6th July 2024 (11 Topics)
Context
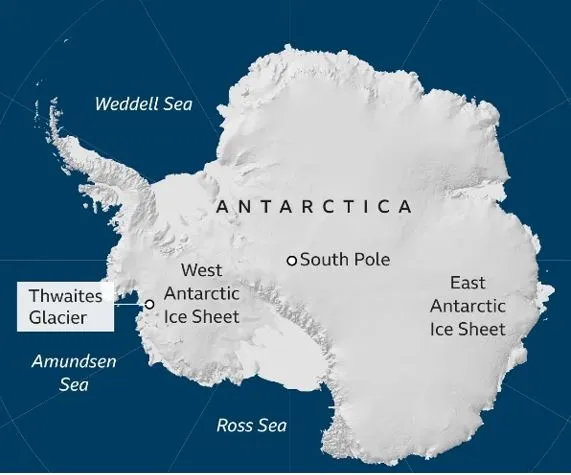
Antarctica, a vast expanse of white, holds a surprising secret: its eastern and western regions froze over at vastly different times. This disparity may hold clues to why West Antarctica is more vulnerable to today's warming trends.
Key-highlights
- Timeline of Freezing: Recent research reveals that Eastern Antarctica locked in its permanent ice sheets about 34 million years ago. However, it took another 7 million years for Western Antarctica to experience the same ice formation. This delay is significant as it correlates with a pivotal shift in Earth's climate from a greenhouse to an icehouse state.
- Impact of Climate Shift: The transition to an icehouse climate initiated the growth of massive ice sheets in Antarctica, reshaping global climate patterns ever since. During the initial major phase of Antarctic glaciation around 34 million years ago, there is no evidence of ice in what is now West Antarctica.
- Climate Conditions: At that time, West Antarctica likely hosted dense broadleaf forests due to a cool-temperate climate that deterred ice formation. In contrast, East Antarctica, particularly in the Northern Victoria Land, had conditions conducive to permanent ice formation, supported by moist air masses from the Transantarctic Mountains.
- Challenges in West Antarctica: The advance of ice towards West Antarctica's Amundsen Sea sector was hindered by milder air and ocean temperatures. However, ice did begin its spread towards the Ross Sea sector earlier, facilitated by favorable climatic conditions and geographical features.
- Current Vulnerabilities: Today, many parts of West Antarctica are below sea level, making them inherently more susceptible to warming-induced ice loss. Even slight increases in temperature can accelerate the melting of the West Antarctic ice sheet, a phenomenon already observed.
Fact Addition
|