

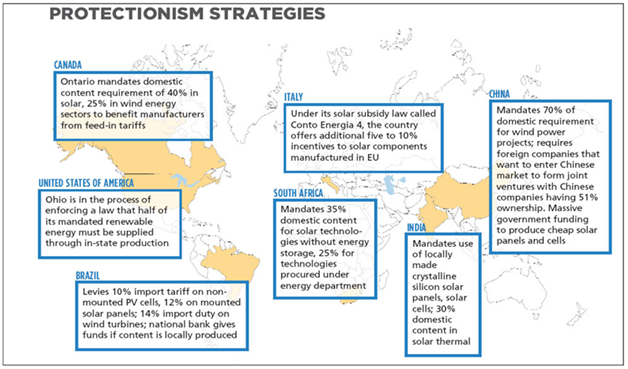
In economics, protectionism is the economic policy of restraining trade between states (countries) through methods such as tariffs on imported goods, restrictive quotas, and a variety of other government regulations. Protectionist policies protect the producers, businesses and workers of the import-competing sector in a country from foreign competitors. According to the proponents, these policies can counteract unfair trade practices, to allow fair competition between imports and goods and services produced domestically. WTO rules allow countries to use methods of protectionism but in a limited manner and in specific cases.
- Tariffs - A tariff is a tax on imports, which can either be specific (so much per unit of sale) or ad valorem (a percentage of the price of the product). Taxing imported goods increase the cost to importers and raises the price of the imported goods in local markets. This gives domestic equivalents a comparative advantage. As such, tariffs are distorting the market forces and may prevent consumers from gaining the benefit of all the advantages of international specialization and trade.
- Quotas - Limiting the number of goods that can be produced abroad and sold domestically limits foreign competition in domestic markets. Once again, they reduce the amount of imports entering an economy and increase the equilibrium price within the market. The government receives no revenue from a quota, as it does with a tariff, unless it can set up a system of licenses.
- Exchange controls - The government could limit the amount of foreign currency available for paying for imports.
- Export subsidies - Export subsidies allow exporters to supply the market with more product than the natural equilibrium would have allowed. Foreign consumers will enjoy increased economic welfare as the price of their purchases fall. Domestic employees might enjoy more wages and job security. But taxpayers are footing the bill for this. Domestic firms might divert trade into exports and ignore the home market. This could lead to increase in domestic prices.
- Exchange Rates - Intervening in the foreign exchange (forex) market to lower a currency's valuation can raise the cost of imports and lower the cost of exports.
- Import Quotas Domestic Subsidies - Subsidizing costs or providing cheap loans to domestic companies can increase their competitiveness against foreign imports.
- Administrative obstacles - Countries can set administrative hurdles. For example, they may require significant levels of paperwork and then deal with these processes slowly making it difficult for importers to compete on a level playing field with other firms.
- Health and safety standards - Countries may set onerously high health and safety standards for goods that are imported, once again making life difficult for importers.
- Environmental standards - Countries can set high environmental standards that they know only domestic firms are likely to be able to achieve, once again making life difficult for importers.
The Transatlantic Trade and Investment Partnership (TTIP) under negotiation between the US and EU has faced harsh criticism.
