17th September 2024 (10 Topics)
Mains Issues
Context
The recent violence in Manipur has reignited discussions about the role of emergency provisions in India's federal structure and their impact on Centre-State relations. This debate focuses on the use of emergency powers under Articles 355 and 356 of the Indian Constitution, especially in light of the ongoing crisis in Manipur.
How is India’s Federal Set-Up?
- India is a federal republic with a division of powers between the Union and State governments, as outlined in the Seventh Schedule of the Constitution.
- States are primarily responsible for maintaining law and order within their territories.
Emergency Provisions:
- Emergency provision is a unique feature of Indian Constitution that allows the Centre to assume wide powers so as to handle special situations.
- The emergency provisions are provided in Part XVIII of the Constitution.
- The Constitution of India provides for three different kinds of abnormal situations which call for a departure from the normal governmental machinery setup by the Constitution:
- National Emergency (Article 352): An emergency due to war, an external aggression or armed rebellion.
- State Emergency or Presidential Rule (Article 356): Failure of constitutional machinery in states
- Financial Emergency (Article 360)
- Articles 355 and 356 deal primarily with the affairs of government in a State under this part.
- Article 355: It mandates the Centre to protect every State from external aggression and internal disturbance, ensuring State governments operate according to the Constitution. It serves as a safeguard against arbitrary use of Article 356.
- Article 356: It allows the imposition of President's Rule if a State government fails to function in accordance with constitutional provisions. This article is unique to India, as other federal systems like those in the U.S. and Australia do not have similar provisions for dissolving State governments.
National Emergency vs State Emergency (Key-Differences)
| National Emergency | State Emergency | |
| Applicability | In situations of war, external aggression or armed rebellion. | In situation of failure of constitutional machinery in State |
| Effect | No authority to the Centre to suspend the Constitution in a state. | The Council of Ministers is dissolved, vacating the office of Chief Minister. Furthermore, the Vidhan Sabha is either prorogued or dissolved, necessitating a new election. |
| Fundamental Rights | It affects Fundamental Rights | It does not affect Fundamental Rights |
| Centre-State Relationship | the relationship of all the states with the Centre changes | the relationship of only one state where the action is taken changes with the Centre |
| Proclamation | Approved by the Parliament within 1 month and thereafter every 6 months and there is no maximum duration prescribed | Approved by the Parliament within 2 months and thereafter every 6 months, and the maximum period that it remains in force is 3 years. |
Judicial Interpretations
- Misuse of Article 356: Historically, Article 356 has been misused to dismiss elected State governments for reasons not strictly related to constitutional breakdown.
- S R Bommai Case (1994): The Supreme Court restricted the misuse of Article 356, stating it should only be used in cases of constitutional machinery breakdown, and is subject to judicial review.
- Widening Scope of Article 355: Subsequent rulings have expanded the scope of Article 355, allowing the Union to take actions to protect States and ensure constitutional governance.
Suggestions and Recommendations
- Sarkaria Commission (1987) suggested that Article 355 should empower the Union to take necessary actions for State protection and governance.
- National Commission to Review the Working of the Constitution (2002) and Punchhi Commission (2010) emphasized that Article 356 should be used only as a last resort in extreme situations.


