

11th September 2025 (16 Topics)
Mains Issues
Context:
Punjab, Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh, and Jammu & Kashmir witnessed severe floods and landslides in August 2025 due to intense rainfall, causing human casualties, property loss, and environmental damage.
Recurring Himalayan Floods and Landslides
- Historical Context:
- 1988, 2013 (Kedarnath), 2021 (Chamoli), and 2025 witnessed major floods and landslides in the Indian Himalayan region.
- Villages in Uttarakhand, Punjab, and Himachal Pradesh were submerged or destroyed, highlighting the recurring vulnerability of these states to climatic and geological hazards.
- Key Factors:
- Himalayan terrain is young and unstable, prone to landslides and flooding.
- Heavy rainfall, glacial melt, and seismic activity contribute to disaster events.
Climate Change as a Threat Multiplier
- Observations:
- Average temperatures in the Indian Himalaya are rising faster than the global average.
- Reduced snowfall and accelerated glacial melt create conditions for Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs).
- ICIMOD reported over 25,000 glacial lakes across five river basins by 2018, increasing flood risk downstream.
- Analysis:
- Climate change is intensifying hydrological hazards.
- Extreme rainfall events are no longer “unprecedented” but part of a growing trend influenced by anthropogenic warming.
Developmental Activities and Disaster Vulnerability
- Hydropower and Infrastructure:
- Himachal Pradesh: 1,144 hydropower plants, 180 operational, 53 under construction.
- Uttarakhand: 40 operational, 87 under various stages of planning/construction.
- Roads, tunnels, and bridges are constructed often without proper ecological impact assessments.
- Tourism and Land Use:
- Rising tourism drives demand for hotels, homestays, and infrastructure, leading to deforestation and destabilization of slopes.
- Removal of deodar and other native trees leads to soil erosion, increasing landslide and flood potential.
- Judicial Observations:
- Supreme Court emphasized that revenue-driven development without ecological sustainability endangers lives and states’ existence.
- Unsafe construction of critical infrastructure (schools, hospitals, tunnels) amplifies human vulnerability.
Policy and Planning Gaps
- Current Limitations:
- Uniform urban-centric development plans are applied in mountainous regions, ignoring local carrying capacity.
- Environmental impact assessments are often insufficient or circumvented.
- Disaster impact assessment and public consultation are rarely integrated into planning processes.
- Expert Recommendations:
- Conduct Lifecycle Analysis before initiating projects in fragile Himalayan ecosystems.
- Undertake independent social and disaster impact assessments with local participation.
- Adopt nature-based solutions and strengthen community-led climate literacy for disaster preparedness.
Way Forward: Integrating Environment, Development, and Risk Management
- Sustainable Infrastructure: Roads, tunnels, and hydropower projects should follow hazard-resilient engineering practices.
- Forest and Soil Conservation: Preserve native vegetation like deodar to stabilize slopes.
- Glacial Monitoring: Early warning systems for GLOFs using satellite imagery and river basin management.
- Local Capacity Building: Train communities in disaster risk reduction and emergency response.
- Climate-Responsive Urban Planning: Avoid critical structures in high-risk zones; integrate risk maps into development planning.


