

6th November 2023 (12 Topics)
Context:
It takes weeks to know drug resistance through culture, drug-resistant studies of H. pylori are seldom carried out in India; empirical treatment using clarithromycin drug is routinely used without knowing the drug-sensitivity.
Drug Resistant H. pylori Detection:
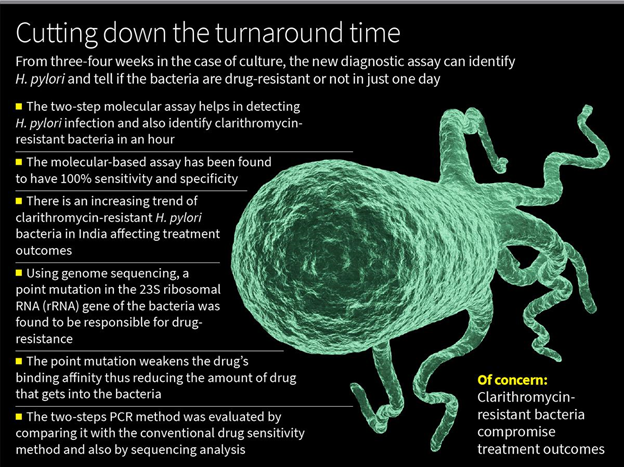
- A two-step PCR-based assay of a small region of the Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) bacteria can help detect H. pylori infection and also identify clarithromycin-resistant bacteria and those that are drug-sensitive in six-seven hours has been developed by a team of researchers from the National Institute of Cholera and Enteric Diseases (ICMR-NICED), Kolkata.
Time required culturing the H. pylori:
- Since H. pylori bacteria grow slowly, it takes about a week to culture the bacteria and a couple of more weeks to test for drug-sensitivity, which the new diagnostic assay bypasses.
- The molecular-based assay has been found to have 100% sensitivity and specificity.
Infections caused by H. pylori:
- Most of the infections caused by the bacterium H. pylori are asymptomatic, 10–15% of them develop peptic ulcer disorders or stomach cancer.
- In India, pylori infections affect 60-70% of the population. H. pylori infection is often acquired during childhood and remains in the stomach throughout life if not treated with antibiotics effectively.
- So, if someone suffers from gastroduodenal diseases along with the detection of H. pylori infection, eradication of the bacteria provides the most effective treatment.
- Importantly, pylori infection is one of the robust known risk factors for gastric cancer.
Genome Sequencing:
- The team from NICED turned to genome sequencing to identify that the drug resistance was due to a point mutation (A to G mutation at 2143 position) in the 23S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) gene of the bacteria.
- To confirm that the point mutation was indeed responsible for drug-resistance, the researchers isolated and amplified 617 base pairs that contained the point mutation and transferred the base pairs to drug-sensitive bacteria.
A two-step PCR-based test to detect H. pylori infection:
- The researchers developed a two-step PCR-based assay to first detect H. pylori infection and then to differentiate resistant isolates from sensitive ones directly from biopsy samples.
- In the initial step of PCR, the 617 base-pair segment containing the point mutation was amplified using DNA templates isolated from biopsy samples.
- In the second PCR step, 183 base pairs amplified by the first PCR step are used as a template.
- For the second PCR step, two allele-specific primer sets have been designed by exploiting the point mutation in the resistant strains.
- The clarithromycin-resistant strains will get amplified only by the resistant-specific primer and not with the sensitive-specific primer.
Significance of H. pylori test in India:
The two-steps PCR method was evaluated by comparing it with the conventional drug sensitivity method and also by sequencing analysis, which showed 100% sensitivity and specificity.
- A two-step PCR-based assay of a small region of the Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) bacteria can help detect H. pylori infection and also identify clarithromycin-resistant bacteria and those that are drug-sensitive in six-seven hours has been developed by a team of researchers from the National Institute of Cholera and Enteric Diseases (ICMR-NICED), Kolkata.
- In India, pylori infections affect 60-70% of the population. H. pylori infection is often acquired during childhood and remains in the stomach throughout life if not treated with antibiotics effectively.
- Bioinformatics study revealed that drug-resistant and drug-sensitive strains had very different binding affinity for the drug — the drug’s binding affinity to the mutant was weaker compared with drug-sensitive bacteria.
More Articles