Mains Issues
Context
The Department for Promotion of industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), Ministry of Commerce and Industry, is set to launch the BHASKAR initiative, under the Startup India programme, to strengthen the startup ecosystem in the country.
About
- BHASKAR stands for Bharat Startup Knowledge Access Registry' (BHASKAR)
- It is a platform designed to centralise, streamline, and enhance collaboration among key stakeholders within the entrepreneurial ecosystem, including startups, investors, mentors, service providers, and government bodies.
- This initiative aligns with the government of India's vision to transform India into a global leader in innovation and entrepreneurship, reinforcing the country's commitment to the startup movement.
- India is currently home to over 1,46,000 DPIIT-recognised startups (and ranks third globally, following the US and China.)
- BHASKAR seeks to leverage this potential by providing an all-encompassing, one-stop digital platform that addresses the challenges faced by entrepreneurs and investors alike.
- Features and Goals
- Personalized BHASKAR IDs: Each stakeholder will receive a unique ID, facilitating easier interaction and efficient discovery of opportunities and partnerships.
- Digital Registry: BHASKAR aims to create the world’s largest digital registry for startup ecosystem stakeholders.
- Central hub: The platform will offer networking, centralized access to resources, and enhanced discoverability to support India's global brand and entrepreneurial growth.
Start-Up Ecosystem of India
- India is the third-largest startup ecosystem globally with over 1.4 lakh DPIIT-registered startups.
- Job Creation
- Direct Jobs: DPIIT-recognized startups have created over 5 lakh direct jobs.
- Recent Growth: In 2023, startups generated 3.9 lakh jobs, marking a 46.6% increase from the previous year and a 217.3% rise over the last five years.
- Startups contributed USD 140 billion in FY23, nearly 4% of India's GDP, highlighting their significant role in economic growth and innovation.
- Unicorn: By January 2024, India boasted 111 unicorn startupsvalued at over US$ 350 billion.
- Inclusivity: The rise of women-led startups, now at 18%, further highlights the inclusivity and potential of this thriving sector.
- Top performing sectors: Retail, Enterprise Applications, Fintech, Transportation & Logistics tech, Food & Agriculture tech, Auto tech, Travel & Hospitality tech, and Edtech.
- New Emerging sectors such as DeepTech, SpaceTech, Artificial Intelligence, and EVs have broadened the Indian startup landscape.
- Several factors have fueled the growth of top-funded sectors, like:
- increased internet penetration
- digitization
- government initiatives
Key Challenges Faced by Indian Startups
- Major issues: Valuationissues, less IPOs , regulatory changes, and macroeconomic and geopolitical trends in 2023
- Capital Access: Hard to secure adequate funding, impacting growth and innovation.
- Investor Challenges: Risk aversion and uncertain market conditions limit investor confidence.
- Sustainable Revenue: Struggles with finding viable business models and achieving profitability.
- Lack of Support: Inadequate physical and technological infrastructure, and limited mentorship and networking opportunities.
- Complexity: Regulatory and tax structures are complex, creating operational challenges.
Government initiatives and policies to nurture the startup ecosystem
Ministry-wise Initiatives
|


Mains Issues
Context
Recent advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), especially in natural language processing (NLP) and generative AI (Gen-AI), have significantly transformed how we interact with technology. Major companies like OpenAI, Google, and Microsoft have developed large language models (LLMs) that excel in text generation and understanding. These models have improved human-computer interactions by providing experiences that closely mimic human understanding. However, the rise of these technologies has also highlighted several challenges and potential areas for improvement.
Challenges with Current LLMs
- High Energy Consumption: LLMs, such as GPT-3 with 175 billion parameters, require enormous amounts of energy for training and operation. Training such models can consume as much energy as an average American household uses in 120 years, and emit significant carbon dioxide, equivalent to running a large data center for a year.
- Limited Control and “Hallucinations”: LLMs, trained on vast datasets, can produce text that seems coherent but may be factually incorrect or nonsensical. This issue arises from the models’ inability to fully understand context or verify factual accuracy.
- Challenges with Syntax: While LLMs are proficient in understanding semantics (meaning), they struggle with syntax (sentence structure). This limitation can lead to errors in generating contextually appropriate text.
How Quantum can solve the challenges?
Quantum Computing offers a promising way to address these limitations. Quantum computing is a new type of computing that uses the principles of quantum mechanics to tackle problems that are too complex for even the most powerful traditional computers. It uses quantum phenomena like superposition and entanglement to perform computations more efficiently than classical systems.
- Quantum Natural Language Processing (QNLP): QNLP leverages quantum computing to enhance language models. It requires fewer parameters than traditional LLMs, potentially reducing energy consumption and improving accuracy. QNLP models can better understand both syntax and semantics simultaneously, addressing the issues of “hallucinations” and misinterpretations.
- Quantum Generative Models for Time-Series Forecasting: A recent development in quantum computing involves using quantum generative models (QGen) to analyze time-series data. A QGen model from Japan has shown the ability to work effectively with both stationary (e.g., commodity prices) and nonstationary data (e.g., stock prices). These models require fewer parameters and computational resources compared to classical methods, offering a more efficient solution for forecasting and anomaly detection.
Implications and Future Directions
- Sustainability: By reducing the energy requirements and improving the efficiency of AI systems, quantum computing can make LLMs more sustainable and cost-effective.
- Accuracy and Efficiency: QNLP and QGen models promise to enhance the accuracy of language processing and time-series forecasting, offering significant improvements over current technologies.
- Research and Development: Continued research in quantum computing and its applications in AI could lead to more sophisticated and environmentally friendly technologies.
Fact Box:
|