Mains Issues
Context:
The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs has approved the construction of the 82.4 km Mokama–Munger section of the Buxar–Bhagalpur High-Speed Corridor in Bihar on Hybrid Annuity Mode (HAM) at a cost of ?4447.38 crore.
Types of Investment Models & PPP in India
Public Investment Model
- Definition: Government mobilises resources (mainly taxes and borrowings) to fund infrastructure and development projects.
- Role in Economy:
- Boosts aggregate demand (Keynesian role).
- Improves productivity via human capital formation and infrastructure.
- Encourages private investment by improving returns (crowding-in effect).
- Limitations: Fiscal deficit constraints, inefficiency in project execution, political interference.
- Examples: PM Gati Shakti, National Highways, Defence manufacturing units.
Private Investment Model
- Definition: Investment by domestic or foreign private entities (FDI/FPI).
- Advantages: Higher efficiency, innovation, competition, flexibility, scale economies.
- Challenges: Policy uncertainty, regulatory hurdles, infrastructure bottlenecks.
- Examples: Tesla’s plans for India (FDI), private equity in startups, foreign institutional flows into stock markets.
Public-Private Partnership (PPP) Model
- Definition: A cooperative arrangement between government and private sector for creating infrastructure and delivering public services.
- Features:
- Risk Sharing: Allocated based on efficiency.
- Open Competitive Bidding for transparency.
- Performance-linked payments.
- Government retains service responsibility ? not privatization.
- Relevance for India: Essential for infrastructure where public finances are limited (roads, ports, airports, metros, health, education).
Types of PPP Model:
|
PPP Model |
Full Form |
Ownership & Operation |
Risk Sharing |
Examples in India |
|
BOT |
Build–Operate–Transfer |
Private party builds and operates for concession period; ownership remains with government; transferred back after concession. |
Construction & operational risk with private; traffic/revenue risk may vary. |
NHAI highway projects (e.g., Golden Quadrilateral stretches). |
|
BOOT |
Build–Own–Operate–Transfer |
Private entity builds, owns, and operates during concession; ownership transferred to government after period. |
Higher risk on private due to ownership during concession. |
Power plants, ports (e.g., Mundra Port). |
|
BOO |
Build–Own–Operate |
Private entity builds, owns, and operates indefinitely; no transfer back. Government purchases services/output. |
All risks on private; govt ensures demand through offtake agreements. |
Power projects where private supplies power to state utilities. |
|
BOLT |
Build–Own–Lease–Transfer |
Private builds and owns, then leases asset to government for fixed period; later transfers back. |
Private takes construction/finance risk; govt ensures lease payments. |
Airports, telecom projects. |
|
DBFOT |
Design–Build–Finance–Operate–Transfer |
Private designs, finances, builds, and operates during concession; asset transferred later. |
Shared risk – design, finance, and construction by private; govt ensures regulation and viability gap funding (if needed). |
Expressway projects (e.g., Delhi–Meerut Expressway, Hybrid Annuity Mode also used). |
|
LDO |
Lease–Develop–Operate |
Govt leases asset to private entity for development and operation. Private invests in modernization and earns revenue. |
Private bears development/operational risk; govt retains ownership. |
Airports (Hyderabad, Bengaluru under GMR/GVK). |
|
OMT |
Operate–Maintain–Transfer |
Govt builds the asset, private operates and maintains during concession. Revenue collected through tolls/fees. |
Operation & maintenance risk on private; no construction risk. |
Highway tolling & maintenance contracts under NHAI. |
Challenges with PPP in India
- Contract disputes ? project delays.
- Land acquisition hurdles ? cost overruns.
- Crony capitalism ? politically connected firms dominate.
- Opportunistic renegotiations ? strain on exchequer.
- High NPAs in infra lending ? banking stress.
- Poor dispute resolution ? lack of investor confidence.
Vijay Kelkar Committee (2015) Recommendations
- Focus on Service Delivery: Not fiscal gains.
- Risk Allocation: Transparent and balanced.
- Viability Gap Funding (VGF): Prudent use to ensure bankability.
- Independent Tribunals: Infrastructure PPP Adjudication Tribunal (IPAT).
- Discourage Swiss Challenge Proposals: To prevent information asymmetry.
- Sector-specific Frameworks: Railways tariff regulator, urban transport.
- Governance: Transparency in SPVs, distinguish between error vs corruption.
- Financing: Allow Zero Coupon Bonds to improve infra funding.
- Capacity Building: PPP Centres of Excellence.
Way Forward
- Strengthen dispute resolution
- Develop robust model concession agreements (MCAs).
- Use Hybrid models (like HAM) to balance risks.
- Enhance institutional capacity of govt agencies in PPP contract management.
- Encourage PPPs in new sectors ? renewable energy, digital infra, water management, solid waste management.
- Align with SDGs & climate commitments ? green infrastructure financing.


