21st June 2024 (11 Topics)
Context
Recent years have seen notable advancements in SCD treatment, including multiple approved medications and breakthroughs in gene therapy. However, there still exists the need for scalable solutions and collaborative efforts among healthcare stakeholders, government bodies, and pharmaceutical companies.
What is SCD?
- Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) is a genetic condition affecting hemoglobin, the protein that carries oxygen in red blood cells.
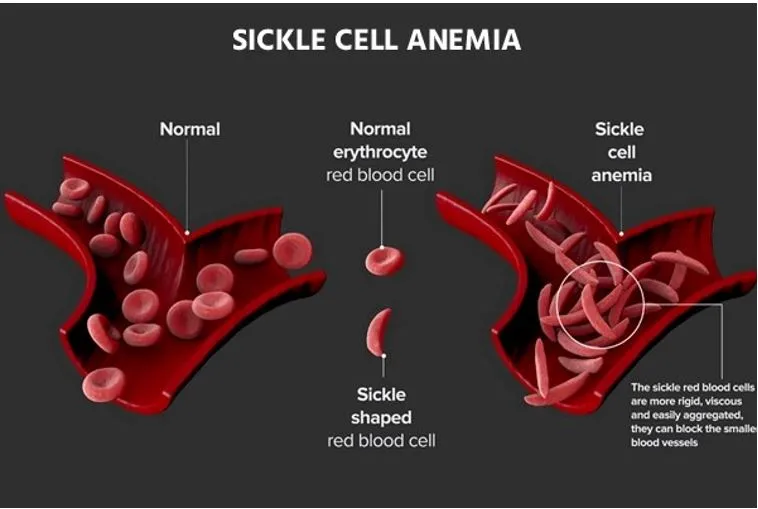
- Genetic mutations cause red blood cells to adopt a crescent shape, disrupting blood flow and leading to severe complications.
- Normally, these cells are round and flexible, but in SCD, they become rigid and crescent-shaped due to a genetic mutation.
- This abnormal shape causes them to stick together and block blood flow, leading to pain, infections, and other serious health problems.
- Global and Indian Burden: SCD affects 20 million people worldwide, with India facing a significant challenge, especially among tribal populations.
- The country has the second-highest prevalence globally, with 1 in 86 births affected.
- Complications and Challenges:
- Patients with SCD suffer from a range of complications, including organ damage, increased infection susceptibility, stroke, and pulmonary issues. Geographic and socioeconomic disparities exacerbate these challenges.
- Despite progress, accessibility to medications like hydroxyurea remains a barrier.
- National Initiatives: The Indian government's National Sickle Cell Anaemia Elimination Mission aims to eradicate SCD by 2047 through awareness enhancement, universal screening, and collaborative interventions.
- World Sickle Cell Day is observed on June 19 every year.