

20th July 2024 (10 Topics)
Mains Issues
Context
In a significant stride towards gender neutrality, the Kerala government has initiated a comprehensive overhaul of school textbooks. The aim is to challenge traditional stereotypes by depicting men and other family members participating in domestic activities such as cooking, alongside women. This pioneering move seeks to instill inclusive values in children from an early age, thereby fostering a more equitable society.
Impact of the Initiative
- Normalize shared responsibilities within the household: The revamped textbooks feature images showing fathers engaged in household chores traditionally considered the domain of women. This visual representation is pivotal in breaking down deep-seated gender stereotypes prevalent in society.
- Social Change: This shift in portrayal is not merely symbolic but sets a precedent for how gender roles are perceived and practiced, particularly among younger generations.
- Holistic Approach to Gender-Neutral Education: This initiative is part of Kerala's broader efforts to promote gender-neutral education. In addition to revising textbooks, the state has introduced gender-neutral uniforms in select schools and is transitioning towards more mixed-gender educational institutions by phasing out single-gender schools.
Kerala's progressive steps reflect its commitment to building a society that is inclusive and equitable. These measures are designed to create an environment where children can grow up with a balanced understanding of gender roles and expectations.


Mains Issues
Context
A recent report by WHO and Unicef has highlighted significant concerns regarding India's immunisation efforts. In 2023, India ranked second globally, following Nigeria, in the number of children who did not receive any vaccines. Specifically, India recorded 1.6 million "zero-dose" children, indicating those who missed out on all routine immunisations.
Key-highlights of the Report:
- DPT Vaccine Coverage: There was a slight decline in coverage for the diphtheria, pertussis, and tetanus (DPT) vaccine from 95% in 2022 to 93% in 2023. This serves as an indicator for zero-dose children.
- Measles Vaccine Coverage: India also ranked third globally in the number of children who did not receive the measles vaccine, with 1.6 million children missing out on this essential immunisation.
- Comparison with Neighbouring Countries: Pakistan and Afghanistan, neighbouring countries, showed relatively lower numbers of unvaccinated children compared to India, indicating varying immunisation challenges across South Asia.
Who are Zero-Dose Children?
- WHO Definition: Zero-dose children are those who have not received any routine immunisation services, particularly the first dose of the DPT vaccine. This metric helps identify gaps in immunisation coverage and guides intervention strategies.
- Risk Factors and Access to Immunisation
- Risk Profile: Children classified as zero-dose in India are primarily those who missed the initial DPT vaccine dose administered around six weeks after birth.
- Health Facility Births: Around 88.6% of births in India occur in health facilities, ensuring access to vaccines like BCG (against tuberculosis) for most newborns.


Mains Issues
Context
A recent global outage, Blue Screen of Death (BSOD), severely impacted computer systems worldwide, disrupting operations in critical sectors such as aviation, banking, stock exchanges, payment systems, and emergency services. The root cause of this disruption was attributed to a technical issue with CrowdStrike Falcon, a cybersecurity platform that provides security solutions for Microsoft Windows devices.
Blue Screen of Death (BSOD)
- The Blue Screen of Death (BSOD) is a critical error screen that appears on Windows operating systems when a severe issue causes the system to crash. It forces the computer to restart unexpectedly, potentially resulting in data loss.
- Cause of the Outage: The outage stemmed from a configuration change within CrowdStrike's Azure backend workloads, affecting the connectivity between storage and compute resources. This interruption subsequently caused failures in Microsoft 365 services that rely on these connections.
Vulnerabilities inherent in interconnected digital services
- The Microsoft outage highlights the vulnerabilities inherent in interconnected digital services.
- It underscores the critical need for robust cybersecurity measures and rapid response protocols to mitigate such disruptions in the future, ensuring the reliability and continuity of essential services globally.
- Causes: Interconnected digital services rely on complex networks and systems that facilitate seamless communication and data exchange. However, several factors contribute to vulnerabilities:
- Dependency on Technology: Modern services heavily depend on technology infrastructure, software applications, and data sharing protocols.
- Cybersecurity Threats: Increasingly sophisticated cyber threats such as malware, phishing, and ransomware exploit vulnerabilities in interconnected systems.
- Human Error: Misconfigurations, lack of cybersecurity awareness, and unintentional actions by users can inadvertently expose vulnerabilities.
- Third-Party Dependencies: Integration with third-party services and APIs introduces additional points of vulnerability if not properly secured.
- Impacts:
- Disruptions and Downtime: Cyberattacks or technical failures can lead to widespread disruptions, causing downtime in critical services like banking, healthcare, and transportation.
- Data Breaches: Vulnerabilities can result in unauthorized access to sensitive data, leading to breaches that compromise privacy and trust.
- Financial Losses: Businesses may incur significant financial losses due to operational disruptions, legal liabilities, and recovery costs associated with cyber incidents.
- Reputational Damage: Public perception and trust in organizations can suffer following a cyber incident, affecting customer loyalty and investor confidence.
- Regulatory Compliance Issues: Non-compliance with data protection regulations and cybersecurity standards can result in legal penalties and regulatory scrutiny.
Fact Box: About CrowdStrike
|