Prelims Articles
Context:
The Ministry of Culture has launched the Gyan Bharatam Mission with a financial outlay of ?482.85 crore (2024–31), alongside hosting the first Gyan Bharatam International Conference (11–13 September 2025, Vigyan Bhawan, New Delhi) to preserve and digitise India’s manuscript heritage.
Mission Overview:
- Gyan Bharatam Mission (GBM) is a Central Sector Scheme approved for 2024–31 with a budget of ?482.85 crore.
- It aims to preserve, digitise, and disseminate India’s manuscript heritage, estimated at over 5 million works covering philosophy, science, medicine, literature, astronomy, and spirituality.
- Over 07 lakh manuscripts are already documented in the Kriti Sampada digital repository under the earlier National Mission for Manuscripts (NMM, 2003).
Key Features:
- Establishment of Manuscript Resource Centres (MRCs) for identification and documentation.
- Manuscript Conservation Centres (MCCs) for scientific and traditional restoration.
- Creation of a National Digital Repository using AI-driven Handwritten Text Recognition (HTR), cloud metadata systems, and IIIF platforms.
- Capacity building in palaeography, conservation, and manuscriptology.
- Public–private and international collaborations for manuscript preservation, translation, and accessibility.
Associated Initiatives:
- Gyan-Setu National AI Innovation Challenge launched to encourage youth and start-ups to use AI for script decipherment, multilingual translation, and digitisation.
- The conference coincides with the anniversary of Swami Vivekananda’s 1893 Chicago address, symbolising India’s knowledge dissemination globally.
- Strong alignment with NEP 2020, which promotes Indian Knowledge Systems (IKS) and teaching in mother tongues.


Prelims Articles
Context:
The Union Tribal Affairs Ministry launched the beta version of “Adi Sanskriti”, a digital platform to preserve, promote, and market tribal artforms and heritage.
Purpose and Components:
- The platform is designed to become the “world’s first Digital University” for tribal knowledge and culture.
- It has three key components:
- Adi Vishwavidyalaya – Digital Tribal Art Academy for online learning of tribal artforms.
- Adi Sampada – Socio-Cultural Repository preserving cultural knowledge, practices, and oral traditions.
- Adi Haat – Digital marketplace enabling tribal artisans to sell products nationwide.
Significance for Tribal Development:
- Promotes economic empowerment by linking artisans directly to a digital market.
- Preserves intangible cultural heritage digitally, ensuring accessibility for education and research.
- Supports the objectives of the Tribal Sub-Plan (TSP) and Vanbandhu Kalyan Yojana by integrating culture, education, and livelihood promotion


Prelims Articles
Context:
Himachal Pradesh was recently declared a “fully literate” state, joining Goa, Mizoram, Tripura, and Ladakh, based on adult literacy rates and Functional Literacy assessment.
Literacy Definition & Measurement
- Definition by Ministry of Education: Ability to read, write, and compute with comprehension, identify, understand, interpret, create, and apply critical life skills such as digital and financial literacy.
- Functional Literacy (FL): Individuals can read, write, perform arithmetic, and carry out daily tasks, including digital transactions.
- ULAS Program: Launched 2022 under Understanding Lifelong Learning for All in Society (ULAS), targeting 100% literacy by 2030 in line with SDG 4 and National Education Policy 2020.
How an Individual is Certified Literate
- Learners are taught reading, writing, arithmetic (up to class 3 level), use of calendars, currency, digital tools.
- Assessed via Functional Literacy and Numeracy Assessment Test (FLNAT) by National Institute of Open Schooling (NIOS).
- Training and testing can be online or offline, conducted by volunteers or students.
How a State Achieves “Fully Literate” Status
- States/UTs conduct surveys or use other data to identify adults who are not literate.
- These adults must clear FLNAT and receive certification.
- Central Govt/Ministry ensures that literacy measurement aligns with standards for comparability across states.

