

4th June 2024 (11 Topics)
Mains Issues
El Nino, the weather phenomenon known for contributing to record-high temperatures in 2023, has recently subsided. This transition paves the way for the onset of La Nina, a cooling phase. However, scientists caution that in the context of human-induced climate change, the cooling effect of La Nina may be minimal.
What is El Nino and La Nina?
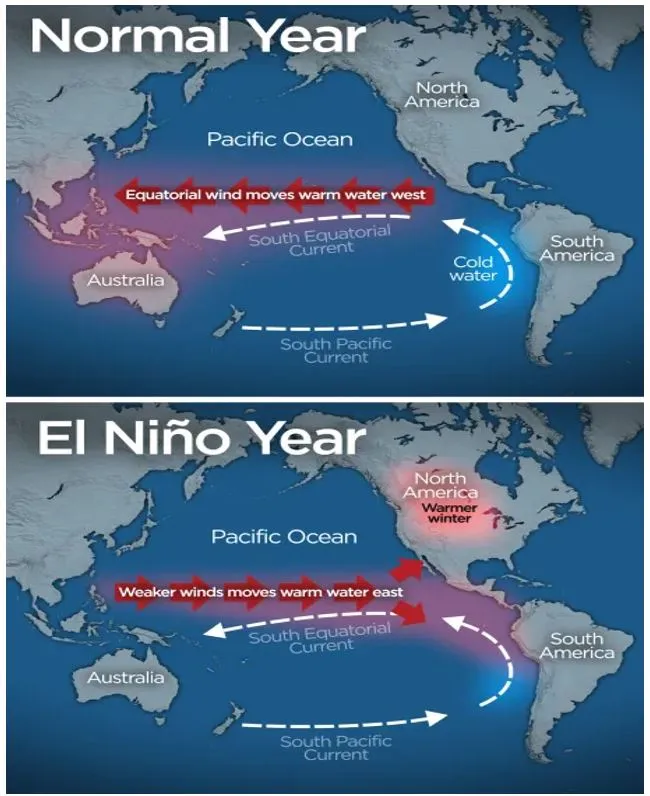
- El Nino and La Nina are two opposing climate trends that deviate from the normal conditions and normally run nine to twelve months, but can often extend.
- These events occur every two to seven years on average (El Nino is more frequent than La Nina), but not on a regular basis and together are referred to as the El Nino-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) cycle by scientists.
- El Nino is typically known as the warm phase (a band of warmer water spreading from west to east in the equatorial Pacific Ocean) and La Nina is identified as the cold phase (a band of cooler water spreads east-west) of ENSO.
- Both El Nino and La Nina can have global effects on weather, wildfires, ecosystems and economics.
El Nino:
- El Nino occurs every two to seven years and lasts nine to 12 months.
- It weakens trade winds across the tropical Pacific, leading to warmer ocean temperatures.
- This warming alters rainfall patterns and wind patterns globally, impacting weather conditions.
- El Nino years are often among the warmest on record due to the release of energy into the atmosphere.
- It typically results in drier conditions in southeast Asia, Australia, and parts of Africa, and wetter conditions in the Horn of Africa and the southern United States.
- Neutral Period:
- After El Nino dissipates, a neutral period ensues before La Nina begins.
- The neutral period may continue to experience above-normal temperatures as the global atmospheric circulation adjusts.
- Neutral conditions are forecasted to persist through July, with equatorial regions experiencing near-to-below normal temperatures.
La Nina:
- La Nina follows El Nino and lasts one to three years.
- It causes cooling of the eastern Pacific Ocean, leading to opposite effects on global weather compared to El Nino.
- La Nina brings wetter conditions to parts of Australia, southeast Asia, and Africa, while causing dry conditions in parts of South America.
- It can contribute to more severe Atlantic hurricanes.
- Despite La Nina's cooling effect, global temperatures are expected to remain high due to ongoing climate change.
Conclusion:
While the transition from El Nino to La Nina offers insights into global weather patterns, the influence of human-induced climate change complicates these natural phenomena.
As La Nina emerges, scientists continue to monitor its impact on weather conditions worldwide, emphasizing the ongoing challenge of mitigating the effects of climate change amidst natural climate variability.
PYQQ1: Most of the unusual climatic happenings are explained as an outcome of the El-Nino effect. Do you agree? (2014) Q2: La Nina is suspected to have caused recent floods in Australia. How is La Nina different from El Nino? (2011)
Which of the statement/s given above is/are correct?
Solution: (d) |


