18th January 2025 (10 Topics)
Mains Issues
Context
China's population dropped by 1.39 million in 2024, reaching 1.408 billion. This marks the third consecutive year of population decline. The main cause is that more people are dying than being born.
Historical Context:
- China’s population has been slowly declining since the 1980s.
- However, the year 2022 was significant because it was the first time since 1961 (during the Great Leap Forward famine) that deaths outpaced births.
- Regional Demographic Crisis: China’s neighbors, including Japan, South Korea, and Taiwan, are also facing similar issues of population decline due to low birth rates and restrictions on immigration.
Why is the population declining?
- Rising costs of living are causing young people to put off or rule out marriage and child birth while pursuing higher education and careers.
- While people are living longer, that's not enough to keep up with rate of new births.
- While spending on the military and flashy infrastructure projects continues to rise, China's already frail social security system is teetering, with increasing numbers of Chinese refusing to pay into the underfunded pension system.
- In China, unmarried women do not have access to fertility treatments like IVF, which is a policy issue affecting the overall birthrate.
Beijing’s Efforts to Address the Issue:
China has tried various methods to reverse this trend:
- Incentives: Offering financial support for raising children, such as subsidies for childcare.
- Social Pressure: Labeling unmarried women as “leftovers” and restricting divorce and abortion to encourage larger families.
- End of One-Child Policy: In 2016, China ended its one-child policy and allowed families to have up to three children (since 2021). The one-child policy caused a preference for male children, leading to a lopsided population. There are now fewer women in the population, further complicating the situation.
- Raising Retirement Age: To manage the aging population, China has started increasing the retirement age from 60 to 63 for men and from 55 to 58 for women in managerial and technical roles.
Despite these efforts, the birthrate continues to fall due to economic factors like high living costs, youth unemployment, and a slowdown in the economy.
Impact of the Economy:
- Economic Challenges: China’s economy grew by 5% in 2024 but is expected to slow down in the future. The high cost of living, especially in urban areas, makes it difficult for young couples to afford children.
- Aging Population: A shrinking working-age population is straining an underfunded pension system, and an aging society is leaning on a creaking health care system.
- Cultural and Social Issues:
- Gender Imbalance: The one-child policy caused a preference for male children, leading to a lopsided population. There are now fewer women in the population, further complicating the situation.
- Youth Unemployment: Many young people in China are unemployed, contributing to the reluctance to have children.


Mains Issues
Context
The US has imposed new sanctions on Russia's oil trade, targeting 183 tankers (ships), which are part of Russia's "shadow fleet." This fleet has been used to bypass Western sanctions and continue selling Russian oil to countries like India and China.
Why are these sanctions significant for India?
- Oil remains a crucial part of the global economy, influencing geopolitical dynamics and national revenues.
- India, as the third-largest consumer of crude oil in the world, is heavily reliant on oil imports.
- Before the war in Ukraine, Russia wasn’t a major oil supplier to India, but since 2022, Russia became one of India’s biggest suppliers due to discounted prices, as Western countries reduced their purchase of Russian oil.
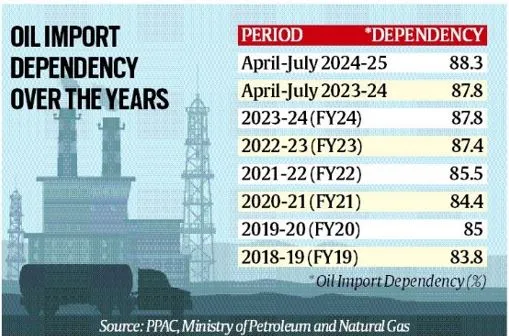
- In 2024, nearly 38% of India’s total oil imports came from Russia. However, these sanctions on Russian tankers could affect the smooth flow of this oil to India.
Impact on India’s Oil Trade
- The Indian economy is “significantly vulnerable” to fluctuations in oil prices. Domestic retail prices of gasoline and diesel surge “like rockets” in response to rising crude oil prices.
- Analysis from the Reserve Bank of India in 2019 found that every $10 per barrel rise in oil prices could lead to a 0.4% increase in headline inflation.
- Not only will China and India have to pay more for the oil they consume, they will need to pay more to have it delivered to their shores because oil tanker rates have also risen.
- Combined with a stronger U.S. dollar and weaker rupee, the impact on the India economy will be magnified.
- Alternative Suppliers: If Russian oil becomes more expensive due to higher shipping costs, Indian refiners might turn to traditional suppliers such as Iraq, Saudi Arabia, and the UAE, which are already India’s top oil sources.
Fact Box:India’s Stand
India’s Strategic Crude Oil Reserves
|