State Literacy Facts (as per 2011 Census & PLFS 2023-24)
- Himachal Pradesh:3% literacy rate (fully literate)
- Other Fully Literate States/UTs: Goa 99.72%, Mizoram 98.2%, Tripura 95.6%, Ladakh 97%
- National Average Literacy (PLFS 2023-24):5% (age 7+)
- Literacy is measured as ability to read & write in any language with comprehension.


Prelims Articles
Context:
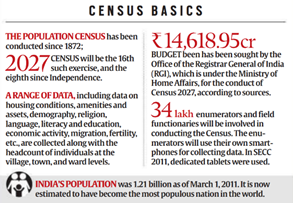
India’s 2027 Census will be conducted digitally for the first time, with geotagging of all buildings to ensure accuracy in enumeration.
Geotagging in Census 2027
- The Census of India, conducted every ten years since 1872, is the most extensive source of demographic, social, and economic data. The 2027 Census will be the 16th Census and the 8th since Independence.
- For the first time, it will be conducted digitally with options for self-enumeration.
- Geotagging refers to marking latitude-longitude coordinates of buildings on a Geographic Information System (GIS) map. This ensures a unique, precise spatial identity for every building.
- During the Houselisting Operations (HLO) phase (April–September 2026), enumerators will geotag buildings using Digital Layout Mapping (DLM).
- A Census House is defined as a building or part of it, recognized as a separate unit due to a distinct entrance. The 2011 Census recorded 84 million houses (306.16 million occupied, 24.67 million vacant).
- 34 lakh enumerators will be deployed using smartphones for data collection; the budget sought for Census 2027 is ?14,618.95 crore.
- Data collected will include number of Census Houses, classification of buildings (residential, non-residential, partly residential, landmark), and households residing in them.
- Geotagging will reduce workload by providing accurate enumeration, workload management, and monitoring of field functionaries.
- Earlier censuses relied on manual sketches; now GIS will replace them.
- Similar geotagging practices are already used in schemes like Pradhan Mantri Awaas Yojana-Gramin (PMAY-G).


Prelims Articles
Context:
The National Action for Mechanised Sanitation Ecosystem (NAMASTE) scheme has validated 84,902 Sewer and Septic Tank Workers (SSWs) and 37,980 Waste Pickers till August 2025, with major milestones achieved in safety, health coverage, and livelihood support.
Launch and Objective:
- NAMASTE was launched in July 2023 jointly by MoSJE and MoHUA.
- Aim: Zero fatalities in sanitation work, mechanisation of sewer/septic tank cleaning, and dignity of sanitation workers.
- Implemented in 4800+ ULBs with an outlay of ?349.70 crore up to 2025–26.
Key Components:
- Profiling of Sewer/Septic Tank Workers and Waste Pickers.
- Occupational safety training, PPE distribution, and Emergency Response Sanitation Units (ERSUs).
- Health insurance under Ayushman Bharat – PMJAY for SSWs and their families.
- Livelihood support through SwachhataUdyami Yojana (SUY) and capital subsidies.
- Integration with existing schemes: SRMS, SBM, DAY-NULM, NSKFDC.
Recent Developments:
- Waste Pickers added as a target group in June 2024.
- Launch of Waste Picker Enumeration App (2025) to profile 2.5 lakh workers.
- 45,871 PPE kits, 354 safety device kits, and health coverage extended to 54,140 workers.
- Capital subsidy of ?20.36 crore provided to sanitation workers and dependents


Prelims Articles
Context:
Kerala government has announced a new medical insurance scheme, NoRKA Care, to provide health cover for Non-Resident Keralites (NRKs) both in India and abroad.
About the Scheme
- The NoRKA Care scheme will be implemented in partnership with New India Assurance.
- It provides cashless medical services up to ?5 lakh at more than 17,000 hospitals across India, including 470 hospitals in Kerala.
- It also provides a personal accident insurance cover of ?10 lakh.
Target Group and Benefits 
- Aims to benefit over 7 million Keralites abroad and within India.
- Coverage includes all pre-existing diseases without waiting period.
- Premium fixed at ?13,400 for a family unit of four (2 adults + 2 children).
- Age eligibility: 18–70 years, with no age bar for dependent children.
Institutional Mechanism
- Implemented through NoRKA-Roots, the field agency of the Department of Non-Resident Keralites Affairs (NoRKA), Government of Kerala.
- Expected to strengthen affordable health care, improve welfare of expatriates, and boost medical tourism in Kerala.
- Addresses challenges in countries like UK and Canada where medical insurance is costly and involves long waiting periods.