Prelims Articles
Context
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has developed Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) software named Parallel RANS Solver for Aerospace Vehicle Aero-thermo-dynamic Analysis (PraVaHa).
About PraVaHa:
- PraVaHa is a Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) software developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) at the Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC).
- It's designed to simulate airflow around various aerospace vehicles, including launch vehicles, re-entry vehicles with and without wings, and internal flows.
- Currently, it can simulate airflow under both Perfect Gas and Real Gas conditions. Work is ongoing to simulate chemical reactions during air dissociation and combustion, particularly relevant for scramjet vehicles.
Need of PraVaHa:
- PraVaHa is crucial for initial aerodynamic design studies of launch vehicles, as it evaluates numerous configurations efficiently.
- Aerospace vehicles face severe aerodynamic and aerothermal loads during launch and re-entry due to external pressure and heat flux. PraVaHa helps in understanding and predicting these loads.
- It's vital for designing the shape, structure, and Thermal Protection System (TPS) required for these vehicles.
- The software is also used to address issues like unsteady aerodynamics and acoustic noise generated during missions.
Significance:
- PraVaHa is expected to replace commercial software for most CFD simulations related to aerodynamic characterization.
- It's not only beneficial for ISRO's programs like Gaganyaan but also aids academia and other institutions working on missile, aircraft, and rocket design.
- In the Gaganyaan program, PraVaHa has been extensively used for the aerodynamic analysis of human-rated launch vehicles, including HLVM3, Crew Escape System (CES), and Crew Module (CM).
Practice MCQ:Q. What does ‘PraVaHa’ stand for in the context of aerospace technology?
Solution: (b) |