|
WTO tries to maintain the scenario of free and fair trade mechanism based on following principles:
|
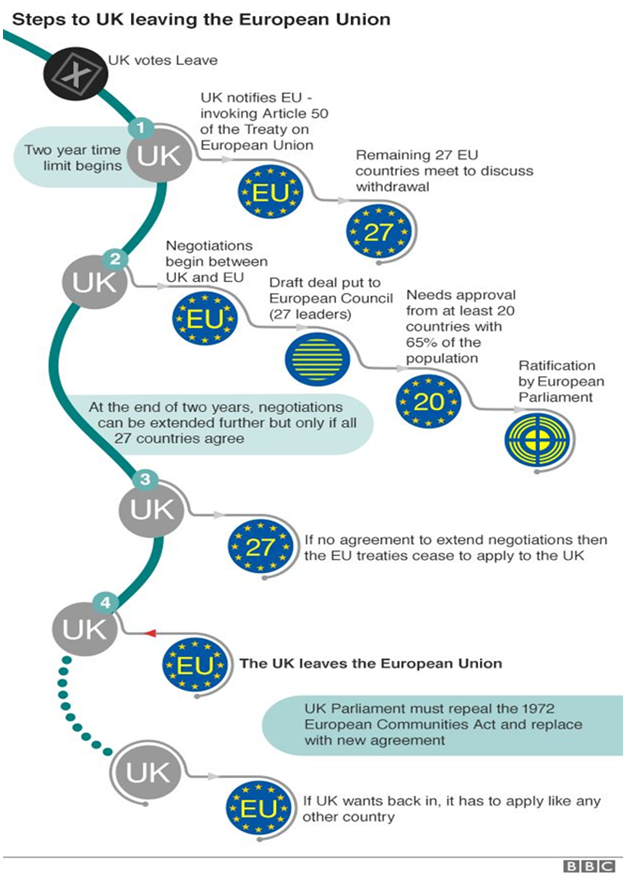
BREXIT, one of the biggest geopolitical risks of 2016, became a reality on June 23 2016 when the "Leave" camp won by a small margin with 51.9 percent of the vote.
The referendum, with an unprecedented voter turnout of 72 per cent, has attracted the attention of the whole world, as its outcome will not only impact the future of the United Kingdom, but also bring about huge and unpredictable changes to the European integration process, as well as to the future of globalization.
From a strategic and global perspective, BREXIT may be defined as the first wave of anti-globalization and rising populism that washes over the world, in particular the advanced nations. What follows next will certainly be more intense and ferocious as globalization and anti-globalization forces engage in fierce battles in different fields involving more countries both in and outside the EU.
What does BREXIT mean?
It is a word that has been used as a shorthand way of saying the UK leaving the EU - merging the words Britain and Exit to get BREXIT.
What was the breakdown across the UK?
- England voted for BREXIT, by 53.4% to 46.6%.
- Wales also voted for BREXIT, with Leave getting 52.5% of the vote and Remain 47.5%.
- Scotland and Northern Ireland both backed staying in the EU.
- Scotland backed - Remain by 62% to 38%,
- Northern Ireland - while 55.8% in Northern Ireland voted Remain and 44.2% Leave.
- For the U.K., BREXIT certainly will weaken its position in the world as well as its "special relationship" with the U.S., even though it will retain its permanent membership in the United Nations Security Council and the pound will continue to be one of the global reserve currencies.
- Scotland announced its intention to hold another referendum on independence immediately after the U.K. referendum. Northern Ireland, with its traditional friction with England, could follow the example of Scotland too.
- BREXIT will disrupt the EU's internal equilibrium. With Britain out, the bloc's seven non-euro countries will account for only 15 per cent of EU economic output, as opposed to more than 30 per cent with Britain in. BREXIT will increase Germany's political and economic supremacy in the EU - a prospect neither Berlin nor its partners welcome.
- BREXIT will harm the EU's cohesion, confidence and international reputation. The biggest consequence of all, therefore, is that BREXIT will undermine the liberal political and economic order for which Britain, the EU and their allies and friends around the world stand.
- From the perspective of EU integration, the EU has been leading the world in global governance, with its regional integration as a litmus test. But the EU and Eurozone in particular have been hit hard by the debt crisis and resultant economic crisis testing the cohesion and viability of the EU and the euro.
- Most recently, the EU has been flooded with refugees from Syria, Iraq and other war-ravaged countries in the Arab world, further straining the fabric of the EU as an example of globalization, especially the principle of freedom of movement of people. All these have stirred up anger and deep-rooted frustration among ordinary people in the EU, directed at governments and elites of those countries.
- BREXIT will make financial markets more sensitive to the vulnerabilities of the 19-nation Eurozone.
- Investors will ask whether, in the light of the BREXIT shock, eurozone governments have the political will and public support to strengthen the architecture of European Monetary Union.
- More ambitious proposals, such as an Italian plan for common EU "migration bonds" to finance the EU's response to the refugee and migrant crisis, will have little chance of being turned into action.
- ndividual eurozone countries will be under intensified market scrutiny.
- Ahead of the British vote, yield spreads widened between German government bonds and those of less financially solid southern European countries. The outlook for Portugal, which is ruled by a shaky coalition of the moderate and radical left, is unsettling investors.