Prelims Articles
Context:
The President has given assent to Manipur’s law regulating issuance and verification of SC/OBC caste certificates amid concerns of fraudulent claims.
Purpose and Scope:
- The 2024 law aims to prevent fraudulent claims of Scheduled Caste (SC) and Other Backward Class (OBC) status and to standardize procedures for issuing caste certificates in Manipur.
- Manipur recognizes seven SC communities and four OBC communities; reservations are 2% for SCs, 17% for OBCs, and 31% for STs.
Procedures and Authority:
- The law specifies the competent authorities for issuance, detailed application procedures, and establishes scrutiny committees to verify caste certificates.
- Scrutiny Committees are empowered to act suomotu and make final decisions on the validity of caste certificates, which can only be challenged in the High Court.
Comparative and Legal Context:
- While some states like Maharashtra and Andhra Pradesh have specific laws or executive orders governing caste certificates, Manipur’s law aligns with a nationwide trend to formalize verification mechanisms.
- Unlike Andhra Pradesh, where the District Collector can verify certificates suomotu, Manipur’s law vests this power in scrutiny committees.


Prelims Articles
Context:
The President has given assent to Manipur’s law regulating issuance and verification of SC/OBC caste certificates amid concerns of fraudulent claims.
Purpose and Scope:
- The 2024 law aims to prevent fraudulent claims of Scheduled Caste (SC) and Other Backward Class (OBC) status and to standardize procedures for issuing caste certificates in Manipur.
- Manipur recognizes seven SC communities and four OBC communities; reservations are 2% for SCs, 17% for OBCs, and 31% for STs.
Procedures and Authority:
- The law specifies the competent authorities for issuance, detailed application procedures, and establishes scrutiny committees to verify caste certificates.
- Scrutiny Committees are empowered to act suomotu and make final decisions on the validity of caste certificates, which can only be challenged in the High Court.
Comparative and Legal Context:
- While some states like Maharashtra and Andhra Pradesh have specific laws or executive orders governing caste certificates, Manipur’s law aligns with a nationwide trend to formalize verification mechanisms.
- Unlike Andhra Pradesh, where the District Collector can verify certificates suomotu, Manipur’s law vests this power in scrutiny committees.


Prelims Articles
Context:
The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) exempted mining proposals of atomic, critical, and strategic minerals from public consultations citing national defence and strategic requirements.
Policy Decision:
- The exemption applies to minerals notified in Part D of the First Schedule of the MMDR Act.
- Minerals include Lithium, Nickel, Tungsten, Titanium, Graphite, uranium, and beach sand minerals.
- Projects are still appraised under the Environment Impact Assessment (EIA) Notification, 2006, and assessed by sectoral expert committees.
Rationale and Strategic Significance:
- The move was requested by the Defence Ministry and Department of Atomic Energy.
- Minerals are crucial for national defence, strategic sectors, communication, navigation, and precision weapons.
- Public consultations are considered exempt due to potential security risks and scarcity of rare earths in India.
Procedural and Legal Context:
- EIA Notification normally mandates public hearings and written responses for development projects.
- This exemption is specific to critical and strategic mineral projects, not general mining.
- The exemption is accompanied by central-level appraisal and sectoral review to maintain environmental oversight.
|
Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Amendment Act, 2023 Key Objectives of the Amendment
Major Amendments
Important Definitions & Terms
|