Mains Issues
Context
India is engaging with the Taliban but remains cautious. India seeks regional stability, security, and better access to Central Asia.
Background
- India had previously been cautious about engaging with the Taliban after the group took control of Afghanistan in August 2021.
- Before that, India had a strong relationship with Afghanistan, helping with development projects, providing scholarships, and building infrastructure like roads and hospitals.
- The fall of Kabul to the Taliban in 2021 disrupted India’s influence, giving rivals like Pakistan and China a greater foothold in the region.
- However, India’s approach to the Taliban has changed recently, as it navigates the new geopolitical reality.
- India has reportedly been in indirect talks with the Haqqani Network, a powerful faction of the Taliban responsible for attacks on Indian interests. However, India is unlikely to have formal relations with the Haqqani faction due to its links with Pakistan and its role in past attacks against India.
Internal Divisions in the TalibanThe Taliban is divided into two main factions:
India is closely monitoring these divisions. Tensions between these factions, especially after the assassination of a key Taliban leader in December 2024, could create opportunities for India to influence the future direction of Afghanistan. |
India’s Approach: Pragmatism and Opportunism
India’s new strategy is shaped by two key ideas:
- Strategic Pragmatism: India is balancing its interests by engaging with the Taliban while setting aside past ideological differences. It focuses on regional stability and security rather than political disagreements.
- Strategic Opportunism: India is also taking advantage of tensions between the Taliban and Pakistan. By condemning Pakistan’s airstrikes in Afghanistan in December 2024, India showed its disapproval of Pakistan's actions, positioning itself as a responsible regional power.
India’s Strategic Interests
India’s engagement with the Taliban helps it secure several strategic goals:
- Regional Connectivity: India wants to use Afghanistan to improve its access to Central Asia, bypassing Pakistan's ports.
- Security: India aims to prevent terrorism and maintain regional stability, especially by countering groups like Lashkar-e-Tayyiba (LeT) and Jaish-e-Mohammed (JeM), which are active in Kashmir.
- Humanitarian and Development Aid: India continues to provide aid and build goodwill among the Afghan people, who have historically supported India's involvement in Afghanistan.
Risks of Engaging with the Taliban
- The biggest risk is the Taliban itself, as it is linked to terrorist organizations and has a history of violence.
- Despite its attempts to appear more moderate, India remains cautious about fully trusting the Taliban.
Why the Taliban is Significant for India?
- Terrorism Threat: India is concerned about Afghanistan becoming a base for groups like Lashkar-e-Tayyaba (LeT), Jaish-e-Mohammad (JeM), and ISKP, which target Indian interests. India aims to prevent Afghanistan from being a hub for anti-India terrorist groups, especially after the Taliban’s return to power.
- Regional Diplomacy: Countries like Russia, China, Iran, and Central Asian nations have normalized ties with the Taliban, pushing India to do the same to secure its influence in Afghanistan and the region.
- Space to Counter Pakistan: Deteriorating Pakistan-Taliban ties give India space to secure its interests in Afghanistan and reduce Pakistan's influence there.
- Chabahar Port: India’s development of Chabahar port in Iran aims to bypass Pakistan’s Karachi and Gwadar ports, ensuring trade with Afghanistan and Central Asia. Engagement with the Taliban is key to enhancing connectivity.
Fact Box:Taliban
|