- Global stock market suffered a collective "Black Friday" crash, with the British stock market down 8 percent and Dow Jones dropping 700 points.
- The Japanese stock index was hit most severely with a historic drop of 7.9 percent triggering "a fuse break." Needless to say, the British pound suffered, with a 10 percent slide versus the U.S. dollar.
- The above figures show that we do live in a globalized world of common interest, with financial as well as political risks transmitting super-fast around the world with no exceptions, as the lines among nations and between politics and economics become unrecognizably blurred. That is what is meant by "shepherd effect" or "butterfly effect."
- The polarization of political ecosystems in Western nations has produced and will continue to have a huge impact on the globalization process, world politics and economics. Even though the world had been forewarned by the referendum in U.K., the outcome still brought about unprecedented consequences.
- Many experts believe that BREXIT might trigger a chain reaction both within the EU and around the world. EU members like Greece, France, Spain, Sweden and Denmark, which already have frictions with Brussels, might follow suit and ask for their own referendum.
- That is why right after the U.K. referendum, Germany, France and other major EU countries urged the U.K. to start negotiation with EU as soon as possible for fear that it could spark other dissenting voices within the EU.
- India is presently the second biggest source of FDI for Great Britain. Indian companies that would set up their factories in the UK could sell their products to the rest of Europe under the European free market system. However, now it will not be an attractive destination for Indian FDI as before.
- With BREXIT, India will lose its gateway to Europe. This might force India to forge ties with another country within the EU, in order to access the large EU market.
- With Britain cutting off ties with the EU, it will be desperate to find new trading partners and a source of capital and labour. With migration from mainland Europe drying up, Britain would be able to accommodate migration from other countries, which will suit India's interests.
- Britain is one of the most important destinations for Indians who want to study abroad. Presently, British universities are forced to offer subsidized rates for citizens of the UK and EU. With BREXIT, however, the universities will no longer be obliged to provide scholarships to EU citizens, which will free up funds for students from other countries. Many more Indian students may be able to get scholarships for studying in the UK.
- BREXIT will affect economic and geopolitical interests of China. Even though the UK, which had $78.5 billion in bilateral trade with China in 2015, is not among China's top trading partners, Brexit could have an outsize impact on China's future export performance."
- One of the losses China will face is that it can no longer use Britain as a gateway to the EU to sell its products.
- Many Chinese companies have made the UK one of their favorite destinations of direct investment. In 2015, Chinese companies completed 22 major acquisitions in the UK. The biggest was the $9 billion purchase of a 33.5% stake by China's General Nuclear Power Corporation in Britain's Hinkley Point nuclear power plant. If the UK economy deteriorates because of the uncertainty and loss of access to the EU market following Brexit, the value of Chinese investments will be impaired.
- A weaker Europe would give space to China to rise in global power matrix. But a strong EU was a counterweight to the US hegemony which China would miss mow.
The decision to leave home could happen suddenly or take a long time after months or even years of the situation getting worse. The main reasons people leave their homes are:
- Conflict: Armies fighting for control may try to weaken the other side by threatening lives of civilians, kidnapping children, raping women, burning crops and forests, destroying houses, schools and health clinics, polluting wells and laying landmines. People flee in fear to escape further pain and loss.
- Oppression: The ruling power may not respect human rights by imposing harsh treatment, especially on people it suspects of disagreeing or opposing it. This means people flee in fear for their safety.
- Hatred: Hostility, retaliation and injustice between ethnicities, religious or other groups can threaten people's lives. As a result, people flee in fear for their lives.
- Environmental issues: Natural disasters and climate change also cause people to flee. Despite the difficulties they face, they are not protected by international refugee laws. In some cases environmental issues cause resource shortages that lead to conflict, creating refugees.
- Today, some 84% of those reaching Europe come from the ten countries that produce the most refugees: Some 84% of those reaching Europe come from the ten countries that produce the most refugees: Syria, Afghanistan, Somalia, Sudan, South Sudan, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Myanmar, Central African Republic, Iraq, and Eritrea. In these countries, large areas are affected by war and severe civil strife.