Mains Issues
Context
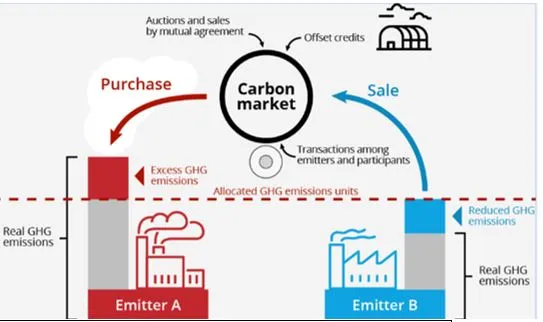
India and Japan are exploring a Joint Crediting Mechanism (JCM) under the Paris Agreement to enhance collaboration in Carbon Trading.
What is Carbon Trading?
- Carbon trading is the process of buying and selling permits and credits to emit carbon dioxide.
- Article 6 of the Paris Agreement provides for the use of international carbon markets by countries to fulfil their Nationally determined contributions (NDCs).
- These markets create incentives to reduce emissions or improve energy efficiency.
- Types of Carbon Markets:
|
Voluntary Markets |
Compliance Markets |
|
|
Advantages of Carbon Markets:
- Promotion of Energy Efficiency: Incentivizes reduction in energy use and transition to cleaner fuels.
- Cost-Efficiency: Companies can choose between investing in emission-reducing technologies or purchasing allowances, based on cost-effectiveness.
- Innovation: Encourages innovation and adoption of low-carbon technologies due to regulatory pressure and market incentives.
Challenges to Carbon Markets:
- Effectiveness Concerns: Some entities may buy credits without reducing emissions themselves, undermining the actual reduction of greenhouse gases.
- Quality Issues: Many credits available may not meet quality standards, lacking additionality (additional emission reductions), verifiability (proper auditing), and permanence (ensuring emission reductions are sustained).
- Deviating Emission Reduction Efforts: Purchasing credits might divert attention from genuine efforts to reduce emissions directly.
- Measurement Difficulty: It's challenging to accurately quantify emission reductions achieved through offset projects like afforestation or renewable energy initiatives.


Mains Issues
Context
In a significant development concerning the integrity of civil services examinations, the Union Public Service Commission (UPSC) has initiated legal action against Puja Manorama Dilip Khedkar, a probationary IAS officer, for alleged forgery and misrepresentation in obtaining disability certificates. The case has brought to light crucial ethical dilemmas and challenges within the framework of public service and governance.
Ethical Concerns Raised
- Integrity and Honesty in Public Service: The cornerstone of public service is integrity. Civil servants are expected to uphold the highest standards of ethical conduct, including honesty in all professional dealings. The alleged actions of Ms. Khedkar, if proven true, challenge this fundamental principle and undermine public trust in the selection process.
- Fairness and Transparency: The Civil Services Examination is designed to be fair and transparent, providing equal opportunities to all aspirants. Any attempt to manipulate the process through fraudulent means not only disadvantages honest candidates but also compromises the credibility of the entire system.
- Accountability and Responsibility: As future administrators entrusted with significant responsibilities, probationary IAS officers are expected to demonstrate accountability for their actions. They are role models for ethical behavior and are accountable to the public they serve, their colleagues, and the institutions they represent.
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Upholding the rule of law is crucial in public administration. The filing of an FIR by the UPSC against Ms. Khedkar underscores the importance of adherence to legal and regulatory frameworks. It serves as a reminder that unethical conduct will be met with stringent legal consequences.
Implications for Governance and Policy
- The case highlights the broader implications for governance and policy formulation:
- Reform in Examination Protocols: There may be a need for stricter verification protocols to prevent such instances of fraud in future examinations. Ensuring the authenticity of disability certificates and other supporting documents should be a priority.
- Enhanced Ethical Training: Training modules focusing on ethics and integrity could be integrated into the curriculum for civil servants. This would reinforce the importance of ethical behavior and equip them with the skills to navigate ethical dilemmas effectively.
- Public Trust and Confidence: Upholding the integrity of the civil services examination is essential for maintaining public trust in the credibility of the bureaucracy. Transparent investigations and swift actions against misconduct are crucial in this regard.
The case of Puja Khedkar serves as a critical examination of ethical standards in public service. It underscores the imperative for civil servants to uphold integrity, transparency, and accountability at all times. As aspirants prepare for the Civil Services Examination, understanding these ethical dimensions is not just a requirement for passing exams but a commitment to the ideals of public service.


