13th June 2024 (13 Topics)
Mains Issues
Context
The World Bank recently released its June edition of the 'Global Economic Prospects' report, offering insights into the current and future state of the global economy. Among its findings, India stands out as a key player, retaining its position as the “fastest-growing major economy” globally, albeit with a projected slowdown in growth.
Key Findings:
- India's Growth Trajectory:
- India is expected to maintain its status as the fastest-growing major economy, with a forecasted GDP growth rate of 6% for the fiscal year 2024-25.
- This growth, while slightly slower, is still robust, primarily driven by strong public and private investment despite a moderation in investment growth.
- In the previous fiscal year (2023-24), India's GDP growth exceeded expectations, reaching 7.8%, contributing significantly to regional growth in South Asia.
- South Asian Region:
- While India's growth is expected to moderate slightly, it will still play a crucial role in sustaining regional growth, with other economies like Bangladesh, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka anticipated to maintain or strengthen their economic activities.
- Fiscal and Trade Balances:
- Fiscal health in South Asian countries is gradually improving, with India's fiscal deficit projected to decrease relative to GDP due to increased revenues.
- Trade deficits are narrowing, particularly in India, contributing to overall economic stability in the South Asian region.
Global Economic Outlook:
- The global economy is showing signs of stabilization in 2024 after a tumultuous period, with GDP growth projected at 2.6% for the year, a slight increase from earlier estimates.
- However, this stabilization remains weak compared to historical standards, with global growth expected to hover around 2.7% in the following years, driven by modest growth in trade and investment.
- Global Inflation Projection: Global inflation is expected to moderate but at a slower pace than previously anticipated, with central banks likely to remain cautious about easing monetary policy.
- Risks to Global Growth: Despite improved near-term prospects, the global outlook remains subdued, with geopolitical tensions, trade fragmentation, higher interest rates, and climate-related disasters posing significant risks.
Factors Driving India's Economic Growth:
- Demographic Dividend: India's large and youthful population serves as a significant driver of economic growth, providing a vast workforce and consumer base.
- Infrastructure Development: Government investments in infrastructure projects, such as roads, railways, and ports, improve connectivity and facilitate economic activities across the country.
- Bharatmala project for roads and Sagarmala project for ports
- Industrial and Services Sector Growth: The industrial and services sectors, including manufacturing, IT services, and finance, have experienced robust growth, contributing significantly to India's GDP.
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI): Liberalization of FDI policies has attracted foreign investment, fostering economic development and technological advancement in various sectors.
- Urbanization and Urban Development: Rapid urbanization has led to the growth of cities as hubs of economic activity, driving demand for housing, services, and consumer goods.
- Innovation and Entrepreneurship: India's thriving startup ecosystem and emphasis on innovation and entrepreneurship have led to the emergence of new businesses and industries, contributing to economic growth.
- Policy Reforms: Structural reforms aimed at simplifying regulations, improving ease of doing business, and promoting investment have bolstered economic growth and competitiveness.
- Strengthened banking system: Gross Non-Performing Assets (NPAs) reduced from 9.1% as of March 2019 to 3.2% as of September 2023 with the implementation of the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC)
- Boosting the manufacturing-focused sectors: Policies like the Production Linked Incentives (PLI) schemes introduced across various sectors (electronics, mobile phones, pharmaceuticals, and food processing).
- India’s manufacturing sector contributes 17% to GDP and employs 27.3 million workers.
- Government aims to raise manufacturing's share to 25% by 2025.
- Sector-specific Initiatives: The government launched initiatives and schemes targeting specific sectors, such as:
- Make in India, Digital India, and Skill India
- Emergence of gig workers, currently constituting 1.5 percent of the workforce, is expected to increase their contribution to total employment to 4.1 percent by 2029-30.
- Social Welfare Programs: The government implements social welfare programs, such as the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) and the National Health Mission (NHM), to alleviate poverty, improve human capital, and enhance social inclusivity.
- Important Government Interventions: Digital India programme, Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana, Startup India, Production-Linked Incentive in strategic sectors, PM Vishwakarma Yojana
Concerns for India
- Inflation has been a persistent concern in India's economy.
- Income inequality: Inequality in India has skyrocketed since the early 2000s, with the income and wealth share of the top one per cent of the population rising to 22.6 per cent and 40.1 per cent, respectively, in 2022-23.
- Infrastructure Bottlenecks: Inadequate transportation networks, power shortages, and urban congestion, hinder productivity, competitiveness, and sustainable development.
- Agrarian Distress: Share of agriculturein India's GDP declined to 15 per cent last fiscal year from 35 per cent in 1990-91
- Unemployment and Underemployment: With the massive increase in educational attainment, the unemployment problem is becoming centred around educated youth. (India Employment Report 2024)
- As per the National Statistical Office’s (NSO) Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) report for 2021-22, the unemployment rate was 4.1%
- Geopolitical Tensions: Trade disputes, geopolitical conflicts (Russia-Ukraine, Israel-Hamas), and geopolitical shifts, can disrupt global supply chains, trade flows, and investor confidence, affecting India's economic prospects.
- Climate Change poses threats to public health, ecological sustainability, and long-term economic growth prospects.


