5th May 2022 (6 Topics)
Context
Recently a new study has shown that even a relatively weak jet from a supermassive black hole can clear the nuclear region of the galaxy of its gas, indicating that they may be playing an essential role in the evolution of their host galaxies.
About
About the study:
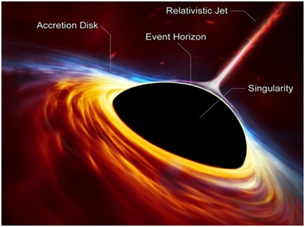
- Why? Supermassive black holes at the centres of galaxies are known to give rise to fast-moving jets of relativistic particles that can traverse large distances through the galaxy and beyond. The jets have long been suspected of driving the evolution of galaxies. However, it has so far remained just a suspicion.
- A new study by an international team of astronomers, including Dipanjan Mukherjee from the Pune-based Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics (IUCAA) has shown that even a relatively weak jet from a supermassive black hole can clear the nuclear region of the galaxy of its gas, indicating that they may be playing an essential role in the evolution of their host galaxies.
- The astronomers found the gas being steadily blown away from the galaxy’s central regions, pushed by the relativistic jet.
- Although the power of the jet observed in radio wavelengths was moderate, it was found to be still capable of clearing out nearly 75% of the central gas reservoir.
- It was the first unambiguous detection of a relativistic jet from a supermassive black hole removing the gas in a galaxy; the release said competing mechanisms that can also cause such outflows have been ruled out.
- The new results from this study provide definitive proof that relativistic jets can indeed substantially affect the host galaxy’s gas.
- This may have a significant impact on how and over what timescales stars are formed in such galaxies, which are topics of active current research
- This research showcases strong synergy between observational results and the simulations of relativistic jets interacting with a dense interstellar medium of a galaxy, carried out by Prof. Mukherjee in 2018.
About IUCAA:
- Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics (IUCAA), Pune was set up in 1988 as an autonomous centre of excellence to help initiate and nurture, research and developmental activities in Astronomy and Astrophysics in the University sector.
- IUCAA was set up with the basic purpose of providing advanced centralized facilities for subjects not adequately covered in the university departments and colleges.
- The IUCAA is set up to promote the nucleation and growth of active groups in Astronomy and Astrophysics at Indian universities.
- IUCAA aims to be a centre of excellence within the university sector for teaching, research and development in Astronomy and Astrophysics.
|
About Black Hole:
|