Prelims Articles
Context
Recently, the Union government has initiated e-auctions for many of the 12,611 identified enemy properties across India. This move aims to effectively utilize these assets while adhering to the legal framework provided by the Enemy Property Act.
What are Enemy Properties?
- Enemy properties refer to any assets—immovable property, shares, debentures, etc.—that belong to, are held by, or managed on behalf of an enemy, enemy subject, or enemy firm.
- The term "enemy" here denotes countries (Pakistan, China) that have engaged in aggression or declared war against India.
- Enemy Property Act, 1968: The Act was enacted following the Indo-China and Indo-Pak conflicts of 1962 and 1965. It stipulated that descendants of individuals who migrated to Pakistan or China would forfeit any rights of succession to their ancestors' properties in India.
- Purpose: The primary objective of the Act is to regulate and take control of properties owned by individuals who moved to Pakistan or China after the wars.
- Key Amendments of 2017: Over time, the Act has undergone several amendments, the most recent being the Enemy Property (Amendment and Validation) Act in 2017.
- The 2017 amendment expanded the definition of "enemy subject" and "enemy firm" to include legal heirs and successors of enemies, irrespective of their nationality.
- It also established that once a property is declared as enemy property, it retains that classification.


Prelims Articles
Context
Following the refusal of three states to participate in the PM-SHRI scheme, the Union government has decided to halt funds allocated to these states under the Samagra Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA). The SSA is a flagship program that supports efforts to improve quality and inclusive education across the country.
About PM-SHRI Scheme
- The Pradhan Mantri Schools for Rising India (PM-SHRI) scheme is a comprehensive initiative aimed at enhancing the quality of education in government schools across India.
- Its goal is to transform these schools into model institutions that demonstrate the implementation of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020.
- The scheme targets upgrading over 14,500 government schools to serve as exemplars of 21st-century educational practices.
- Scheme Details
- Scope: The PM-SHRI scheme covers centrally operated schools, state government-run schools, Kendriya Vidyalayas (KVs), and Navodaya Vidyalayas (NVs).
- Financial Allocation: With a budget exceeding Rs 27,000 crore for the next five years, the scheme is funded with the Centre bearing 60% of the financial burden, while states contribute the remaining 40%.
- Objectives: It aims to equip students with 21st-century skills, making them "future-ready" through high-quality education.
Fact Box: About Samagra Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA)
|


Editorials
Context
The issue of menstrual leave has recently gained attention in India due to a Supreme Court decision on a writ petition seeking directives for its implementation under the Maternity Benefits Act, 1961. This has sparked debates regarding the need for policy measures to accommodate menstruation-related needs in workplaces and educational institutions.
Legal and Policy Debates
- Judicial Disposition and Executive Authority: The Supreme Court ruled against directives for menstrual leave under the Maternity Benefits Act, 1961, stating that such decisions fall within the domain of the executive. There is ongoing debate on whether menstrual leave should be explicitly provided under existing legislation or through new policy frameworks.
- Polarized Views and Concerns: Proponents argue that menstrual leave is essential for accommodating biological needs and promoting gender equity.
- Government Initiatives and Draft Policies: The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare has proposed the Draft National Menstrual Hygiene Policy, 2023, advocating for inclusive measures across gender identities.
Socio-Cultural Perspectives
- Cultural Perceptions and Taboos: Menstruation is both celebrated for its role in fertility and stigmatized as impure or dirty in various socio-cultural contexts.
- Biological Realities and Social Conditioning: Menstruation involves a range of bodily experiences from discomfort to incapacitation, yet societal norms often dictate silence and invisibility around these issues.
- Global Policy Experiences: Internationally, policies on menstrual leave vary, reflecting cultural norms and efforts to address gender disparities in workplace accommodations.
Future Directions and Challenges
- Moving Towards Inclusive Policies: There is a growing recognition of menstruation as a critical policy area requiring inclusive and rights-based approaches.
- Need for Public Discourse and Education: Addressing menstruation-related policies requires broader public discourse to challenge stereotypes and promote acceptance.
- Ensuring Implementation and Impact: Concrete measures are needed to ensure effective implementation of menstrual leave policies that cater to diverse needs sensitively. Upholding the rights of individuals who menstruate involves overcoming barriers such as stigma, discrimination, and institutional resistance.
Mains Question:
Q. Discuss the socio-cultural and legal dimensions of menstrual leave policies in India. Evaluate the challenges and opportunities in implementing such policies to promote gender equity and address biological needs effectively in workplaces and educational institutions.


