

18th May 2022 (8 Topics)
Context
- A United Nations report has revealed that many parts of India fall under the list of regions that are vulnerable to drought
- The report also stated that India’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP) reduced by 2 to 5 per cent between 1998 and 2017 due to severe droughts in the country.
Analysis
What is Drought?
- Drought is deficient precipitation over a long period resulting in a water shortage causing adverse impacts on the human and larger ecological scenarios.
- Drought occurs from erratic rainfall and its distribution but the spread and intensity depend on factors such as surface and groundwater resources, agro-climatic features, crop choices, socio-economic vulnerabilities of the population, etc.
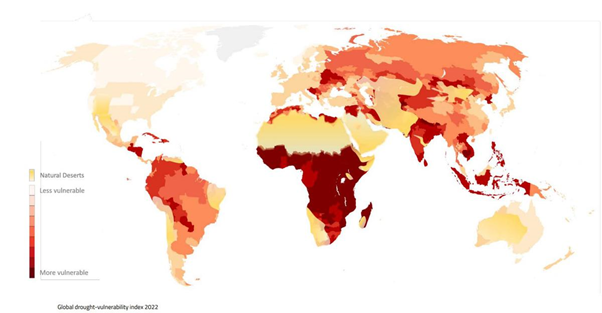
What are the concerns?
- According to World Bank estimates, drought conditions can force up to 216 million people to migrate by 2050.
- Other factors at play along with drought could be water scarcity, declining crop productivity, rise in sea levels, and overpopulation.
- Weather, climate and water hazards have accounted for 50 per cent of all disasters and 45 per cent of all reported deaths since 1970, World Meteorological Organisation data has revealed.
- Every Nine in ten of the deaths of disasters have occurred due to drought in developing countries.
- Between 2020 and 2022, 23 countries have faced drought emergencies.
About Drought in Numbers’ report
- The Drought in Numbers report is a collection of data on the effects of droughts on our ecosystem and how they can be mitigated through efficient planning for the future.
- The report also helps inform negotiations surrounding key decisions by the UNCCD’s 197 member parties at the 15th Conference of Parties (COP15), currently underway in Abidjan.
- Drought, land restoration, and related aspects such as land rights, gender equality and youth empowerment are among the top considerations at COP15.
|
What is COP 15?
|
Drought Profile of India
- Extreme Drought affected areas: Rajasthan, especially areas to the west of the Aravali hills and Kachchh regions of Gujarat.
- Severe Drought Prone Areas: Eastern Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Eastern parts of Maharashtra, interior parts of Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka Plateau, northern parts of Tamil Nadu and parts of Jharkhand and interior Odisha
- Moderate Drought Affected Area: Northern parts of Rajasthan, Haryana, southern Uttar Pradesh, parts of Gujarat, Maharashtra except the region of Konkan, Jharkhand and Coimbatore plateau and interior Karnataka.
National Commission on Agriculture in India classified droughts into:
- Meteorological drought occurs in case of rainfall deficiency and resulting water shortage
- Hydrological drought– the Water level in surface and subsurface water sources falls below specific levels
- Agricultural drought is characterised by 4 back to back weeks of meteorological drought
- Ecological drought is when the productivity of an ecosystem fails due to shortage of water.
Impacts of drought
- Human impacts: More than a billion people around the world were affected by drought in 2000-19, making it the second-worst disaster after flooding. Africa was the worst hit, with 134 droughts, of which 70 occurred in East Africa.
- The impact of drought is, however, not uniform across genders. Research shows that women and girls in emerging and developing countries suffer more in terms of education levels, nutrition, health, sanitation, and safety as a result of droughts.
- The burden of water collection also disproportionately falls on women (72 per cent) and girls (9 per cent). The report notes that they may spend up to 40 per cent of their caloric intake fetching water.
- Environmental impacts: According to a report, the global warming reaches 3° C by 2100, drought losses could be five times higher than today’s levels.
- The largest increase in drought losses is projected in the Mediterranean and the Atlantic regions of Europe.
- Australia’s mega drought in 2019-2020 contributed to “megafires” resulting in one of the most extensive losses of habitat for threatened species.
- About three billion animals were killed or displaced in the Australian wildfires.
- On a related note, 84 per cent of all terrestrial ecosystems are threatened by changing and intensifying wildfires.
- Social impacts:
- Widespread disruption in rural areas on account of migration of the population.
- Increasing school dropout rates.
- Greater indebtedness.
- Alienation from land and livestock assets.
- Loss of social status among the most vulnerable sections.
- Erosion of social capital.
|
Some drought management agencies in India
|