Prelims Articles
Context
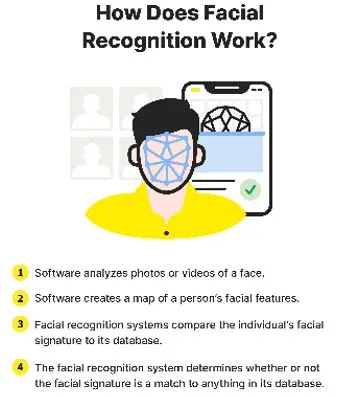
Recent findings from a study highlight concerns about the potential misuse of facial recognition technology, such as the Digi Yatra app. While Digi Yatra aims to streamline airport check-ins and boarding, there is significant apprehension regarding the abuse of biometric data by private entities.
About
- Developed by: Digi Yatra Foundation and the Ministry of Civil Aviation
- Objective: To provide air travelers with a hassle-free, frictionless, and health-risk-free experience.
- Functionality: It uses facial biometrics as a single token to digitally confirm travel, identification, and health data.
- Technology: It is based on a Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI) ecosystem with Privacy by Design principles to ensure security and privacy of biometric and personal information.
- Process: It links a traveler’s boarding pass to a facial recognition system (FRS) for quicker identification and smoother passage through boarding gates and pre-security checks.
Fact Box: Face Recognition Technology
|


Prelims Articles
Context
A 24-year-old student has died from the Nipah virus in the southern Indian state of Kerala.
What is Nipah?
- Nipah virus is a zoonotic virus transmitted from animals to humans. The virus was first identified in Malaysia in 1998.
- It is transmitted to humans mainly from fruit bats, pigs, contaminated fruits, or through human-to-human transmission.
- Symptoms: Symptoms can range from asymptomatic infection to acute respiratory infection.
- Initial symptoms: headache, muscle pain, vomiting, and sore throat, later leading to severe respiratory issues, atypical pneumonia, and neurological issues such as encephalitis. O
- Other symptoms: dizziness, drowsiness, and altered consciousness.
- Nipah can cause a lethal, brain-swelling fever in humans.
- Fruit bats are known as the reservoir of the virus, and all the outbreaks in Kerala had been reported during the May-September period – the rainy season.
- Nipah is classified as a priority pathogen by the World Health Organization (WHO) because of its potential to trigger an epidemic.
- There is no vaccine to prevent infection and no treatment to cure it.
Other important zoonotic viruses:
|


Prelims Articles
Context
An ambitious project of the Central government of reintroducing Cheetahs in India successfully completed two years after being declared extinct in 1952.The Cheetah Action Plan (CAP) is India’s initiative to reintroduce African cheetahs into the country’s ecosystems.
What is Project Cheetah?
- Launched in: 2022
- Project Cheetah is India’s ambitious attempt to introduce African cats in the wild in the country. Cheetah were the only large carnivore species that went extinct in Independent India.
- The project is the first-ever intercontinental translocation of the big cats.
- As part of the project, 20 cheetahs have been brought to the Kuno National Park in Madhya Pradesh so far -- eight from Namibia in September 2022 and 12 from South Africa in February 2023.
- Current status:
- Since they arrived in India, eight adult cheetahs -- three females and five males -- have died.
- Seventeen cubs have been born in India, with 12 surviving, bringing the total number of cheetahs, including cubs, in Kuno to 24. Currently, all are in enclosures.
- Objective: Introduce African cheetahs to India to conserve the species and restore degraded dry-open forest/savanna ecosystems. The cheetahs are intended to boost eco-tourism and benefit local communities.
- Timeline: The population is expected to reach Kuno National Park’s carrying capacity in about 15 years and the wider landscape in 30-40 years.
- Why Kuno National Park? Kuno was chosen as the most suitable location among ten surveyed sites due to its habitat and prey base. However, cheetahs have been held captive here longer than planned.
- Additional sites like Banni Grasslands in Gujarat and Nauradehi Wildlife Sanctuary in Madhya Pradesh are being considered for cheetah introduction.
Current Issues with the Project
- Extended Captivity: The cheetahs have faced prolonged captivity, far beyond the planned 1-2 months. This extended confinement has led to concerns about their readiness for the wild.
- Radio-collared males and females were supposed to be released in stages but have faced delays. The extended captivity may affect their ability to adapt to the wild.
- Cheetah Fatalities: Several cheetahs have died due to health issues or accidents. Problems include pre-existing health conditions, improper management, and environmental stressors.


