26th July 2024 (8 Topics)
Illegal coal mining remains a significant issue in India, leading to severe consequences, including worker fatalities and environmental degradation. Despite national legislation governing coal mining, illegal activities continue to thrive, driven by economic, social, and regulatory factors.
Underlying Reasons for the Prevalence of Illegal Coal Mining:
|
Socio-Economic Factors |
Political Factors |
Regulatory Factors |
|
|
|
Impact of Illegal Coal Mining:
- Worker Safety: Lack of safety equipment and protocols exposes workers to severe health risks, including respiratory issues and toxic gas inhalation.
- Hazardous Conditions: Illegal mines lack proper structural support, making them prone to cave-ins, landslides, and explosions.
- Environmental Degradation: Unregulated mining activities lead to significant environmental damage, affecting local ecosystems and communities.
- Economic Impact: Illegal mining undermines legal mining operations and leads to substantial revenue losses for the government.
Required Measures
- Strengthening Regulatory Frameworks: The government must improve monitoring and enforcement of mining regulations in remote areas. It will enhance resources and capacity for regulatory agencies to effectively manage mining activities.
- Socio-Economic Development: Poverty and unemployment should be addressed in coal-rich regions through targeted economic development programs. Support alternative livelihoods to reduce dependence on illegal mining.
- Training and Safety Protocols: Government should implement comprehensive training programs for miners on safety procedures and emergency response. Ensure that safety equipment and protocols are enforced in all mining operations.
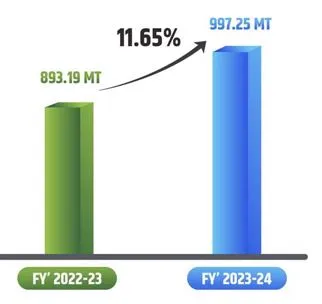
Fact Box: Coal Mining in IndiaIndia has the 4th largest coal reserves in the world, with significant deposits located in the eastern and central parts of the country, particularly in Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Odisha, West Bengal, Madhya Pradesh, and Andhra Pradesh. India's coal production reached 893.19 million tonnes in 2022-23. For 2023-24, production increased to 997.25 million tonnes, achieving an 11.65% growth. The coal sector contributes over Rs. 70,000 Crore annually to the central and state governments through royalties, GST, and other levies.
|
More Articles