

9th June 2022 (6 Topics)
Context
In a medical trial, 12 patients in the US were completely cured of rectal cancer without requiring any surgery or chemotherapy.
About
Findings:
- The trial showed that immunotherapy alone – without any chemotherapy, radiotherapy, or surgeries that have been staples of cancer treatment.
- It could completely cure the patients with a particular kind of rectal cancer called ‘mismatch repair deficient’ cancer”.
- The trial used a monoclonal antibody called dostarlimab every three weeks for six months for the treatment of a particular kind of stage two or three rectal cancer.
- All 12 patients had completed the treatment and were followed for six to 25 months after.
- The response too was rapid, with symptoms resolving in 81% of the patients within nine weeks of starting the therapy.
What is this deficiency, and how was it cured?
- ‘Mismatch repair deficient’ cancer is most common among colorectal, gastrointestinal, and endometrial cancers.
- Patients suffering from this condition lack the genes to correct typos in the DNA that occur naturally while cells make copies.
- The immunotherapy belongs to a category called PD1 blockades that are now recommended for the treatment of such cancers rather than chemotherapy or radiotherapy.
- PD1 is a type of protein that regulates certain functions of the immune system, including by suppressing T cell activity, and PD1 blockade therapy looks to release the T cells from this suppression.
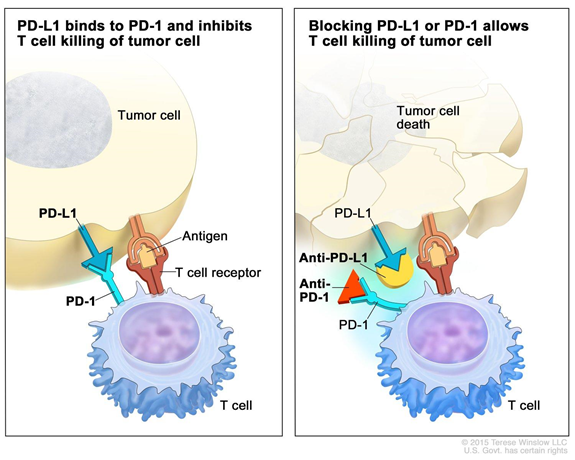
Dostarlimab:
- Dostarlimab, an immunotherapy drug from GlaxoSmithKline, is a type of monoclonal antibody that blocks proteins called checkpoints which are made up of immune system cells, such as T cells, and some cancer cells.
- These checkpoints help keep immune responses from acting too strong and may prevent T cells from killing cancer cells.
- When these checkpoints are blocked, T cells are free to kill cancer cells more efficiently.
- Examples of checkpoint proteins found on T cells or cancer cells include PD-1, PD-L1, CTLA-4 and B7-1. Some immune checkpoint inhibitors, called PD-1 inhibitors, are already used to treat various types of cancers.
More Articles


