

Context
James Webb Space Telescope caught Cartwheel Galaxy that is located about 500 million light-years away and appears like a wheel of a wagon.
About
- Cartwheel Galaxy, located about 500 million light-years away in the Sculptor constellation, has been caught with the James Webb Space Telescope.
- The structure appears like a wheel of a wagon, and Webb reveals the galaxy's central black hole along with the information about star formation.
- Astronomers called the galaxy a ‘ring galaxy’ because of its two rings – a bright inner ring surrounded by a colourful one.
- The appearance of the galaxy is justified by the high-speed collisions that have taken place internally between a large spiral galaxy and a smaller galaxy which is not visible in the image.
- The rings have been discovered with an extremely hot dust filled bright core consisting of gigantic young star clusters.
- The outer ring, expanded for 440 million years, consists of star formation and supernovas.
- Cartwheel galaxy has been explored earlier with the Hubble Space Telescope but the same had failed may be due to the thick layer of dust which obstructs the view. Webb with an infrared gaze explored the uncovered part of the Cartwheel galaxy.
- Webb Telescope had not just revealed the observations of the galaxy’s present structural formations but also determined that Cartwheel is in a very transitory stage.

About James Webb Space Telescope:
- It is the most powerful infrared telescopeof National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA).
- It is also considered a successor of the Hubble Telescopeand will extend and complement its discoveries.
- JSWT will observe in near-infrared lightrather than light in the visible part of the spectrum (unlike Hubble) and thus it will have a much greater capacity to see obscure stars and galaxies
- Collaboration: It is a joint venture of NASA(US), ESA (Europe), and CSA (Canada)
- Webb was formerly known as the “Next Generation Space Telescope” (NGST)and it was renamed in 2002 after a former NASA administrator, James Webb.
- The JWST observatory includes three main elements-
- the Integrated Science Instrument Module (ISIM)
- the Optical Telescope Element (OTE)
- the Spacecraft Element which comprises the spacecraft bus and the sunshield
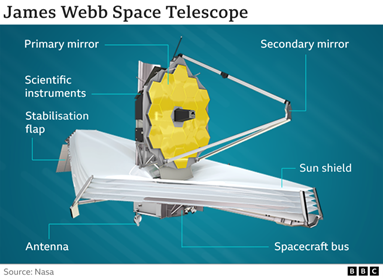
Key features of JWST are-
- JWST will operate in an orbit around the Earth-Sun L2 Langrage point, ~ 1.5 million kilometres away from Earth. This makes its operation, pointing and stability requirements much simpler in comparison with HST
- It orbits around the Earth at an altitude of ~570 km above it.
- The telescope and the instruments will operate at the extremely low temperature of -233°C, which prevents the instrument's own infrared emission from overwhelming the signals from the astronomical targets