Prelims Articles
Context
September 16 is designated as the International Day for the Preservation of the Ozone Layer by the United Nations to protect the fragile shield of the Ozone layer, which protects the planet Earth from the harmful ultraviolet radiations from the Sun. India has been celebrating this day since 1995. The theme for this year is “Montreal Protocol: Advancing Climate Actions”.
What is Ozone (O3)?
- Ozone (O3) is a reactive gas made up of three oxygen atoms. The word ‘ozone hole’ refers to areas or regions harmed by damaging UV radiations.
- It is found in the stratosphere (15-30 km above Earth) and at ground level.
- Characteristics: Pale blue gas with a distinct odor. Measured in Dobson Units (DU); typical concentration is around 300 DU.
- Dobson Unit (DU) is the unit of measurement for measuring the amount of ozone in a column of air above the Earth’s surface.
- Ozone Layer Depleted
- Regions Affected: Mainly Antarctica and the Arctic, with greater recognition in Antarctica.
- Mechanism: Depletion is linked to low stratospheric temperatures and the presence of halogen source gases (e.g., chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and halons) which weaken the ozone layer.
- Impact of Human Activities: Industrial activities and consumer goods contribute to ozone depletion through emissions of ozone-depleting substances.
Harmful Effects of Ozone Depletion
- Human Health: Increased UVB radiation leads to higher risks of skin cancer, cataracts, and other health issues.
- Flora: UVB radiation negatively affects plant growth and development.
- Marine Life: UVB impacts phytoplankton, affecting the marine food chain.
- Terrestrial Life: Increased UVB alters biogeochemical cycles, impacting greenhouse gas levels.
Montreal ProtocolAdopted: September 16, 1987
|


Editorials
Context
The Supreme Court of India recently dismissed a petition by former civil servants, academics, and activists in the case of Ashok Kumar Sharma and Others vs Union of India. The petition sought to suspend existing and future licences for the export of military equipment to Israel, citing concerns over international humanitarian law violations amid ongoing conflict in Gaza. The Court's decision raises questions about judicial review limits on executive foreign policy decisions, especially concerning international humanitarian law.
Judicial Review Limits
- Court's Dismissal Rationale: The Supreme Court declined to rule on the merits, focusing instead on procedural aspects. It stated that international obligations are not binding in this context, as Israel was not a party to the case. This approach overlooks the fact that the challenge was directed at the Indian government and companies, not Israel.
- International Obligations and Domestic Law: The Court's reasoning contradicts its previous judgments, which emphasized interpreting domestic law in light of international obligations. Despite the ICJ's detailed orders and obligations under conventions like the Genocide Convention, the Court failed to enforce these international norms domestically.
- Foreign Policy and Contractual Concerns: The Court cited potential breaches of contract and other fallout as reasons for dismissing the petition. It overlooked that the government could invoke force majeure to halt arms exports due to international legal obligations, thus prioritizing commercial interests over humanitarian concerns.
Fallout of the Decision
- Impact on Humanitarian Crisis: The Supreme Court's dismissal could impede efforts to halt military aid to Israel, amidst severe humanitarian crises in Gaza. This inaction might contribute to the ongoing devastation and international criticism of Israel’s conduct.
- Judicial Review in Foreign Policy: The decision underscores the constraints of judicial review over executive actions in foreign policy, especially in contexts involving humanitarian law violations. It highlights a gap in enforcing international legal commitments within domestic judicial frameworks.
- Legal and Ethical Implications: The Court's stance raises significant concerns about India’s adherence to its international legal obligations, potentially undermining global trust in India's commitment to human rights and humanitarian laws.
Practice Question
Q. Amid the ongoing humanitarian crisis in Palestine and international condemnation of Israel’s actions, the Supreme Court’s inability to compel India to halt military aid to Israel underscores the limitations of judicial review over executive foreign policy decisions, particularly regarding humanitarian law violations. Comment