Mains Issues
Context
The PLI scheme is expected to attract investments of Rs 3-4 lakh crore in the next four years and generate 2 lakh jobs as large projects in sectors, including semiconductor and pharmaceutical intermediaries, are expected to take off.
What is the role of PLI Scheme in Indian Economy?
- Production Linked Incentive scheme (PLI) has become a crucial part of the vision of making India a $ 5 trillion economy. In the post-pandemic scenario, PLI is proving to be a huge catalyst in creating ‘AatmaNirbhar Bharat’.
- The scheme currently targets 14 sectors of strategic and economic importance for India’s economic growth.
- The 14 sectors are: (i) Mobile Manufacturing and Specified Electronic Components, (ii) Critical Key Starting Materials/Drug Intermediaries & Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, (iii) Manufacturing of Medical Devices (iv) Automobiles and Auto Components, (v) Pharmaceuticals Drugs, (vi) Specialty Steel, (vii) Telecom & Networking Products, (viii) Electronic/Technology Products, (ix) White Goods (ACs and LEDs), (x) Food Products, (xi) Textile Products: MMF segment and technical textiles, (xii) High efficiency solar PV modules, (xiii) Advanced Chemistry Cell (ACC) Battery, and (xiv) Drones and Drone Components.
- The purpose of the PLI Schemes is to
- attract investments in key sectors and cutting-edge technology
- ensure efficiency and bring economies of size and scale in the manufacturing sector
- make Indian companies and manufacturers globally competitive
- These schemes have the potential of significantly boosting production, employment and economic growth over the next five years or so.
Significance of PLI Scheme for Economy:
It aims to enhance the country's manufacturing capacity, offering various benefits.
- Stimulating Economic Growth: It provides financial incentives to manufacturers, encouraging both domestic and foreign investment in critical sectors. This injection of funds is geared towards fostering economic growth and industrial development.
- Reduced Reliance on Imports: The scheme aims to reduce India's dependence on imported goods. It results in a more balanced trade deficit and a stronger Indian rupee.
- Promoting Export Competitiveness: Another objective of the scheme is to boost export competitiveness. By incentivizing production for export-oriented industries, it aims to elevate India's position in global trade and reduce reliance on imports.
- Job Creation: Increased local manufacturing under the PLI scheme is anticipated to generate significant employment opportunities. It is estimated to create around 60 lakh new jobs over the next five years, thus contributing to the country's socio-economic development.
PYQQ. Consider, the following statements : (2023) Statement-I : India accounts for 3.2% of global export of goods. Statement-II : Many local companies and some foreign companies operating in India have taken advantage of India's ‘Production-linked Incentive’ scheme. Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
Solution: (d) |