Prelims Articles
Context
The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) has embarked on a critical mission to combat sickle cell disease, a prevalent health concern in India.
A key obstacle in this fight is the lack of hydroxyurea formulations specifically designed for paediatric patients, making precise dosing a challenge.
To address this pressing issue, the ICMR has issued a call to collaborate on the joint development and commercialization of paediatric formulations of hydroxyurea.
About Sickle Cell Disease:
- Sickle cell disease is one of India's most prevalent monogenic disorders, posing substantial health risks.
- India faces a significant burden of sickle cell disease, with over 20 million affected individuals.
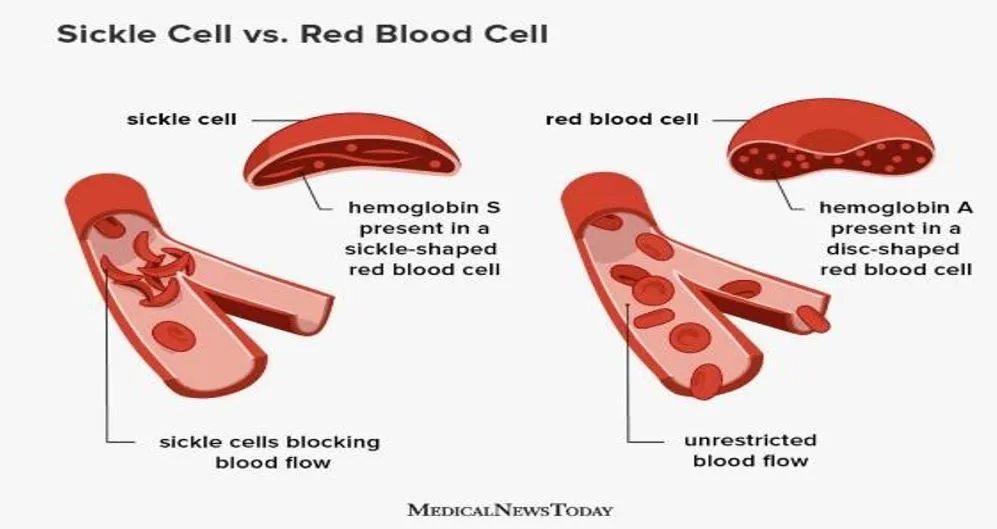
- It is an inherited blood disorder marked by defective hemoglobin.
- It inhibits the ability of hemoglobin in red blood cells to carry oxygen.
- Sickle cells tend to stick together, blocking small blood vessels causing painful and damaging complications.
- Symptoms: Anemia, Pain crisis, or sickle crisis, acute chest syndrome, splenic sequestration (pooling). stroke, jaundice, priapism (painful obstruction of the blood vessels in the penis by sickle cells)
- Treatment: Blood transfusions, Vaccinations and antibiotics, Folic acid, Hydroxyurea, Bone marrow transplant.
|
Red Blood Cells (normal Haemoglobin) |
Cells with Sickle Cell Haemoglobin |
|
They are smooth, disk-shaped, and flexible, like doughnuts without holes. |
They are stiff and sticky. When they lose their oxygen, they form into the shape of a sickle or crescent, like the letter C. |
|
They can move through the blood vessels easily. |
These cells stick together and can’t easily move through the blood vessels. This can block small blood vessels and the movement of healthy, normal oxygen-carrying blood. The blockage can cause pain. |
|
Normal red blood cells can live up to 120 days. |
Sickle cells only live for about 10 to 20 days. They may be destroyed by the spleen because of their shape and stiffness. The spleen helps filter the blood of infections. |
 |
|
Hydroxyurea's Role:
- Hydroxyurea, a myelosuppressive agent, shows promise in treating sickle cell disease and thalassemia.
- However, current hydroxyurea formulations are not suitable for paediatric use, complicating treatment protocols. This gap complicates treatment, as administering appropriate doses to children becomes cumbersome and less accurate.
- ICMR has now called for joint development and commercialization of low-dose or paediatric oral formulations of hydroxyurea.
- The aim is to facilitate better titration of the drug, reducing dose-related side effects and ensuring more accurate administration.
- This move aligns with the launch of the National Mission to eliminate Sickle Cell Anaemia/SCD by 2047, highlighting the government's commitment to tackling this health challenge.
Government Interventions
|
PYQQ. Consider the following statements in the context interventions being undertaken under Anaemin Mukt Bharat Strategy : (2023)
How many of the statements given above are correct?
Solution: (c) Statement 1 is incorrect: Prophylactic Iron Folic Acid supplementation (not Prophylactic calcium) given to children, adolescents, women of reproductive age and pregnant women, irrespective of anemia is a key continued intervention. |


Prelims Articles
Context
Recent research has delved into the fascinating phenomenon of altruism across various species, sparking interest among scientists seeking to unravel its genetic and behavioral underpinnings.
One notable area of investigation focuses on social amoebae like Dictyostelium discoideum, providing valuable insights into the evolution of cooperative behavior in nature.
Key-findings of the Research
- Studies on social amoebae, particularly Dictyostelium discoideum, have uncovered significant findings regarding the genetic basis of altruism.
- Researchers have identified "green-beard" genes that enable individuals carrying the same gene variant to recognize and cooperate with each other preferentially.
- Furthermore, mechanisms such as gene expression and protein binding have been observed to facilitate cooperation and deter exploitation within social groups of amoebae.
- Green-beard genes, named for their hypothetical ability to "recognize" and cooperate with others bearing the same gene, play a crucial role in fostering altruistic behavior.
- Alternatively, these genes can induce harmful behavior towards those with different gene variants.
- The Role of Tgr Genes: Two genes, tgrB1 and tgrC1, have been identified in Dictyostelium discoideum, which regulate altruistic behavior. These genes facilitate cell recognition and cooperation, ensuring that altruistic amoebae recognize and cooperate with their kin.
- These findings not only shed light on the genetic mechanisms driving altruism but also offer broader insights into the evolution of cooperation and sociality across diverse species.
Fact Box: About Altruism:
|
Practice MCQ :Q: What are "green-beard" genes, as discussed in the context of social amoebae research?
Solution: (B) |