Editorials
Context
Recent discussions have focused on enhancing disaster resilience in the face of increasing natural disasters and the substantial gap in insurance coverage, particularly between developed and developing economies. The need for alternative insurance methods, such as parametric products, has gained attention to address challenges in verifying losses from extreme weather events.
Challenges in Traditional Insurance Methods
- Limitations of Indemnity-Based Insurance: Traditional insurance relies on physical assessments of damage for payout eligibility. Verification becomes difficult in widespread disasters affecting economically disadvantaged communities.
- Growing Gap in Insurance Coverage: In 2023, global natural disaster losses amounted to $280 billion, with only $100 billion insured. Developing economies face wider gaps in insurance coverage compared to developed counterparts.
- Call for Alternative Insurance Approaches: Parametric insurance products are gaining traction for their real-time trigger-based payouts. These products offer payments based on predefined weather parameters like rainfall or wind speed, bypassing the need for physical damage verification.
Adoption and Implementation of Parametric Insurance
- Global Adoption Trends: Disaster-prone countries, particularly islands, have increasingly adopted parametric insurance for climate adaptation. Trust between states and insurers has improved over time, leading to more nuanced pricing and payout triggers.
- Examples of Parametric Insurance Implementation: Morocco secured $275 million in parametric insurance cover post a 6.8 magnitude earthquake. India's experience includes parametric crop insurance and initiatives for extreme precipitation and cyclones.
- Expansion Beyond High-Impact Disasters: Initially focused on earthquakes and cyclones, parametric insurance is now exploring coverage for low-impact, high-frequency events like rain and heat.
Strategies for Effective Parametric Insurance Use
- Key Factors for Governments: Precision in setting trigger thresholds and robust monitoring mechanisms are crucial. Experience sharing among governments aids in improving product effectiveness and transparency in pricing.
- Role of Multilateral Institutions: Multilateral support enhances regional pooling of risks and strengthens bargaining power with insurers. South Asia, as a climate-vulnerable region, could benefit from collaborative risk pooling and negotiation strategies.
- Challenges and Opportunities in Implementation: Ensuring widespread retail payout dissemination and encouraging long-term household premium payments are challenges, especially in poorer populations. Success stories from New Zealand and Turkey highlight the feasibility of implementing parametric insurance in earthquake-prone regions.
Mains Question:
Q. Discuss the significance of parametric insurance products in enhancing disaster resilience in developing countries. Evaluate the challenges in their adoption and implementation, and suggest measures to maximize their effectiveness in mitigating the financial impact of natural disasters.


Editorials
Context
Recent debates surrounding employment in India have intensified due to conflicting data interpretations between government and financial institutions. Prime Minister Narendra Modi's reference to RBI's KLEMS data to challenge reports of rising unemployment has sparked discussions on the reliability of employment statistics.
Prime Minister's Data Interpretation
- Citation of RBI's KLEMS Data: PM Modi highlighted RBI's KLEMS data to underscore significant job creation in recent years.
- Emphasis on Infrastructure Development: He emphasized ongoing infrastructure projects as crucial for future employment opportunities.
Challenges in Data Collection
- Complexity of the Indian Economy: The predominance of the unorganized sector (94% of labor force) complicates accurate data collection efforts.
- Reliance on Periodic Surveys: Data from surveys like ASUSE are constrained by outdated census and urban frame survey data.
Discrepancies in Reported Employment Trends
- Methodological Differences: Variations in defining employment between official reports (PLFS) and private assessments (CMIE) contribute to conflicting employment figures.
- Public Perception vs Official Statistics: Ground-level reports often diverge from official data, highlighting higher unemployment rates and social discontent.
Mains Question:
Q. Critically evaluate the challenges in assessing and interpreting employment data in India. Discuss the impact of economic complexities and methodological disparities on the accuracy of employment statistics. What steps should be taken to enhance transparency and reliability in reporting employment figures?




