19th July 2022 (7 Topics)
Context
The first two cases of the Marburg virus, a highly infectious Ebola-like disease, have been confirmed officially by Ghana after test results were verified by a Senegal laboratory.
- This outbreak is only the second time that the disease has been detected in West Africa.
About
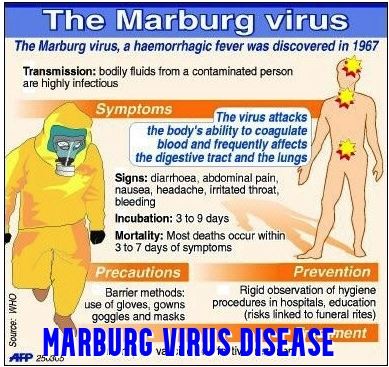
About Marburg virus disease:
- According to WHO, Marburg virus disease (MVD), earlier known as Marburg haemorrhagic fever, is a severe, often fatal hemorrhagic fever.
- Marburg, like Ebola, is a filovirus; and both diseases are clinically similar.
- Rousettus fruit-bats are considered the natural hosts for Marburg virus.
- However, African green monkeys imported from Uganda were the source of the first human infection.
- It was first detected in 1967 after simultaneous outbreaks in Marburg and Frankfurt in Germany; and in Belgrade, Serbia.
- The disease has an average fatality rate of around 50%.
Symptoms:
- Common symptoms of Marburg virus disease include- high fever, severe malaise, severe headache, Muscle aches and pains.
- Patients may also see severe watery diarrhoea, nausea & vomiting, abdominal pain & cramping on the third day following the contracting.
- These symptoms persist for a week.
Diagnosis
- It can be difficult to clinically distinguish Marburg virus disease (MVD) from other infectious diseases such as malaria, typhoid fever, shigellosis, meningitis and other viral haemorrhagic fevers.
- Confirmation that symptoms are caused by Marburg virus infection are made using the following diagnostic methods:
- antibody enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA);
- antigen detection tests;
- serum neutralization tests;
- reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) assay; and
- virus isolation by cell culture.
- Samples collected from patients are an extreme biohazard risk and laboratory testing on non-inactivated samples need to be conducted under maximum biological containment conditions.
- All biological specimens must be packaged using the triple packaging system when transported nationally and internationally.
Treatment
- No treatment or vaccine has been developed for Marburg, yet.
- Patients are treated through rehydration with oral or intravenous fluids.
More Articles