A “sudden stratospheric warming” event took place in early January 2021, according to weather forecasting models.
Context
A “sudden stratospheric warming” event took place in early January 2021, according to weather forecasting models.
About
What is sudden stratospheric warming (SSM)?
- The term sudden stratospheric warming refers to what is observed in the stratosphere.
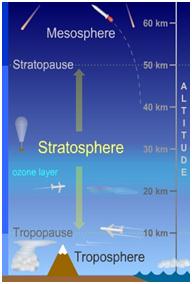
- It is a rapid warming (up to about 50 °C in just a couple of days), between 10 km and 50 km above the earth’s surface.
- The stratosphere is the layer of the atmosphere from around 10 km to 50 km above the Earth’s surface.
- However, usually a few weeks later, knock-on effects on the jet stream can be seen, which in turn effects weather lower down (in the troposphere).
- However, the stratospheric sudden warming doesn’t happen every year, and it doesn’t always affect weather when it does.
- It was first discovered in 1952.
How does it occur?
- Every year in winter, strong westerly winds circle around the pole high up in the stratosphere.
- This is called the stratospheric polar vortexand it circulates around cold air high over the Arctic.
- In some years, the winds in the polar vortex temporarily weaken, or even reverse to flow from east to west.
- The cold air then descends very rapidly in the polar vortex and this causes the temperature in the stratosphere to rise very rapidly, as much as 50°C over only a few days; hence the term sudden stratospheric warming.
- As the cold air from high up in the stratosphere disperses, it can affect the shape of the jet stream as the cold air sinks from the stratosphere into the troposphere.
- It is this change in the jet stream that causes our weather to change.
|
Any role of climate change?
|
What is Polar Vertex?
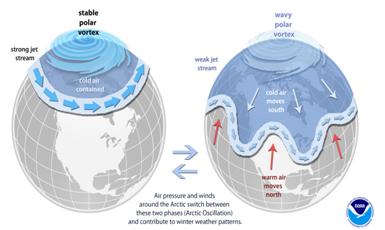
- Polar Vertex can refer to one of two different, but related, weather patterns.
- The polar vortex is a large area of low pressure and cold air surrounding both of the Earth’s poles. It ALWAYS exists near the poles, but weakens in summer and strengthens in winter.
- The term "vortex" refers to the counter-clockwise flow of air that helps keep the colder air near the Poles.