Mains Issues
Context
In order to revive India’s slowing economic growth, the focus should be on boosting consumption. As per reports, private investments (capex) have not picked up as expected, and government spending (capex) has also declined.
What are the current issues in the economy?
- Middle Class and Inflation: The middle class is hoping for relief from high food prices, which would lead to higher disposable incomes, especially in urban areas. In December, the inflation rate was 5.22%, largely due to a seasonal drop in food prices, like fruits and vegetables.
- The global economy in 2025 is expected to be unpredictable, with disinflation (slowing inflation) happening at uneven rates across different regions.
- While disinflation could help households with limited financial resources, inflation pressures may rise due to uncertainty in the global economy. As a result, interest rate decisions may become more difficult and uncertain.
- Need of consumption:
- Private investment and manufacturing were identified as the main factors slowing down India's growth. This is the right time to spark economic growth by stimulating consumer demand. This, in turn, could lead to more investments in the economy.
- Private consumption (spending by individuals) is improving, largely due to the rise of e-commerce and quick commerce (q-commerce), where goods are delivered quickly. While this growth is good for competition, there should be no restrictive policies that hinder this trend.
What is Consumption?
- Consumption refers to the use or purchase of goods and services by individuals or households. When people buy food, clothing, electronics, or even pay for services like healthcare or education, they are engaging in consumption.
- It is the end-point of economic activity, as it involves the final use of products and services.
- Significance:
- Consumption is a key driver of economic growth. In any economy, the more people consume, the more businesses produce and sell, which leads to higher demand and increased production.
- A strong level of consumption signals that the economy is healthy, as people are confident enough to spend money on goods and services.
Role of Consumption in Economic Growth:
- Demand Creation: When consumers spend money, it creates demand for goods and services. This leads to businesses needing to produce more, which can drive investment in factories, technology, and infrastructure.
- Boosting Production and Employment: Increased consumption encourages companies to hire more people, increase production, and expand businesses. This can create jobs and help reduce unemployment.
- Economic Stabilizer: In times of economic downturns, when investment or business spending might be low, increased consumption can help keep the economy stable and prevent a recession.
- Government Policies: Governments often try to encourage consumption through policies that increase people’s disposable income, like tax cuts, subsidies, or lower interest rates on loans.


Prelims Articles
Context
Prime Minister Narendra Modi distributed around 65 lakh SVAMITVA Property Cards in over 50,000 villages across 10 States (Chhattisgarh, Gujarat, Himachal Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Mizoram, Odisha, Punjab, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh) and 2 Union Territories (Jammu & Kashmir, Ladakh). The event marks a major achievement, the distribution of nearly 2.25 crore property cards under the SVAMITVA scheme.
About SVAMITVA Scheme
- Launched: 2020 on National Panchayati Raj Day (April 24)
- Survey of Villages Abadi and Mapping with Improvised Technology in Village Areas (SVAMITVA) Scheme is a Central Sector scheme of the Ministry of Panchayati Raj.
- It provides a ‘Record of Rights’ to village household owners with the issuance of legal ownership cards (Property cards/Title deeds) to the property owners by mapping land parcels using drone technology and GIS technology.
- The abadi area includes inhabitant land, inhabited areas contiguous to Abadi and wadis/basties in rural areas.
- SVAMITVA Scheme Achievements:
- 3.17 lakh villages have been surveyed, including full coverage in Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, and several Union Territories.
- 92% of villages have completed drone surveys, and property cards have been issued in 1.53 lakh villages.
- States like Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Haryana, and Uttarakhand have made significant progress, with some achieving 100% drone surveys and property card preparation.
- Over 67,000 sq. km of rural land has been surveyed, valued at Rs. 132 lakh crore.
- Impact on Rural India:
- The scheme helps rural families get a legal record of their property (Property Cards), which strengthens land rights and governance.
- It enables easier access to bank loans, resolves land disputes, and secures women’s property rights, boosting financial inclusion and economic growth.
- It has improved infrastructure planning and created social stability in rural India.
National Panchayati Raj Day
|


Prelims Articles
Context
The Department of Telecommunications launched NBM 2.0, an upgraded version of the previous National Broadband Mission (launched in December 2019). The Sanchar Saathi mobile app (an extension of the existing website) has been also launched.
Key Goals of NBM 2.0:
- Fiber Connectivity Expansion:
- The mission aims to extend fiber optic broadband to 7 lakh villages by 2030 (up from 50,000 currently).
- 90% of anchor institutions like schools, anganwadis, health centers, and panchayat offices should be connected by fiber by 2030.
- Increase Rural Subscribers: The target is to raise the share of rural broadband subscribers from 45% to 60% by 2030.
- Improving Fixed Internet Speeds: Ensuring faster internet speeds in rural areas and improving wireless connectivity.
- Right of Way and 5G:
- The Mission focuses on making it easier to lay telecom infrastructure by facilitating Right of Way (permissions for laying fiber and telecom towers).
- Efforts will be made to improve 5G connectivity by developing better street infrastructure for telecom equipment.
- Collaboration between Union and State Governments is necessary to streamline permissions for telecom infrastructure.
Fact Box:National Broadband Mission 1.0
Sanchar Saathi Mobile App
|