Editorials
Context
The concept of 'women-led development' has gained prominence, particularly during India's G20 Presidency, and reflects the government's commitment to empowering women as key players in development. This approach has been underscored by recent legislative and institutional changes aimed at enhancing women's roles in governance, particularly in the Rajya Sabha (Council of States).
Legislative and Institutional Measures
- Women’s Representation in Rajya Sabha: The house has introduced progressive measures to enhance women’s roles in the Rajya Sabha. Notably, the Nari Shakti Vandan Adhiniyam (Women’s Reservation Bill) 2023 led to the reconstitution of the vice-chairpersons’ panel, exclusively featuring women (P.T. Usha)
- Initiatives in the Rajya Sabha Secretariat: Women officers now handle critical roles previously dominated by men, including House duty and chamber management. An app called ‘Vahan’ supports female officers with transportation during late hours, while gender sensitization workshops foster a culture of parity.
- Impact on Gender Parity: The Rajya Sabha Secretariat has seen increased female participation in key roles, including human resources and legislative sections. Women are also appointed to senior positions and recognized for their performance. Events like Women’s Day celebrations are organized by female employees, showcasing their contributions and talents. Such measures reflect a broader commitment to integrating women into all facets of parliamentary and administrative functions.
Practice Question
Q. In light of global trends where women are increasingly leading governance and development initiatives, evaluate the current status of women’s representation and participation in India’s legislature.


Editorials
Context
Since the enforcement of the Surrogacy (Regulation) Act and the Assisted Reproductive Technologies (Regulation) Act, 2021, several concerns have emerged, particularly regarding the prohibition on payments to surrogate mothers. These concerns are currently being challenged in the Supreme Court for their constitutional validity. The debate centers on whether the prohibition on payments to surrogates adequately addresses potential exploitation and if it properly compensates the labor involved in surrogacy.
Concerns with Prohibition on Payments
- Legal and Ethical Issues: The Surrogacy Act prohibits any form of payment to surrogates, limiting compensation to medical expenses and insurance coverage. This prohibition may exploit surrogates by undervaluing their labor and failing to address the power imbalances between surrogates, commissioning parents, and clinics.
- Impact on Surrogate Mothers: Historically, surrogate mothers received payments for their services, which has been replaced by the altruistic model where compensation is limited to expenses and insurance. The argument that this prohibition equates to a form of child sale has been debated. Additionally, the disparity in how surrogate labor is valued compared to other medical and legal professionals involved raises concerns about fairness and recognition of the labor involved.
- Parliamentary Recommendations: Prior to the Act’s enactment, the Parliamentary Standing Committee recommended allowing "reasonable compensation" beyond just medical expenses. It suggested compensation for lost wages, psychological counseling, and other support for surrogates. This recommendation reflects the recognition of surrogacy as a significant labor and suggests that fair compensation should be provided to avoid exploitation and ensure ethical practices.
Fallout of the Act
- Underground Practices: The prohibition has led to instances where surrogacy arrangements go underground, with reports of illegal surrogacy rackets. This suggests that while the law aims to regulate surrogacy, it may inadvertently push practices into exploitative environments.
- Struggles in Surrogacy Arrangements: The shift has made it challenging for intending parents to find willing surrogates.
- Supreme Court’s Role: The Supreme Court’s examination of these issues will be critical in determining whether the prohibition on payments adequately addresses concerns of fairness and exploitation. The Court’s decision will impact the future regulation of surrogacy and ensure that surrogates are fairly compensated for their labor.
Practice Question
Evaluate the implications of the prohibition on payments to surrogate mothers as prescribed by the Surrogacy (Regulation) Act and the Assisted Reproductive Technologies (Regulation) Act, 2021.