31st May 2024 (14 Topics)
Context
May 31st marks World No Tobacco Day, WHO’s global campaign to raise awareness about the dangers of tobacco use and advocate for effective policies to reduce consumption. This year's theme, "Protecting Children from Tobacco Industry Interference," underscores the critical need to safeguard people from the manipulative tactics of the tobacco industry.
The Impact of Tobacco
- Tobacco is the leading preventable cause of disease and death worldwide.
- Health: In India, nearly 26 crore people consume tobacco, and over 60 lakh people employed in the tobacco industry are at risk of health issues due to skin absorption of tobacco.
- Environmental Cost: Beyond human health, tobacco cultivation depletes soil nutrients, requiring more fertilizers and causing deforestation. Processing 1 kg of tobacco requires 5.4 kg of wood.
- Economic Costs: A 2021 study estimated that tobacco's health impacts cost India over Rs 1.7 lakh crore in 2017-2018, compared to the Union Budget's health allocation of Rs 48,000 crore that year.
- Cleaning up tobacco waste costs an additional Rs 6,367 crore annually. These figures exclude the environmental costs of soil erosion and deforestation.
- Annually, tobacco production and consumption generate around 1.7 lakh tonnes of waste.
- Child labour: Indian bidis feature on the US’s 2022 List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor.
Awareness and Control Programs
- India is a signatory to the WHO’s Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (FCTC) since 2005.
- The Cigarettes and Other Tobacco Products Act (COTPA) 2003 regulates tobacco production, advertisement, and consumption.
- The National Tobacco Control Program (NTCP), launched in 2007, aims to enforce COTPA and FCTC, raise awareness about tobacco harms, and support cessation efforts. Tobacco taxation is also used to control consumption.
- India banned foreign direct investment (FDI) in tobacco manufacturing in 2010.
Implementation Challenges
- Despite existing measures, enforcement is weak. Smokeless tobacco products often do not comply with COTPA packaging guidelines, and smuggled products are poorly regulated.
- Fines for COTPA violations have not been updated since 2003, remaining low and ineffective. Indirect advertising through surrogate products like elaichi allows tobacco brands to bypass direct advertisement bans.
- Proposed Amendments: Amendments to COTPA proposed in 2015 and 2020 aimed to regulate surrogate advertisements, increase fines, and require licensing for tobacco production and distribution. However, these amendments have not been passed.
- Taxation and Affordability: India's low tobacco taxes have not kept pace with rising incomes, making tobacco products more affordable. The tax burden is 51% for cigarettes, 22% for bidis, and 64% for smokeless tobacco products, below the FCTC’s recommended 75%. Despite efforts, tax evasion and illegal trade persist.
- Lobbying and Policy Interference: Effective lobbying by the tobacco industry has led to tax exemptions and policy influence.
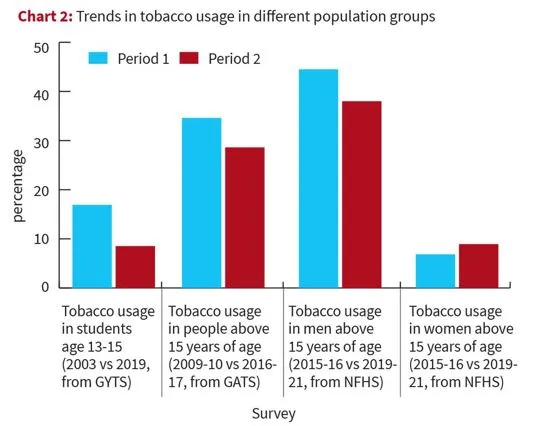
Fact Box: Prevalence in India
|