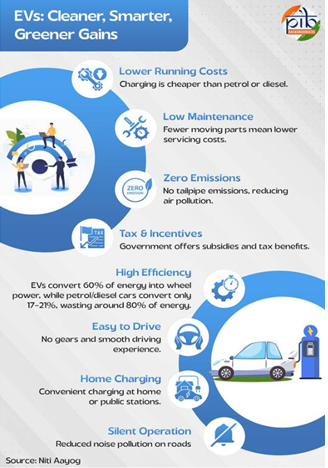
Achievements
- Strong policy ecosystem with multi-dimensional schemes (FAME, PLI, PM e-Bus Sewa).
- Rapid expansion of charging infrastructure (8,885 PCS installed by June 2025).
- Localization drive with >80% battery value manufactured in India.
- Significant employment generation and rise in women workforce participation in EV manufacturing.
Challenges
- High upfront costs of EVs compared to ICE vehicles.
- Battery supply chain dependence on imports for lithium, cobalt, and nickel.
- Charging ecosystem gaps in rural and semi-urban areas.
- Financial viability concerns for bus operators despite government support.
Way Forward
- Strengthening Supply Chains: Secure raw materials through international partnerships (e.g., Australia, Africa, Latin America).
- Affordable Financing Models: Incentivize banks and NBFCs for EV loans with lower interest rates.
- Grid Modernization: Integrate renewable energy with EV charging infrastructure.
- Technology & R&D Support: Encourage indigenous innovation in solid-state batteries and hydrogen fuel cells.
- Urban-Rural Balance: Expand EV incentives and infrastructure to smaller cities and rural areas.
More Articles