Prelims Articles
Context
The Preston Curve illuminates a crucial relationship between life expectancy and per capita income in countries worldwide. Preston's groundbreaking research revealed a pattern where wealthier nations generally enjoy longer life spans compared to their less affluent counterparts. This connection underscores the profound influence of economic prosperity on public health outcomes.
About the Preston Curve:
- Proposed by: American sociologist Samuel H. Preston in 1975
- The essence of the Preston Curve lies in its observation that as a country's per capita income increases, so does its average life expectancy.
- This correlation is attributed to various factors associated with higher income levels, including
- improved access to healthcare
- better education
- cleaner environments
- enhanced nutrition
- For instance, India's journey from an average per capita income of Rs 9,000 in 1947 to approximately Rs 55,000 in 2011 corresponded with a remarkable increase in life expectancy from a mere 32 years to over 66 years.
- Patterns in Development Indicators: The Preston Curve extends beyond life expectancy, encompassing a range of development indicators such as infant and maternal mortality rates, education, and healthcare access. These indicators tend to improve alongside rising per capita income, reflecting broader societal advancements facilitated by economic growth.
- Debates and Perspectives: Despite the compelling correlation between income levels and development outcomes, experts diverge on the causal relationship between the two.
- Some economists advocate for prioritizing economic growth as the pathway to improving development indicators, citing examples like India and China's rapid progress.
- However, others argue that improvements in life expectancy and other indicators are not solely driven by economic growth. Instead, advancements in medical technology, including life-saving vaccines, play a significant role in enhancing public health even in low-income settings.
Fact Box:
|
Related PYQQ. Increase in absolute and per capita real GNP do not connote a higher level of economic development, if
Solution: (c) |
Practice MCQsQ:What does the Preston Curve primarily illustrate?
Solution: (b) |


Prelims Articles
Context
Chinese firms aiming for offshore listings have hit a regulatory roadblock, leading to prolonged delays and lower valuations. Despite Beijing's pledge to ease the process and positive market indicators, the IPO drought persists, hindering capital raising in a slowing economy.
About Offshore Listings:
- Offshore listings are critical fundraising channels for Chinese companies. These deals also account for a bulk of the revenue global investment banks make in Asia.
- These listings not only provide access to global capital markets but also contribute significantly to the revenue of investment banks operating in Asia.
Fact Box: Initial Public Offering (IPO)
|


Prelims Articles
Context
Shriram Finance Ltd. (private non-banking financial company (NBFC)), has recently announced the raising of funds totaling $425 million and EUR 40 million through a syndicated term loan transaction.
The three-year external commercial borrowing facility was structured as a social loan.
About External Commercial Borrowings (ECBs)
- ECBs are commercial loans obtained by eligible resident entities from recognized non-resident entities. These loans serve as a source of funding for various business activities.
- Parameters: ECBs must adhere to specific parameters, including minimum maturity periods, permitted and non-permitted end uses, maximum all-in-cost ceiling, and other regulatory requirements.
- Routes for ECBs: ECBs can be raised through either the automatic route or the approval route, depending on certain criteria.
- Approval Route: Under the approval route, prospective borrowers submit their requests to the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) through an Authorized Dealer (AD) category-I Bank.