Prelims Articles
Context
Anaemia in India has long been believed to be primarily caused by iron deficiency, but a new study has shown that this view might be too narrow. The study suggests that factors such as Vitamin B12 deficiency, folate deficiency, and even air pollution might also be contributing to the high levels of anaemia in India.
Key-highlights of the Study
The study, involving over 4,500 people from 8 Indian states, found that:
- Iron deficiency isn’t the only cause: Only 9% of the participants had iron-deficiency anaemia.
- A significant portion of the anaemia cases (about 22%) were caused by unknown factors. This could include Vitamin B12 deficiency, folate deficiency, blood disorders, or environmental issues like air pollution.
- Anaemia Prevalence:
- According to the NFHS-5, anaemia has worsened in India, especially among women and children, even with years of interventions like iron supplementation.
- High Anaemia in Some Regions: In states like Assam, the prevalence of anaemia was very high (50-60%), but iron deficiency was much lower (only about 18%). This suggests other factors, like poor hygiene or malnutrition, could be playing a role in the region.
What is Anaemia?
- Anaemia occurs when the body doesn’t have enough red blood cells (RBCs) or hemoglobin.
- Hemoglobin is the main protein in red blood cells. It carries oxygen, and delivers it throughout body. It is essential for transporting oxygen to different parts of the body.
- Without enough RBCs or hemoglobin, a person can experience symptoms like weakness, fatigue, paleness, and dizziness.
- Anaemia may be caused by several factors. The most common nutritional cause of anaemia is iron deficiency although deficiencies in folate, vitamins B12 and A are also important causes.
Fact Box:Government Initiatives to Combat Anaemia and Malnutrition in India
|


Editorials
Context
The QS World Future Skills Index has ranked India’s job market as second only to the US in terms of readiness to recruit for advanced digital and green technologies. However, the report also highlights significant gaps in India’s ability to harness these new technologies, especially in the education system and its alignment with industry needs.
India’s Market Readiness and Skills Deficit
- High Market Preparedness: India has a near-perfect score of 99.1% in terms of market readiness to recruit for advanced technologies, indicating a strong demand for skills in digital and green technologies.
- Low Capacity to Harness New Technologies: Despite this preparedness, India ranks 25th overall in its ability to harness the opportunities opened by these new technologies, highlighting a critical gap in the workforce’s capabilities.
- Skills Mismatch: India scores poorly (59.1%) in the “skill-fit” parameter, the lowest among 30 countries, reflecting a mismatch between the skills available in the workforce and those demanded by employers in advanced technologies.
Challenges in India’s Education System
- Ineffective Post-Graduate Courses: The fact that two-thirds of post-graduate seats in Indian engineering colleges were vacant last year highlights that M-tech courses are not providing the required value addition to students.
- Curriculum Challenges: Engineering colleges face challenges in updating curricula to keep up with rapid technological advancements, especially at smaller and lower-rung colleges that struggle to attract top faculty.
- Need for Faculty Development: There is a pressing need for faculty training programs, possibly leveraging expertise from top institutes like IITs, to ensure that teachers stay updated with state-of-the-art knowledge in emerging fields.
Insufficient Investment in Research and Development
- Low R&D Expenditure: India’s research and development expenditure is only 0.65% of its GDP, significantly lower than the global average of 1.79%, which hampers the development of new technologies and innovations.
- Policy Response: While the government is aware of the challenge and has mandated the inclusion of courses in advanced technologies like AI, robotics, and cybersecurity, aligning the education system with industry needs will require more comprehensive reforms.
- Long-Term Solutions: The alignment of India’s educational ecosystem with the knowledge economy will require sustained action on improving faculty training, curriculum development, and increasing investment in R&D.
Practice Question
Q: India’s job market is well-prepared to recruit for advanced technologies, yet the country faces significant challenges in terms of aligning its education system with the needs of a rapidly evolving knowledge economy. Critically analyze the factors contributing to this mismatch and suggest measures to address the gaps.