Prelims Articles
Context
The Satnami sect has recently made headlines due to their protest against the government in Chhattisgarh regarding the desecration of Jaitkham, a sacred religious site located in the Baloda Bazar district.
Who are the Satnamis?
- The Satnamis are a predominantly Scheduled Caste sect living mainly in Chhattisgarh and parts of Madhya Pradesh.
- Guru Ghasidas, an 18th-century saint is revered as the spiritual leader of the Chhattisgarh Satnamis.
- Furthermore, the Satnamis find their roots in the teachings of Kabir, a 15th-century Bhakti poet who advocated for the worship of an immanent, formless Absolute.
- 1657: A mendicant named Birbhan, inspired by the teachings of Kabir, founded a Satnami community in Narnaul in present-day Haryana in 1657. Initially, most Satnamis belonged to an “untouchable” caste engaged in leatherwork.
- Features:
- They rejected ritual and superstition
- They forbid caste distinctions within their community.
- Displaying sympathy towards the poor and skepticism towards authority and wealth
History of Protests
- Revolt Against Aurangzeb: During the Mughal era, the Satnamis rose against Aurangzeb's oppressive tax demands, leading to a significant rebellion in Punjab and Haryana. Despite facing severe suppression, they fought valiantly for their rights.
- Revival under Guru Ghasidas: Guru Ghasidas led the revival of the Satnami community in the mid-18th century, emphasizing the worship of one true God and rejecting idol worship. His teachings allowed the Satnamis to transcend social restrictions and embrace their spirituality.
Fact Box:Guru Ghasidas (1756-1836)
Kabir Das (1440-1518)
|


Prelims Articles
Context
Prime Minister Narendra Modi is poised to participate in the annual G7 summit held in Italy. The summit holds significant importance in addressing pressing global issues, particularly amidst ongoing geopolitical tensions such as the Ukraine conflict.
About the G7 Summit:
- Founded: 1975
- The G7 is an intergovernmental political and economic forum of industrialized democracies.
- Composition: United States, the United Kingdom, France, Italy, Germany, Canada, and Japan. European Union (EU) is a “nonenumerated” member.
- It is not a formal institution with a charter and a secretariat. The presidency rotates annually among member states.
- Currently presided over by Italy, the G7 aims to tackle global challenges while upholding the principles of the rules-based international system.
- Agenda and Focus: At the upcoming summit, a primary focus will be addressing the
- Ukraine conflict
- ongoing Middle East crisis and its implications for the global agenda
Fact Box: Alternatives of G7
|


Prelims Articles
Context
Following Mauritius' successful adoption (first country to adopt the Jan Aushadhi Scheme) of India's 'Jan Aushadhi Scheme', Nepal has approached India to establish Jan Aushadhi Kendras in its country. This move aims to provide Nepalese citizens with access to low-cost, high-quality generic medicines manufactured in India.
About the Scheme:
- Pradhan Mantri Bharatiya Janaushadhi Pariyojana (PMBJP) is a flagship scheme of the Indian government, aimed at making quality generic medicines available at affordable prices.
- This is achieved through dedicated outlets called Pradhan Mantri Bharatiya Janaushadhi Kendras (PMBJK).
- Currently, India boasts over 10,000 PMBJKs across the country, serving as vital hubs for dispensing affordable medicines to the public.
- Aim: to reduce out-of-pocket expenditure for consumers/patients by offering quality medicines and surgical items at affordable prices.
- By popularizing generic medicines, the scheme seeks to address the financial burden associated with healthcare and promote access to essential drugs for all segments of society.
- Implementing Agency: The scheme is executed by the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Bureau of India, an autonomous society under the Department of Pharmaceuticals.
- Through its extensive network of PMBJKs, the scheme ensures the availability of a wide range of generic medicines, catering to diverse healthcare needs across India.


Prelims Articles
Context
The recent report on India's consumer price inflation for May 2024 has garnered attention due to its implications for the country's economic landscape. Consumer price inflation is a crucial indicator of the cost of living for citizens and plays a significant role in shaping monetary policy decisions by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
Key Findings:
- Easing of Consumer Price Inflation: In May 2024, India witnessed a slight easing in consumer price inflation, reaching a one-year low of 4.75%, down from 4.83% in April.
- Stagnant Food Prices: Food prices, however, remained unchanged, with a significant spike of 8.7%, particularly impacting urban households with a sharper rise of 8.83%.
- Comparison to Previous Year: This is in contrast to the previous year when retail inflation stood at 4.31%, with food prices rising less than 3%.
- Surge in Vegetable Prices: Vegetable prices surged by 27.3% in May, contributing to the overall inflationary pressure, while other food items like cereals, eggs, fruits, and pulses also experienced significant inflation rates.
- Challenges for Monetary Policy: Despite retail inflation staying below 6% since September 2023, it remains above the central bank’s target of 4%, posing challenges for monetary policy management.
- Projections and Policy Response: Projections suggest a potential moderation in food inflation, which could lead to a policy response from the RBI, such as a reduction in the policy interest rate to mitigate economic pressures.
Fact Box: About Consumer Price Inflation (CPI)
|


