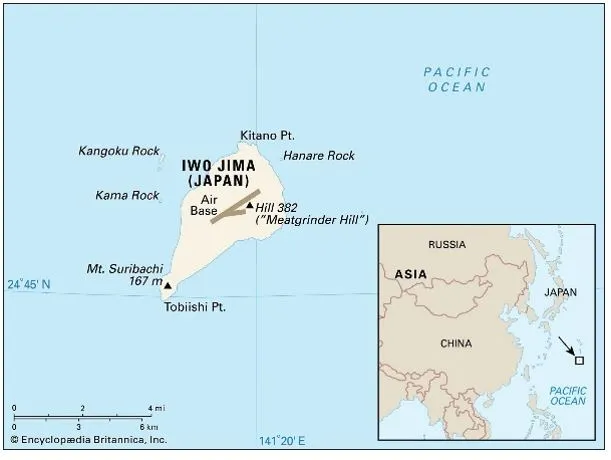
About Iwo Jima
- The Japanese island of Iwo Jima is part of the Volcano Islands archipelago, or group of islands.
- It lies in the western Pacific Ocean, about 760 miles (1,220 kilometers) south-southeast of Tokyo, Japan.
- This small volcanic island is a site of a strategic air base located between the Mariana Islands and Japan.
- Area: Just 8 square miles in size.
- Today the island is off-limits for civilians and decayed warship parts litter its brown beaches, while rust-covered abandoned tanks sit in lush greenery.
Fact Box: World War II (1939-1945)
- Factors Responsible for World War II:
- Treaty of Versailles: harsh conditions imposed on Germany after World War I led to resentment and economic hardship
- Rise of Fascism and Nazism: Dictatorial regimes in Germany (under Hitler) and Italy (under Mussolini) sought expansionist policies.
- Economic Turmoil: The Great Depression exacerbated tensions and weakened international cooperation.
- Participating Countries:
- Axis Powers: Germany, Italy, Japan (later joined by others like Hungary, Romania, and Bulgaria).
- Allied Powers: United States, United Kingdom, Soviet Union (after being invaded by Germany in 1941), China, France (after its liberation). India (as a part of the Allied Nations), sent over two and a half million soldiers to fight under British command against the Axis powers.
- Important Locations:
- Europe: Major battles were fought in France (Normandy, Battle of the Bulge), Germany (Berlin), Italy (Anzio, Monte Cassino), and Eastern Europe (Stalingrad).
- Pacific Theater: Significant battles occurred in Pearl Harbor, Midway, Guadalcanal, Iwo Jima, and Okinawa.
- North Africa: Key battles were fought in El Alamein and Tobruk.
- Outcome:
- Allied Victory: The Allies emerged victorious, leading to the defeat of Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy in Europe, and Imperial Japan in the Pacific.
- Formation of the United Nations: The war led to the creation of the United Nations, aimed at preventing future conflicts through international cooperation.
- Cold War: Tensions between the Soviet Union and Western Allies escalated, leading to the Cold War, characterized by ideological and political rivalries.
- Decolonization: The war hastened the decline of European colonial empires, leading to the independence movements in Asia and Africa.
|