Prelims Articles
Context:
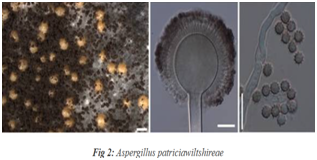
Indian scientists at MACS–Agharkar Research Institute, Pune, have discovered two new species of Aspergillus (section Nigri) in the Western Ghats and reported two species for the first time from India.
New Species Identified
- Aspergillus dhakephalkarii and Aspergillus patriciawiltshireae were identified as novel species by an Indian team using advanced taxonomic methods.
- Additionally, aculeatinus and A. brunneoviolaceus were reported for the first time in India.
- This marks the first discovery of new Aspergillus section Nigri species by an Indian team.
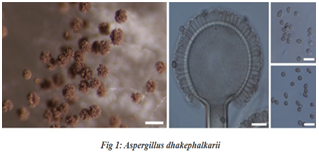
Taxonomic and Genetic Approach
- The study followed the integrative or polyphasic taxonomic approach, considered the global gold standard.
- Identification used ITS and CaM genes, while BenA and RPB2 were employed for phylogenetic analysis.
- Maximum likelihood multi-gene phylogeny confirmed distinct lineages of the new species with high statistical support.
Ecological and Industrial Relevance
- Black aspergilli are crucial in citric acid production, food fermentation, enzyme technology, and agriculture.
- The Western Ghats, a UNESCO biodiversity hotspot, are underexplored for microbial diversity, highlighting the need for conservation and systematic research.
- The phosphate-solubilisation potential of these fungi indicates agricultural and ecological significance.


Prelims Articles
Context:
Recent ecological research highlights the active role of trees in shaping fundamental environmental processes such as water cycles, soil formation, and biodiversity conservation, challenging the view of trees as passive organisms.
Ecological Significance
- Trees regulate rainfall patterns through transpiration and redistribution of water.
- They act as “terraformers”, creating soil from barren rock and releasing oxygen to sustain life.
- Function as rainmakers above ground and water managers below ground, maintaining ecological balance.
Scientific Discoveries
- Concepts such as the “wood wide web” show underground communication networks through fungal associations.
- Researchers like Harriet Rix and Suzanne Simard highlight how trees shape air, water, soil, and biodiversity.
- Evolved over 400 million years, trees remain critical to climate regulation and ecosystem stability.
Cultural and Spiritual Linkages
- Trees like peepal, banyan, rudraksha, deodar are revered as sacred in Indian traditions.
- Scientific studies validate their role in health, wellness, and biodiversity conservation.
- Ancient wisdom underscores that no plant is without ecological utility.


Editorials
Context:
During Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s visit to Colombo in April 2025, India and Sri Lanka revisited long-standing concerns over the fisheries crisis in the Palk Straits and the sovereignty of Katchatheevu island.
The Fisheries Issue
- Livelihood vs. Conservation: Indian mechanised bottom trawling in Sri Lankan waters depletes fish stocks and damages coral beds, violating both ecological imperatives and UNCLOS principles.
- Impact on Communities: Artisanal fishers in Tamil Nadu and Sri Lanka’s Northern Province face declining near-shore resources, creating a livelihood conflict within Tamil communities themselves.
- Policy Response Needed: Sustainable solutions require distinguishing between trawler operators seeking profit and traditional fishers dependent on subsistence fishing.
The KatchatheevuIssue:
- Treaty Settlement: The 1974 India–Sri Lanka Maritime Boundary Treaty placed Katchatheevu under Sri Lankan sovereignty, a legally binding settlement consistent with international law.
- Clarifying Misconceptions: Historical evidence, including Portuguese, Dutch, and Jaffna administrative records, supported Sri Lanka’s stronger claim, making retrieval politically rhetorical.
- Rights and Precedents: Fishing rights are distinct from sovereignty, with international precedents (ICJ Minquiers&Ecrehos case, 1953; Rann of Kutch arbitration, 1968) underscoring the sanctity of boundary treaties.
Towards Cooperative Solutions
- Joint Resource Management: Article 123 of UNCLOS encourages cooperation in semi-enclosed seas, enabling quota-sharing, seasonal rights, and joint research on marine conservation.
- Deep-Sea Fishing Alternatives: Promoting deep-sea fishing within India’s EEZ could reduce pressure on near-shore waters and lessen illegal crossings into Sri Lankan territory.
- Diplomatic Engagement: Multi-level engagement, including government-to-government talks, state/provincial dialogues, and community participation, is essential to preserve India–Sri Lanka cultural and civilisational ties.
Practice Question:
“Discuss the challenges and opportunities in resolving the Palk Strait fisheries dispute between India and Sri Lanka. How can cooperative mechanisms reconcile livelihood security, ecological sustainability, and treaty obligations?” (250 words)