Editorials
Context
The First Advance Estimates (FAE) of National Accounts for 2024-25 have been released, showing a real GDP growth of 6.4% and a nominal GDP growth of 9.7%. These figures are lower than the Reserve Bank of India’s revised expectations, reflecting a slowdown in the economy compared to earlier projections.
Real and Nominal GDP Growth Estimates
- Real GDP Growth: The real GDP growth for 2024-25 is projected at 6.4%, with an improvement expected in the second half of the year (6.7%) compared to the first half (6%). This represents a recovery from Q2 growth, which was 5.4%.
- Nominal GDP Growth: The nominal GDP growth estimate stands at 9.7% for 2024-25, falling short of the 10.5% forecasted in the Union Budget. This shortfall could affect revenue projections and fiscal management.
- GDP vs GVA Growth: The sharp decline in real GDP growth from 8.2% in 2023-24 is significant, but GVA growth has seen a smaller drop. Manufacturing experienced a marked slowdown, with GVA growth falling from 9.9% in 2023-24 to 5.3% in 2024-25.
Capital Formation and Investment Outlook
- Fixed Capital Formation (GFCF): The Gross Fixed Capital Formation rate has remained stable around 33.4% from 2021-22 to 2024-25, with expectations to maintain this level in 2025-26. Continued government investment is crucial to sustain growth.
- ICOR and GDP Growth Projections: The Incremental Capital Output Ratio (ICOR) is expected to be 5.1 in 2025-26, suggesting a realistic growth rate of 6.5% for real GDP, with India relying heavily on domestic demand.
- Government Investment: The Government of India’s capital expenditure has been slow in 2024-25, with a shortfall of ?5.14 lakh crore, which is 46.2% of the target. Accelerating capital expenditure in the remaining months is vital to achieve growth targets.
Long-term Growth Prospects and Challenges
- Medium-term Growth: Over the next five years, India’s real GDP growth rate is expected to average around 6.5%, in line with IMF projections, with nominal GDP growth reaching 10.5%-11%.
- External Conditions and Global Uncertainty: While global conditions may remain uncertain, India will need to depend primarily on domestic demand to sustain growth, especially as international factors remain unpredictable.
- Sustained Government Capital Expenditure: To support private investment and ensure long-term growth, the government needs to maintain a robust capital expenditure program, ideally growing at least 20% compared to revised estimates for 2024-25.
Practice Question
Q: Critically analyze the First Advance Estimates (FAE) of GDP growth for 2024-25. Discuss the factors contributing to the projected slowdown and the implications for India’s medium- to long-term economic growth prospects.


Editorials
Context
India's current macroeconomic policy are focusing on fiscal challenges, slowing government spending, and the need for structural reforms to boost investment and growth. It reflects on the effects of the pandemic and the government’s fiscal stance in the face of a global and domestic slowdown, considering the future fiscal priorities for the Indian economy.
Government Spending and Fiscal Policy
- Slowing Government Capital Expenditure: As of November, the Centre has spent only 46.2% of its capital expenditure target, down from 58.5% in the previous year. States have similarly underutilized their capital expenditure allocation.
- Fiscal Consolidation and Deficit Concerns: India's combined fiscal deficit stands above 7% of GDP, one of the highest globally, with interest payments consuming 19% of the Centre's expenditure. Hence, there is a pressing need for fiscal consolidation to build fiscal space and reduce debt risks.
- Countercyclical Fiscal Policy: To stimulate growth, it is essential for the government to meet its capital expenditure targets while also focusing on reducing the fiscal deficit. Efficiencies in spending and incentivizing investment are crucial.
Investment and Private Sector Challenges
- Private Investment Constraints: Despite tax cuts, private corporate investment has remained stagnant. Corporate savings have increased significantly, but the fixed capital formation rate has declined, indicating a gap between available resources and actual investment.
- Utilizing Domestic and Foreign Savings: India faces a dual issue of underutilized domestic savings and foreign savings, with inflows exceeding the current account deficit. Therefore, the constraint is not a lack of resources but the lack of effective investment.
- Tax Reforms and Corporate Strategy: A proposal for a tax on non-business income, offset by investment credits, could encourage more investment. Additionally, addressing income tax issues and simplifying the tax structure should remain a priority for better resource allocation.
Agricultural and Structural Reforms
- Agricultural Marketing Reforms: Many states have adopted private markets and allowed direct farm gate sales, but only 14 states have notified the necessary rules. Agricultural supply chain development is critical for improving farmer income and food supply.
- Food Supply and Regulation: As food consumption patterns evolve, with rising demand for processed foods, simplifying agricultural regulations and coordinating better with states can improve food supply chains and reduce price spikes.
- Reform Implementation at the Ground Level: Despite the Centre’s efforts to simplify laws, businesses continue to face challenges at the local government level. More effective implementation at state and local levels is necessary for successful reforms.
Practice Question
Q: Evaluate the effectiveness of India's current fiscal policy in addressing the macroeconomic slowdown. Discuss the role of government expenditure, structural reforms, and investment incentives in shaping India’s economic recovery.