Hurricane Dorian is a strong tropical cyclone currently affecting the Bahamas and the South-eastern United States. At least 5 people have dies and 21 injured.
Context
- Hurricane Dorian is a strong tropical cyclone currently affecting the Bahamas and the South-eastern United States. At least 5 people have dies and 21 injured.
- It is one of the most powerful storms ever to hit Atlantic. Despite getting downgraded to Category 2, it is expected to remain very powerful for the next few days.
ABOUT
- Hurricane - A hurricane is a large rotating storm with high speeds of wind that gust at least 74 mph that forms over warm waters in tropical areas.
- Hurricanes have three main parts, the calm eye in the center, the eyewall where the winds and rains are the strongest, and the rain bands which spin out from the center and give the storm its size
- . In the southern hemisphere, hurricanes rotate in a clockwise direction, and in the northern hemisphere they rotate in an anti-clockwise direction. This is due to what’s called the Coriolis Force, produced by the Earth’s rotation.
How are hurricanes formed?
- Hurricanes begin as tropical disturbances in warm ocean waters with surface temperatures of at least 80 degrees Fahrenheit (26.5 degrees Celsius). Those low-pressure systems are fed by energy from warm seas.
- A storm with wind speeds of 38 miles (61 km) an hour or less is classified as a tropical depression. It becomes a tropical storm—and is given a name, according to conventions determined by the World Meteorological Organization—when its sustained wind speeds top 39 miles (63 km) an hour.
- Hurricanes are enormous heat engines that deliver energy on a staggering scale. They draw heat from warm, moist ocean air and release it through condensation of water vapor in thunderstorms.
- Hurricanes spin around a low-pressure center known as the eye. Sinking air makes this 20- to 40-mile-wide (32- to 64-kilometer-wide) area notoriously calm. But the eye is surrounded by a circular “eye wall” that contains the storm’s strongest winds and rain.
Measurement
- The size of Hurricane is mainly measured by the Saffir-Simpson scale – other scales are used in Asia Pacific and Australia.
The system divides storms into five categories:
- Category 1: Winds 74 to 95 mph (Minor damage)
- Category 2: Winds 96 to 110 mph (Extensive damage — Can uproot trees and break windows)
- Category 3: Winds 111 to 129 mph (Devastating — Can break windows and doors)
- Category 4: Winds 130 to 156 mph (Catastrophic damage — Can tear off roofs)
- Category 5: Winds 157 mph or higher (The absolute worst and can level houses and destroy buildings)
Naming
- Hurricanes are given names by the World Meteorological Organisation (WMO) so that they can be distinguished.
- Each year, tropical storms are named in alphabetical order according to a list produced by the WMO.
- That name stays with the storm if it develops into a hurricane.
- The names can only be repeated after six years.
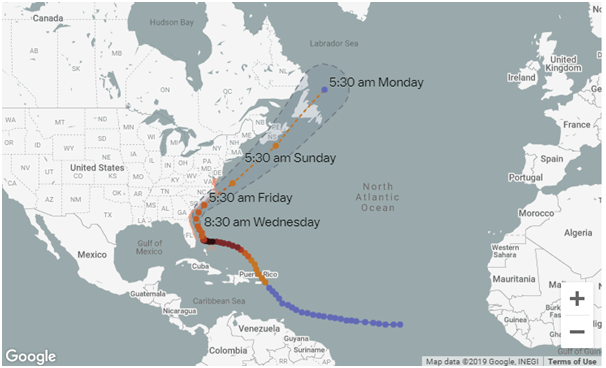
Hurricane Dorian
- Dorian is estimated to be the second-most-powerful hurricane ever recorded in the Atlantic Ocean and ties the record for the most-powerful storm to make landfall, according to the National Weather Service
- The storm is not currently expected to make landfall in the US; it should instead stay uncomfortably close offshore.
- The storm could bring several inches of rain or more for parts of Florida and the Southeast.
- The deadliest aspect of a hurricane tends to be storm surge (flooding caused by seawater pushed onshore by the hurricane’s winds).
- Reason behind downgrading of Category of Dorian: Dorian has slowed down because a high pressure ridge that was steering the storm westward has weakened. Now, the storm is essentially waiting for another external force before it starts moving quickly again.