Prelims Articles
|
S.No. |
Term |
About |
|
1. |
Gross domestic product (GDP) |
GDP is the value of the finished domestic goods and services produced within a nation's borders. |
|
2. |
Gross national product (GNP) |
GNP is the value of all finished goods and services produced by a country's citizens, both domestically and abroad.15 |
|
3. |
Gross Value Added (GVA) |
GVA is the value of goods and services produced in a country minus input costs, including raw materials. It adjusts GDP by adding subsidies and deducting taxes on products. |
|
4. |
Non-Banking Financial Company (NBFC) |
NBFC is a company registered under the Companies Act, 1956 engaged in the business of loans and advances, acquisition of shares/stocks/bonds/debentures/securities or other marketable securities. It does not have a full banking license and cannot accept deposits from the public. |


Editorials
Context
The debate surrounding property rights has a rich history, especially in the post-colonial era. The right to property, initially considered a fundamental right and later a constitutional right, has been a subject of contention between courts and legislatures.
Controversy Surrounding Property Rights:
- Introduction to the Issue: Property rights in India have experienced significant changes, especially regarding the interpretation and application of compensation for property acquisition. This has led to a complex legal history involving the judiciary and legislature.
- Debate Over Compensation: Initially, the Supreme Court of India interpreted compensation in Article 31(2) of the Constitution as "a just equivalent of what the owner has been deprived of," leading to several amendments by the legislature to limit judicial scrutiny over compensation.
- Word Substitution: The Constitution (Twenty-Fifth Amendment) Act, 1971 replaced the word "compensation" with "amount," intending to prevent courts from questioning the adequacy of compensation, which was a strategic move to facilitate property acquisition by the state.
Global Gender Gap Concerns and Policy Implications:
- Widening Gender Gap: The debate over property rights has parallels in discussions on gender equality, highlighting how legal and policy changes can impact marginalized groups differently.
- Impact on Property Ownership: The shift from fundamental to constitutional rights for property ownership reflects broader policy implications, similar to how gender-based policies can influence workforce participation and social equity.
- Concerns Over Social Stigma: Ensuring fair compensation for property acquisition without perpetuating social stigma is crucial, akin to addressing menstrual health without reinforcing gender stereotypes.
Challenges of Implementation and Ensuring Inclusivity:
- Implementation Hurdles: Implementing fair compensation for property acquisition involves significant challenges, including ensuring transparency, accountability, and adherence to principles of natural justice.
- Enforcement Challenges: Misuse or inappropriate enforcement of property acquisition laws can lead to public distrust and legal challenges, highlighting the need for robust legal frameworks and enforcement mechanisms.
- Promoting Inclusivity and Individual Support: Recognizing diverse property ownership experiences and tailoring support to individual needs is essential for fostering an equitable legal environment, similar to promoting inclusivity in gender-related policies.
UPSC Mains Questions
Q. Discuss the evolution of property rights in India, focusing on the constitutional amendments and their implications on the right to compensation. How has judicial interpretation influenced these changes?


