

15th October 2022 (8 Topics)
Context
The country’s first ballistic missile nuclear submarine (SSMN) INS Arihant has carried out a successful launch of a Submarine Launched Ballistic Missile (SLBM) validating India’s second strike nuclear capability.
Background
-
- Arihant was launched on 26 July 2009, the anniversary of Vijay Diwas (Kargil War Victory Day).
- After extensive sea trials, on 23 February 2016, she was confirmed as ready for operations, commissioned in August 2016, and deployed operationally in 2018.
- In November 2019, India formally declared its nuclear triad, stated in its nuclear doctrine, operational. After INS Arihant has begun prowling. The deep seas carry ballistic missiles equipped with nuclear warheads.
Ballistic Missiles: A ballistic missile is a type of missile which uses projectile motion to deliver warheads on a target. These weapons are guided only during relatively brief periods. Key highlights of the launch
- The successful user training launch of the SLBM by INS Arihant is significant and proved crew competency and validation. The SSBN (Sub-surface ballistic nuclear) program. It is a key element of India’s nuclear deterrence capability.
- The missile was tested to a predetermined range and impacted. The target area in the Bay of Bengal with very high accuracy.
The Agni series of missiles constitute the backbone of India’s nuclear weapons delivery. Which also includes the Prithvi short-range ballistic missiles and fighter aircraft. About INS Arihant:
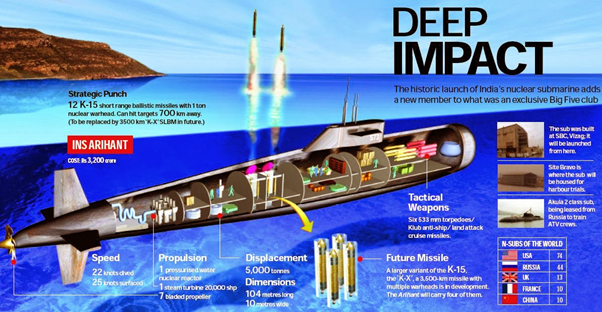
- INS Arihant (SSBN 80) is a Strategic Strike Nuclear Submarine. The lead ship of India's Arihant class of nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarines.
- The 6,000-tonne vessel was built under the Advanced Technology Vessel (ATV)
- Design: It has four vertical launch tubes, which can carry 12 (three per launch tube) smaller K-15 missiles or four larger K-4 missiles. The K-4 has a longer range of 3,500 km (2,200 mi).
- General Features:
- Length: 111 m
- Beam:15 m
- Speed: Submerged: 24 knots (44 km/h; 28 mph); Surfaced: 15 knots (28 km/h; 17 mph)
- Commissioned: August 2016
- Status: in active service
- Homeport: Visakhapatnam
India’s Nuclear Doctrine:
India’s nuclear doctrine can be summarized as follows:
- Building and maintaining a credible minimum deterrent;
- A posture of "No First Use" nuclear weapons will only be used in retaliation against a nuclear attack on Indian territory, or on Indian forces anywhere;
- Nuclear retaliation to a first strike will be massive and designed to inflict unacceptable damage.
- Nuclear retaliatory attacks can only be authorized by the civilian political leadership through the Nuclear Command Authority.
- Non-use of nuclear weapons against non-nuclear weapon states;
- However, in the event of a major attack against India, or Indian forces anywhere, by biological or chemical weapons, India will retain the option of retaliating with nuclear weapons;
- A continuance of strict controls on the export of nuclear. Missile-related materials and technologies, participation.
- In the Fissile Material Cut-off Treaty negotiations, and continued observance of the moratorium on nuclear tests.
- Continued commitment to the goal of a nuclear-weapon-free world, through global, verifiable, and non-discriminatory nuclear disarmament.