Editorials
Context:
Prime Minister Narendra Modi attended the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) Summit in Tianjin, China, where India and China discussed bilateral ties and multilateral cooperation under the SCO framework.
SCO Summit Outcomes
- Institutional Expansion: The Tianjin Declaration established four new security centres, including the SCO Anti-drug Center, and announced the creation of the SCO Development Bank.
- Developmental Agenda: Leaders adopted the SCO Development Strategy for the next decade, focusing on cooperation in energy, green industry, and the digital economy.
- Global Governance Role: China proposed the Global Governance Initiative, emphasizing multilateralism, sovereign equality, and rule-based international order.
India–China Bilateral Understanding
- Strategic Trust Building: Leaders stressed the need to consolidate strategic mutual trust through peaceful coexistence, dialogue mechanisms, and mutual respect.
- Expanding Exchanges: China proposed deeper cooperation in trade, technology, education, culture, and poverty alleviation to foster people-to-people bonds.
- Border Issue Management: Both sides reiterated that border disputes should not define bilateral ties and emphasized maintaining peace along the Line of Actual Control (LAC).
Future Roadmap
- Global South Leadership: India and China, as major developing nations, share common interests in development, world stability, and reforming global governance.
- BRICS Presidency Synergy: With both countries set to hold BRICS presidency successively, they pledged to support each other in strengthening South–South cooperation.
- Shared Global Vision: Both nations agreed to oppose unilateralism and hegemonism, and work together towards building a community with a shared future for humanity.
Practice Question
“India–China relations oscillate between cooperation and confrontation. In the light of recent developments at the Tianjin SCO Summit, critically analyze the prospects and challenges of bilateral ties between India and China within the framework of multilateral organisations. (250 words)


Editorials
Context:
Israel’s recent military strike inside Qatar targeting Hamas’s negotiating team has drawn global criticism and raised concerns over violation of international law.
Nature of Israeli Strikes
- Targeted Operation: Israel attacked Hamas’s political leadership in Qatar, claiming it was a countermeasure after recent militant assaults in Gaza and Jerusalem.
- Civilian Impact: Hamas confirmed six deaths, while concerns grew about the safety of Israeli hostages still in captivity.
- Lack of Settlement Efforts: Prime Minister Netanyahu is prioritising Hamas’s elimination rather than negotiating a sustainable ceasefire agreement.
International Reactions and Legal Concerns
- Qatar’s Condemnation: Qatar labelled the attack a violation of sovereignty and a breach of international law, citing UN Charter Article 2(4).
- Global Criticism: The UN and various governments warned that Israel’s unilateral actions undermine regional stability and expand the conflict.
- Trump’s Displeasure: Even the U.S., Israel’s key ally, expressed unhappiness, signalling growing disapproval of Netanyahu’s approach.
Broader Geopolitical Implications
- Regional Escalation: Israel’s recent strikes across Lebanon, Syria, Yemen, and Iraq highlight its expanding conflict strategy.
- Palestinian Statehood Issue: Growing international momentum in the UN General Assembly could press Western nations to formally recognise Palestine.
- Domestic Unrest in Israel: Mass protests demanding a ceasefire and hostage release reflect internal political challenges to Netanyahu’s hardline policies.
Practice Question
“Israel’s recent military actions raise questions about the balance between state security and adherence to international law. Critically examine the implications of unilateral military interventions on regional stability and global governance.” (250 words)