Editorials
Context
As India grapples with its health-care landscape, cost considerations play a pivotal role in shaping service delivery and patient care. Equitable and sustainable health-care policies are crucial to address disparities and ensure access for all.
Controversy Surrounding Healthcare Costs:
- Introduction to the Issue: Healthcare costs in India are increasingly influencing service delivery and patient care, necessitating discussions on rate-setting to ensure equitable access and quality care.
- Debate Over Price Caps: While affordability is crucial, imposing uniform price caps on medical procedures could compromise healthcare quality and slow down advancements in medical technology and treatments.
- Impact of Financial Pressure: Studies indicate that hospitals under financial strain due to price caps report increased patient dissatisfaction and hinder the development of new treatments, highlighting the need for balanced pricing strategies.
Global Gender Gap Concerns and Policy Implications:
- Broader Economic Implications: Properly implemented rate standardization can reduce healthcare disparities, but it is vital to maintain the economic stability of healthcare providers to ensure sustained quality care.
- Dynamic Pricing Models: International examples, like Thailand's tiered pricing system, offer insights into balancing cost and care by adjusting prices based on medical complexity and patient financial status, which could be adapted for India's diverse economic landscape.
- Legal and Regulatory Challenges: Effective healthcare cost management requires legislative reforms tailored to local demographic and economic conditions, emphasizing the need for robust legal frameworks to support rate standardization and high-quality care.
Challenges of Implementation and Ensuring Inclusivity:
- Technology Integration: Advanced technologies, such as telemedicine and AI, are revolutionizing healthcare by improving diagnostics, care coordination, and reducing costs, particularly in remote areas.
- Innovations in Chronic Condition Management: Mobile health apps and wearable devices play a crucial role in managing chronic conditions outside hospitals, cutting costs, and enhancing patient outcomes. Ensuring these technologies reach all population segments is essential for widespread impact.
- Role of Data in Policy Shaping: Data-driven insights are crucial for informed healthcare policy decisions, helping to set nuanced rate frameworks and foresee the long-term impacts of rate fixation on healthcare innovation and accessibility.
UPSC Mains Questions
Q. Examine the role of technology in transforming healthcare delivery in India. How can telemedicine and AI be integrated to improve access and reduce costs in remote areas?


Editorials
Context
The Agnipath scheme implication on India's defence pensions, military effectiveness, and the broader socio-political landscape is under intense debate. It highlights the urgent need for reforms to address the rising defence pension expenditure and ensure sustainable military modernization.
Controversy Surrounding the Agnipath Scheme:
- Introduction to the Issue: The Agnipath scheme, has sparked significant political debate, particularly in the context of upcoming Lok Sabha elections. The scheme involves a four-year enlistment for soldiers, known as Agniveers, and aims to reduce defence pension costs.
- Political Stances: The opposition opposes the Agnipath scheme, promising to abolish it if elected, while the current government supports it as a means to provide employment opportunities for the youth and strengthen societal ties with the military.
- Impact on Military Modernization: The scheme's primary goal is to curb the burgeoning defence pension bill, which hampers funds available for military modernization. However, concerns about its impact on military effectiveness and the lack of a comprehensive solution for post-service employment remain.
Global Gender Gap Concerns and Policy Implications:
- Rising Pension Costs: Defence pension expenditure has been a growing concern for decades, with costs escalating significantly. The Kargil Review Committee Report (1999) and other studies have highlighted the unsustainable nature of these expenses.
- Proposed Solutions: Various solutions, such as lateral induction of military personnel into Central Armed Police Forces (CAPFs) and other government services, have been proposed but have not been implemented due to bureaucratic and attitudinal challenges.
- Immediate Need for Reform: The implementation of the One Rank One Pension (OROP) scheme further increased pension costs. Immediate action is required to address this issue, with proposals for lateral movement of armed forces personnel into national security roles offering potential savings and efficiency improvements.
Challenges of Implementation and Ensuring Inclusivity:
- Technological Integration: Advanced technologies, such as telemedicine and AI, are revolutionizing healthcare by improving diagnostics, care coordination, and reducing costs, particularly in remote areas.
- Innovations in Chronic Condition Management: Mobile health apps and wearable devices play a crucial role in managing chronic conditions outside hospitals, cutting costs, and enhancing patient outcomes. Ensuring these technologies reach all population segments is essential for widespread impact.
- Role of Data in Policy Shaping: Data-driven insights are crucial for informed healthcare policy decisions, helping to set nuanced rate frameworks and foresee the long-term impacts of rate fixation on healthcare innovation and accessibility.
UPSC Mains Questions
Q. Critically analyze the Agnipath scheme in the context of India's defence pension expenditure. How can lateral induction of military personnel into other government services serve as a solution to the burgeoning pension costs?