Prelims Articles
Context
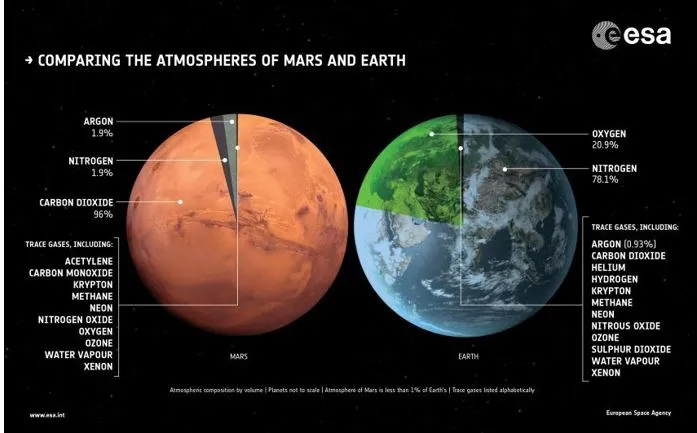
Recent discoveries have challenged assumptions about Mars' climate, with researchers detecting frost on equatorial volcanoes. This finding contradicts expectations of hot, arid conditions in the planet's equatorial regions and suggests a more complex climate system than previously thought.
Key Findings:
- Frost Discovery: Researchers have detected frost atop volcanoes in Mars' Tharsis region, near the planet's equator. This discovery challenges previous assumptions about the planet's climate, which were thought to preclude frost formation in equatorial regions due to high temperatures.
- The frost was observed within the calderas of Martian volcanoes, large hollows at their summits.
- The frost, with a thickness of about a hundredth of a millimeter (roughly the width of a human hair), covers a significant area within the calderas of Martian volcanoes.
- Although ephemeral, lasting only a few hours after sunrise before evaporating in sunlight, this frost contributes to the cycling of water between the Martian surface and atmosphere during the cold seasons.
- The frost was first spotted by ESA's ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter (TGO) atop the massive Olympus Mons volcano (nearly three times the height of Mount Everest)
- Factors (likely) responsible for frost formation:
- The researchers propose that a unique microclimate created by air circulation above these mountains allows for the formation of frost despite Mars' thin atmosphere and relatively high daytime temperatures.
- The presence of frost on Martian volcanoes suggests the possibility of an ancient climate cycle on Mars, involving past precipitation and even snowfall on these volcanic peaks.
Fact Box:
About Frost
|


Prelims Articles
Context
A recent report highlights the sharp increase in nitrous oxide emissions from agricultural activities. Nitrous oxide, a potent greenhouse gas, is being emitted at alarming rates due to the use of chemical fertilizers and animal waste on croplands.
Key Findings:
- Surging Emissions: Between 1980 and 2020, nitrous oxide emissions soared by 40%, primarily driven by the intensified use of chemical fertilizers and animal waste in agriculture.
- Top Emitters: Countries like China, India, and the US are among the top 10 emitters of nitrous oxide. Brazil, Russia, Pakistan, Australia, Indonesia, Turkey, and Canada also contribute significantly to these emissions.
- Rapid Increase in Nitrogen Fertilizers: The use of commercial nitrogen fertilizers has seen a dramatic rise, from 60 million metric tonnes in 1980 to 107 million metric tonnes in 2020.
- Additionally, animal manure contributed 101 million metric tonnes in 2020, resulting in a combined usage of 208 million metric tonnes.
Fact Box: About Nitrous Oxide (N20)
|


