

31st October 2023 (7 Topics)
Context:
According to a new study, the rapid melting of West Antarctica’s ice sheet due to warm waters around it is now unavoidable.
About the study:
- The study, ‘Unavoidable future increase in West Antarctic ice-shelf melting over the twenty-first century’, was published by the journal Nature recently.
- The study says that if lost completely, the ice sheet would raise the global mean sea level by 3 meters or 17.4 feet — a potentially devastating consequence for millions of people living in vulnerable coastal cities across the world, including in India.
Key Findings of the study:
- Comprehensive Assessment: Scientists utilized a high-resolution computer model of the Amundsen Sea for an extensive evaluation of West Antarctic warming.
- Over 4,000 years of simulations were run, considering various fossil fuel burning trajectories and natural climate variations.
- Grim Findings: Regardless of scenarios, significant and widespread warming in the Amundsen Sea is projected, with increased ice shelf melting.
- Up to 2045, little variation is seen between scenarios, including the 5°C scenario in line with the Paris Agreement.
- Impact on Sea Level Rise: The study predicts heightened sea level rise, impacting global coastal communities, including India.
- Vulnerable areas may face challenges in affording defenses against rising seas, potentially leading to population displacement.
What is an Ice Sheet?
- An ice sheet is essentially a mass of glacial ice that covers more than 50,000 square kilometers’ of land.
|
There are two major ice sheets in the world today: Greenland ice sheet and Antarctica ice sheet.
|
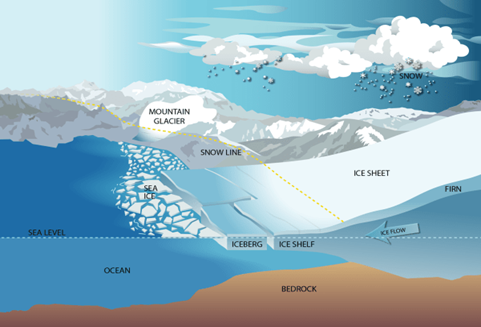
|
According to a report by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA),”Over time, when ice sheets gain mass, they contribute to a fall in global mean sea level, and when they lose mass, they contribute to a rise in global mean sea level.” |
How Antarctica Ice is melting?
- Melting Process: Warm ocean waters cause melting of ice shelves, stabilizing glaciers.
- Impact on West Antarctica: Amundsen Sea faces this process, leading to depleting ice shelves, faster glacier flow, and shrinking ice sheet.
- Differentiating Ice Types: Ice shelves and sheets stabilize land-based glaciers, distinct from sea ice formed by freezing seawater.
Concerns associated:
- Thinning or disappearance speeds up glacier flow, raising sea levels.
- Melting glaciers add to rising sea levels, which in turn increases coastal erosion and elevates storm surge as warming air and ocean temperatures create more frequent and intense coastal storms like hurricanes and typhoons.
|
The Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets are the largest contributors of global sea level rise. Right now, the Greenland ice sheet is disappearing four times faster than in 2003 and already contributes 20% of current sea level rise. |
More Articles