- The majority of arrivals to the European Union in 2016 have come via the Mediterranean. Since the beginning of the year, more than 4,600 people have died or gone missing while attempting to reach Italy from the North African coast. This is the highest recorded number of deaths in the Mediterranean to date.
- The highest number of migrants arrives in Greece and Italy, often after a perilous journey across the sea. In Greece, around 62,000 people are waiting to have their asylum applications processed, with about 11,400 of them held in facilities on the Greek islands. Each month, less than 1,000 asylum decisions are given, with more than that number of asylum seekers arriving. In Italy, over 11,000 people per month applied for asylum in 2016, and on average between 6,000 and 8,000 are processed every month. Faced with this unprecedented situation, both countries have struggled to provide decent reception facilities with even basic services.
- The EU Common European Asylum System (CEAS) is a set of EU laws, completed in 2005. They are intended to ensure that all EU member states protect the rights of asylum seekers and refugees. The CEAS sets out minimum standards and procedures for processing and deciding asylum applications, and for the treatment of both asylum seekers and those who are recognized as refugees. Implementation of CEAS varies throughout the European Union. A number of EU states still do not operate fair, effective systems of asylum decision-making and support, leading to a patchwork of 28 asylum systems producing uneven results.
- Asylum seekers have no legal duty to claim asylum in the first EU state they reach, and many move on, seeking to join relatives or friends for support, or to reach a country with a functioning asylum system. However, the "Dublin" regulation stipulates that EU member states can choose to return asylum seekers to their country of first entry to process their asylum claim, so long as that country has an effective asylum system.
- EU countries in the north, the desired destination of many refugees, have sought to use this Dublin system to their advantage, at the expense of the south, where most refugees first arrive. Yet these efforts have been obstructed by failures of asylum systems in the south. Domestic and European courts have ruled against asylum seekers being returned to Greece, notably in a landmark case in 2011 that found Belgium in violation of the European Convention on Human Rights for exposing an Afghan national to detention, harsh living conditions, and risks arising from shortcomings in Greece's asylum system after a return.
- To address the uneven application of CEAS and the problems of the Dublin system, a reform of the CEAS was proposed in 2016. Among the proposed reforms is one that risks endangering the right to asylum in the EU, with an obligation to verify first if asylum seekers could find protection outside the EU. Some EU countries have already voiced opposition to some of the reforms, notably the obligation to take refugees from other EU countries.
- Prioritize saving lives at sea through sustained search and rescue operations along the main migration routes in the Mediterranean. Renew efforts to obtain permission to operate in Libyan waters so that EU-flagged vessels can assist in search and rescue operations there.
- Ensure that any efforts to "externalize" migration management do not worsen access to protection and respect for human rights, including by:
- Designing, implementing, monitoring and reporting publicly on EU migration cooperation arrangements with third countries to ensure this cooperation does not trap people in abusive situations, prevent them from accessing fair asylum procedures, or lead to refoulement.
- Delinking development aid from migration control in those countries where this linkage appears to be in place.
- Ensuring that programs developed with security forces and other government agencies in countries of origin do not contribute to human rights violations.
- Ensuring that migration cooperation with Libyan authorities, including the training of Libyan Coast Guard and Navy officers, has a strong human rights component, with monitoring and accountability for any abuses and independent, impartial and transparent monitoring of conditions and treatment in Libyan detention centers to ensure that they meet basic standards. The EU should suspend the training program if abuses continue.
- Increase safe and legal channels into the EU to reduce demand for smuggling and dangerous journeys.
- Accelerating the pace of relocations and setting up a timeline for the implementation of the relocation targets. The European Commission should open infringement procedures against member states that are failing to comply with their relocation obligations.
- Ensure that all beneficiaries of protection already in the EU enjoy the right to family reunification without onerous conditions or waiting periods. There should be no distinction between subsidiary protection and refugee status with respect to family reunification rights.
- Governments also need to stop blaming refugees and migrants for economic and social problems, and instead combat all kinds of xenophobia and racial discrimination. Doing otherwise is deeply unfair, stirs up tensions and fear of foreigners, and sometimes leads to violence - even death.
arrangement or institution. Those principles are:
WTO negotiations are stuck in gridlock.
Developing nations are not getting due membership in UNSC.
Related Articles



