- For the 1st time, three new migratory birds form East Asia have been spotted in Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
- The migratory birds spotted were Horsfield’s Bronze Cuckoo, Zappey’s Flycatcher and Javan Pond Heron.
- The Andaman and Nicobar island area is an essential stop over for migratory birds following the East Asian-Australasian Flyway.
Context
- For the 1st time, three new migratory birds form East Asia have been spotted in Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
- The migratory birds spotted were Horsfield’s Bronze Cuckoo, Zappey’s Flycatcher and Javan Pond Heron.
- The Andaman and Nicobar island area is an essential stop over for migratory birds following the East Asian-Australasian Flyway.
About
- A number of new sightings has increased post the 2004 Indonesian tsunami. The new records include the Mugimaki Flycatcher (Ficedulamugimaki), Blue-winged Pitta (Pitta moluccensis), Chinese Egret (Egrettaeulophotes) and the Chinese Paradise Flycatcher (Terpsiphoneincei).
- During their migration from north to south, these birds make a stopover at the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
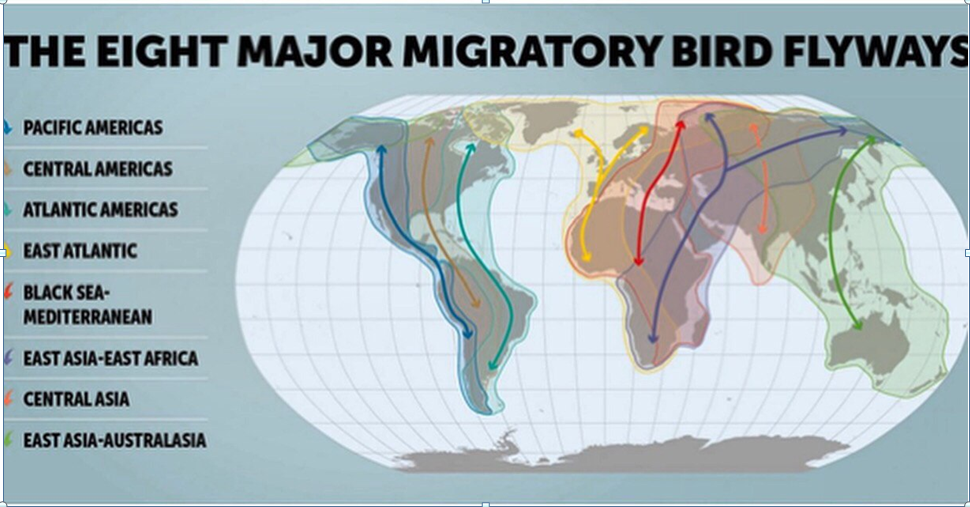
- These birds use Andaman and Nicobar Islands for a few week rest before they can fly along the East Asian-Australasian Flyway (EAAF). The EAAF extends from Arctic Russia and North America to the south Australian boundaries and includes the most of the east Asian regions including Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands, with just about 0.25 % the country’s landmass, is home to about 350 species of exotic birds, according to an official estimate.
- Horsefield’sBroze Cuckoo (ChalsitesBasalis)
- Green and brown plumage on its back
- Tiny bird – 15 cm and 22 g
- Famous for its repeated, loud and piercing whistle.
- Zappey’s Flycatcher (Cyanoptilacumatilis)
- Song bird that breeds in China and spends the winters in the Malay peninsula, Sumatra and Java
- Java Pond Heron (ArdeolaSpeciosa)
- Found in Thailand and Cambodia.
- Larger than Horsefield’sBroze Cuckoo and Zappey’s Flycatcher
Significance
- Identifying flyways is an important measure towards joint conservation of the migratory birds as it passes through more than 30 countries during its annual cycle.
- The flyways travelled by birds each spring and fall inspire our model for organizational alignment.
|
What is a flyway?
Flyways in India :
1. Central Asian Flyway
2. East Asian-Australasian Flyway
3. Asian East African Flyway
|