

4th June 2024 (11 Topics)
El Nino, the weather phenomenon known for contributing to record-high temperatures in 2023, has recently subsided. This transition paves the way for the onset of La Nina, a cooling phase. However, scientists caution that in the context of human-induced climate change, the cooling effect of La Nina may be minimal.
What is El Nino and La Nina?
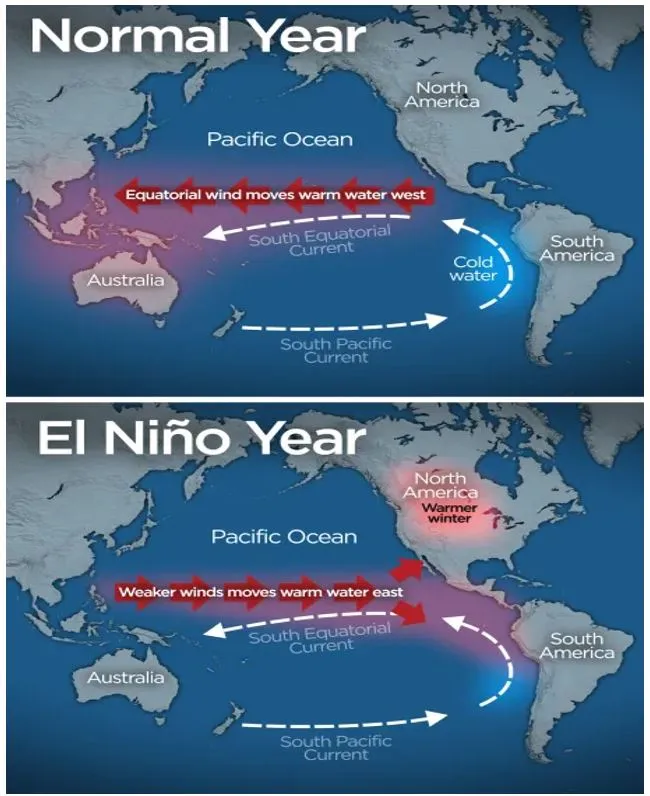
- El Nino and La Nina are two opposing climate trends that deviate from the normal conditions and normally run nine to twelve months, but can often extend.
- These events occur every two to seven years on average (El Nino is more frequent than La Nina), but not on a regular basis and together are referred to as the El Nino-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) cycle by scientists.
- El Nino is typically known as the warm phase (a band of warmer water spreading from west to east in the equatorial Pacific Ocean) and La Nina is identified as the cold phase (a band of cooler water spreads east-west) of ENSO.
- Both El Nino and La Nina can have global effects on weather, wildfires, ecosystems and economics.
El Nino:
- El Nino occurs every two to seven years and lasts nine to 12 months.
- It weakens trade winds across the tropical Pacific, leading to warmer ocean temperatures.
- This warming alters rainfall patterns and wind patterns globally, impacting weather conditions.
- El Nino years are often among the warmest on record due to the release of energy into the atmosphere.
- It typically results in drier conditions in southeast Asia, Australia, and parts of Africa, and wetter conditions in the Horn of Africa and the southern United States.
- Neutral Period:
- After El Nino dissipates, a neutral period ensues before La Nina begins.
- The neutral period may continue to experience above-normal temperatures as the global atmospheric circulation adjusts.
- Neutral conditions are forecasted to persist through July, with equatorial regions experiencing near-to-below normal temperatures.
La Nina:
- La Nina follows El Nino and lasts one to three years.
- It causes cooling of the eastern Pacific Ocean, leading to opposite effects on global weather compared to El Nino.
- La Nina brings wetter conditions to parts of Australia, southeast Asia, and Africa, while causing dry conditions in parts of South America.
- It can contribute to more severe Atlantic hurricanes.
- Despite La Nina's cooling effect, global temperatures are expected to remain high due to ongoing climate change.
Conclusion:
While the transition from El Nino to La Nina offers insights into global weather patterns, the influence of human-induced climate change complicates these natural phenomena.
As La Nina emerges, scientists continue to monitor its impact on weather conditions worldwide, emphasizing the ongoing challenge of mitigating the effects of climate change amidst natural climate variability.
PYQQ1: Most of the unusual climatic happenings are explained as an outcome of the El-Nino effect. Do you agree? (2014) Q2: La Nina is suspected to have caused recent floods in Australia. How is La Nina different from El Nino? (2011)
Which of the statement/s given above is/are correct?
Solution: (d) |
More Articles


