

5th May 2022 (6 Topics)
Context
NASA and the German Aerospace Center are permanently shutting down the Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy (SOFIA).
About
About Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy (SOFIA):
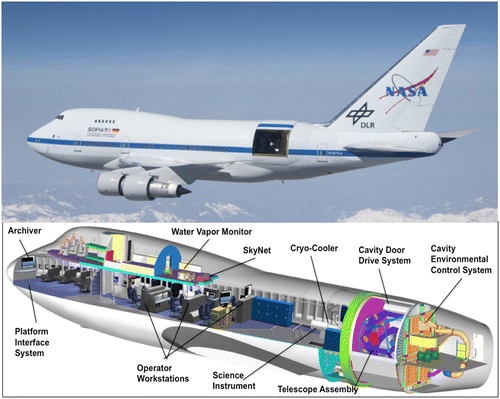
- SOFIA, the Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy, is a Boeing 747SP aircraft modified to carry a 7-meter (106-inch) reflecting telescope.
- Flying into the stratosphere at 38,000-45,000 feet puts SOFIA above 99 percent of Earth’s infrared-blocking atmosphere, allowing astronomers to study the solar system and beyond in ways that are not possible with ground-based telescopes.
- SOFIA is made possible through a partnership between NASA and the German Space Agency.
- It has made approximately 800 scientific flights since it became operational in
- SOFIA is designed to observe the infrared universe.
- Many objects in space emit almost all their energy at infrared wavelengths and are often invisible when observed with visible light.
Key discoveries of SOFIA:
- SOFIA has been collecting data to understand star birth and death and the formation of new solar systems.
- It has also been keeping a close eye on planets, comets and asteroids in our solar system, nebulas and galaxies, celestial magnetic fields and black holes at the centre of galaxies.
- In 2020, NASA announced that SOFIA discovered water molecules (H2O) on the sun-facing side of the Moon.
- The site is the Clavius Crater, located in the Moon’s southern hemisphere.
- SOFIA is the only instrument after Herschel that has the capability of observing singly ionized carbon, which is now understood to be an important tracer of the molecular gas in the local universe.
- SOFIA also identified atmospheric circulation patterns in Jupiter.
- It also mapped the magnetic field within G47, one of Milky Way’s spiral arms.


