17th August 2022 (8 Topics)
Context
NASA's BioSentinel is likely to carry microorganisms to deep space to help scientists better understand the effects of deep space radiation on biological lifeforms.
About
What’s in the plan?
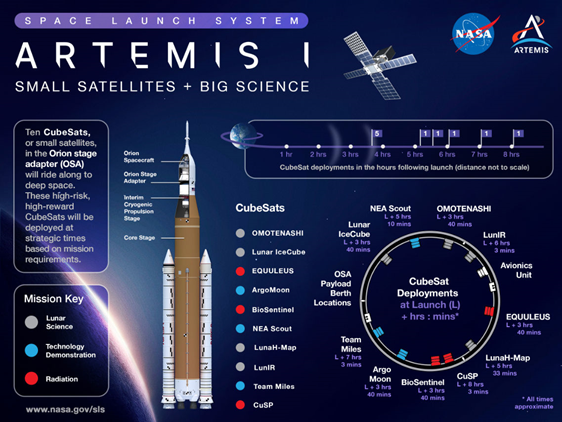
- BioSentinel, a shoebox-sized CubeSat, will carry microorganisms in the form of yeast into deep space so that scientists can fill critical gaps in the knowledge about the health risks of radiation in deep space.
- The primary objective of BioSentinel is to monitor the vital signs of yeast to see how the microorganisms fare when exposed to the radiation of deep space.
- A key component of BioSentinel’s mission is a novel biosensor.
- NASA refers to it as a “miniature biotechnology laboratory” that is designed to measure how living yeast cells respond to long-term space radiation exposure.
- It has a set of microfluidic cars, which allows the controlled flow of extremely small volumes of liquids, to provide a habitat for yeast, along with a way for scientists to observe them in real-time.
- The BioSentinel will carry a radiation detector instrument which characterises and measures radiation.

Why Yeast?
- Yeast cells have biological mechanisms that are similar to human cells, including DNA damage and repair.
- Due to this, scrutinising yeast in space will help us better understand the risks of space radiation to humans as the space agency plans missions to the Moon and beyond.
About NASA’s Artemis I Mission
- Artemis I is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions that will enable human exploration to the Moon and Mars.
- NASA’s Artemis mission is touted as the next generation of lunar exploration, and is named after the twin sister of Apollo from Greek mythology.
- Artemis is also the goddess of the moon.
- It is an uncrewed space mission where the spacecraft will launch on SLS, the most powerful rocket in the world.
- It will travel 2,80,000 miles from the earth for over four to six weeks during the course of the mission.
- The Orion spacecraft is going to remain in space without docking to a space station, longer than any ship for astronauts has ever done before.
- The SLS rocket has been designed for space missions beyond the low-earth orbit and can carry crew or cargo to the moon and beyond.
- The learnings from the Artemis programme will be utilised to send the first astronauts to Mars.