Prelims Articles
Context
The Centre has proposed eco-sensitive areas (ESAs) in six states, including Karnataka, Maharashtra, and Goa, to safeguard the Western Ghats. However, these states are seeking a reduction in the extent of ESAs to facilitate development projects.
Key Demand: Rationalizing ESAs
- The states are advocating for a rationalization of ESAs, which currently cover 56,825 sq km in the Ghats.
- They argue that reducing the ESAs would allow for essential development activities in the region.
- State’s demands:
- Karnataka's Opposition: Karnataka opposes the original draft based on the K Kasturirangan panel report, citing potential impacts on livelihoods.
- Goa's Demands: Goa seeks a reduction in ESAs in specific talukas to accommodate development projects.
What are ESAs?
- ESAs are designated areas surrounding national parks and wildlife sanctuaries aimed at preserving the ecological balance and biodiversity of sensitive regions like the Western Ghats.
- They act as buffer zones between highly protected areas and places with less protection.
- These areas restrict certain activities to prevent environmental degradation and maintain the natural habitat.
- Purpose: to lessen human impact on these special places.
- Extent: Usually within 10 km of park or sanctuary boundaries. If there are important natural pathways beyond 10 km, they might stretch further.
- They're similar to ecotones, those transition zones between different ecosystems.
- Notified by: They are notified by the Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change, Government of India around Protected Areas, National Parks and Wildlife Sanctuaries.
Fact Box:Categories of Activities in ESAs
About Western Ghats
|


Prelims Articles
Context
|
S.No. |
Term |
About |
|
1. |
Consumer Price Index (CPI) |
CPI is a measure of the average change overtime in the prices paid by consumers for a market basket of consumer goods and services. |
|
2. |
Eco-Sensitive Zones (ESZ) |
Ecologically sensitive zones (ESZ) are intended to protect ‘protected areas’ – national parks and wildlife sanctuaries – by transitioning from an area of lower protection to an area of higher protection. Land within 10 km of the boundaries of national parks and wildlife sanctuaries is to be notified as eco-fragile zones or Eco-Sensitive Zones (ESZ). |
|
3. |
Microclimate |
Microclimate is the suite of climatic conditions measured in localized areas near the earth's surface. |
|
4. |
Precipitation |
Precipitation is any liquid or frozen water that forms in the atmosphere and falls back to the earth. I |


Editorials
Context
The theme for International Fatty Liver Day this year, observed annually in June, is 'Act Now, Screen Today.' This theme emphasizes the urgency of addressing non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), now reclassified as Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), due to its rising prevalence and significant health implications.
Growing Burden
- Prevalence and Statistics: MASLD affects approximately 25-30% globally. In India, fatty liver prevalence among adults is 38.6%, while it is around 36% among obese children.
- Link with Metabolic Syndrome: High MASLD prevalence rates are noted in individuals with diabetes (55.5%-59.7%), obesity (64.6%-95%), and severe metabolic syndrome (73%).
- Diet and Insulin Resistance: Excessive intake of refined carbohydrates and sugars leads to insulin resistance, promoting fatty liver development and progression to severe conditions like steatohepatitis and cirrhosis.
Challenges of Early Detection and Screening
- Asymptomatic Nature: Fatty liver disease often goes undetected in early stages due to the lack of symptoms, making comprehensive health screenings essential.
- Screening Components: Effective screening includes physical examinations (BMI, abdominal girth, waist-to-hip ratio), blood tests (sugar profile, lipid profile, liver function tests), and abdominal ultrasounds.
- Advanced Diagnostic Tools: Technologies like vibration-controlled transient elastography assess liver stiffness and fibrosis, facilitating early detection and monitoring of liver disease progression.
Personalisation and Integrated Approaches
- Customized Screening: Screening tests and frequencies should be personalized based on risk factors such as family history, lifestyle, and pre-existing health conditions.
- Comprehensive Management: Integrated strategies combining dietary modifications, regular physical activity, and effective weight management are crucial for mitigating liver disease risks.
- Awareness and Lifestyle Choices: Emphasizing the impact of lifestyle choices on liver health is critical. Regular health screenings and informed dietary habits are essential for long-term health.
UPSC Mains Questions:
Q. Examine the role of personalized and integrated approaches in managing fatty liver disease. How can lifestyle modifications and regular screenings contribute to better liver health outcomes?


Editorials
Context
The disparities in healthcare expenditure in India highlight significant inequalities. The Household Consumption Expenditure Survey (HCES) of 2022-23 brings to light the critical issue of unequal access to healthcare, underscoring the need for systemic reforms in the public healthcare sector.
Disparities in Healthcare Expenditure
- Survey Findings: The HCES reveals stark disparities in healthcare spending between rural and urban areas. In rural India, monthly medical expenses per head are ?89 for hospitalization and ?180 for other health needs, compared to ?123 and ?258 in urban areas.
- Income-Based Inequality: The top 5% of the population spend over 100 times more on hospital care than the bottom 5%. When analyzed further into percentiles, the disparity between the richest 1% and the poorest is even more pronounced.
- Implications of Averages: These averages are misleading, as they mask the reality of massive hospital bills that many cannot afford, highlighting the unequal burden of healthcare costs.
Challenges in Public Healthcare Access
- Dependence on Private Sector: Due to the inadequate state-run healthcare system, those struggling financially often resort to private healthcare services, leading to significant out-of-pocket expenses.
- Systemic Failures: Public figures opting for private healthcare is indicative of the failing public system, which lacks the trust and capability to provide quality health services.
- Cost Implications: While medicines remain relatively affordable, the high cost of private healthcare services exacerbates financial strain on the majority.
Policy Responses and the Way Forward
- Ayushman Bharat Scheme: The scheme has expanded insurance coverage significantly, with 345.6 million cards issued and almost 30,000 hospitals empaneled. However, it involves complex eligibility and treatment checks, falling short of universal healthcare.
- Universal Healthcare Necessity: A system providing high-quality healthcare to all without barriers, as seen in welfare states, is essential for equitable access.
- Government Priorities: While investing heavily in infrastructure, the government must address public healthcare gaps to achieve the Viksit Bharat ambition of a developed India by 2047. Immediate and massive upgrades in public healthcare infrastructure and services are crucial.
UPSC Mains Questions:
Q. Evaluate the effectiveness of the Ayushman Bharat scheme in addressing healthcare disparities in India. How does it compare to the concept of universal healthcare in equality-oriented welfare states?


Editorials
Context
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is planning to allow the private sector to produce the Launch Vehicle Mark-III (LVM3), India’s most powerful launch vehicle. This move is similar to the retirement of NASA’s Space Shuttle program, which led to a boom in the US commercial space sector.
Impact on Infrastructure and Global Demand
- Transfer of Technical Knowledge: The transfer of technical knowledge from ISRO to the private sector for LVM3 production will spread crucial space expertise. These capabilities could then strengthen India’s supply of launch vehicles to meet growing global demand for launch services.
- Increasing Production: Currently, ISRO makes two LVM3s per year, but by leveraging the private sector’s advantages, the goal is to increase this number to six. This enhancement will expedite ISRO’s plans and ensure timely launch schedules.
- Global Opportunity: A shortage in launch services worldwide presents an opportunity for India. Increasing the frequency of LVM3 flights for exclusive use or ride-sharing will draw greater interest from clients.
Future Endeavors and Achievements
- Future Goals: ISRO can focus on goals that include human spaceflight for the forthcoming Gaganyaan mission, building a Next Generation Launch Vehicle (NGLV), a more advanced, partially reusable heavy launch vehicle, and eventually placing an Indian space station in the LEO.
- Successful Launch: In 2022, ISRO’s commercial arm successfully launched the LVM3 for a large commercial order, deploying 36 satellites to LEO. The private sector’s involvement will make more such missions possible.
- Driving Innovation: ISRO is testing semi-cryogenic technology to boost the LVM3’s lift capacity and range. This is currently the most cost-efficient way to achieve orbit.
Potential for Private Sector Innovations
- Transfer of Technical Knowledge: ISRO’s transfer of LVM3 production knowledge will disseminate critical space expertise across India’s private sector, enhancing launch vehicle supply to meet global demand.
- Scaling Production: Leveraging private sector capabilities aims to increase LVM3 production from two to six annually, expediting ISRO’s plans and ensuring timely launches.
- Innovation and Cost Efficiency: Private firms can build on ISRO’s innovations, enhancing LVM3’s capabilities and introducing cost-efficient solutions for multiple payload deliveries.
UPSC Mains Questions:
Q. Evaluate the role of policy reforms since 2020 in fostering private sector participation in India’s space sector. How can these reforms boost India’s position in the global space market?