26th December 2024 (13 Topics)
Mains Issues
Context
December 26, 2004 marks the 20th year since the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake and tsunami. The 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake and tsunami was a turning point in our understanding of tsunamis and earthquake risks. It led to significant advancements in early warning systems, scientific research, and disaster preparedness.
What Happened on December 26, 2004 (brief background)?
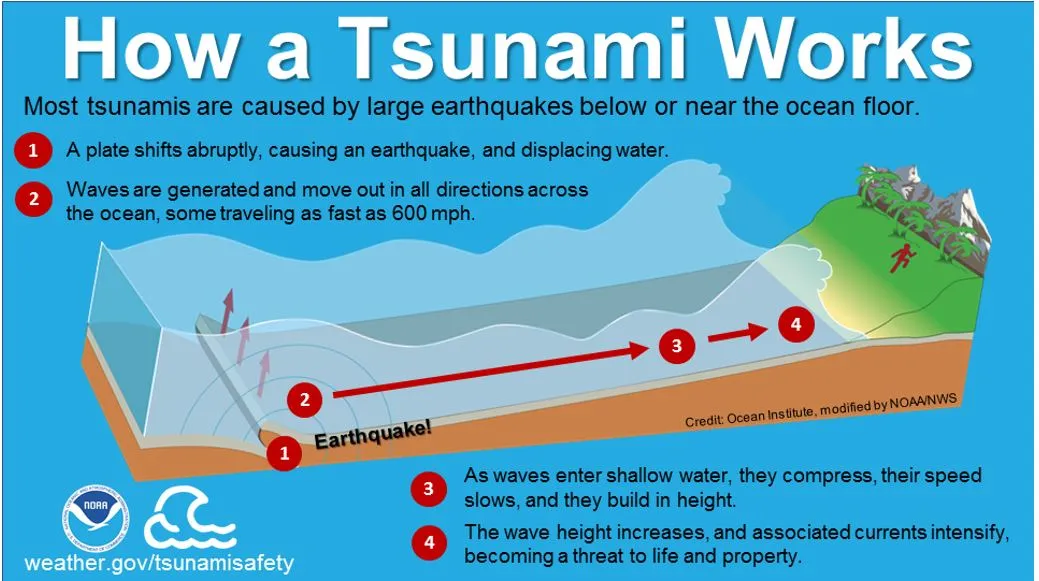
- On December 26, 2004, a massive earthquake of magnitude 1 occurred off the coast of Sumatra, Indonesia.
- This earthquake triggered one of the deadliest tsunamis in history, causing widespread destruction across 17 countries bordering the Indian Ocean. The tsunami killed around 227,000 people and displaced 1.7 million more.
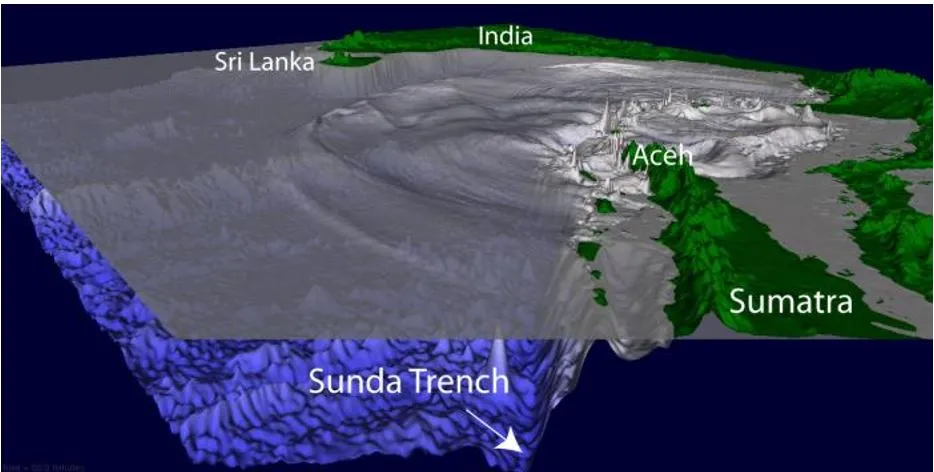
- Tectonic Background: The earthquake occurred in the Sunda Trench, where the Indo-Australian plate is being forced beneath the Burma microplate (part of the larger Eurasian plate).
- The earthquake involved the rupture of a 1,300 km long fault, starting from Sumatra in the south to the Coco Islands in the north.
- The tsunami was triggered by the longest faultline rupture from an earthquake ever observed, seconds before 7.59 am on December 26, 2004.
- The gap between the India plate and the Burma microplate was at least 1,200 kilometres (750 miles) long.
- It produced huge waves that were over 30 metres (100 feet) high, delivering energy equal to 23,000 Hiroshima atomic bombs and wreaking havoc.
- Indonesia is a vast archipelago nation on the Pacific “Ring of Fire,” which is a region of high seismic activity that stretches across the Pacific basin from Japan through Southeast Asia.
- Impact of the Tsunami:
- The tsunami waves traveled across the Indian Ocean, affecting countries like Indonesia, India, Sri Lanka, Thailand, Malaysia, the Maldives, and more.
- Some places, such as the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, saw 90% of the population wiped out. The disaster caused immense loss of life and property, especially in coastal regions.
- The tsunami generated by this earthquake was unprecedented in size. Scientists had not anticipated such a massive event in this region.
- Prior to this, there had been only two recorded tsunamis in the region (1881 and 1883), which were much smaller.
Two Decades of Change: Lessons Learned
- Global coordination: By 2005, the Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO had been tasked with coordinating a worldwide tsunami mitigation strategy. Central to this effort was the creation of the Indian Ocean Tsunami Warning and Mitigation System (IOTWMS) — a network of organisations designed to monitor and alert countries at risk.
- Today, India, Indonesia, and Australia serve as the nerve centers for tsunami warnings across 26 nations in the Indian Ocean.
- Tsunami Early Warning Systems: In the aftermath of the 2004 disaster, significant steps were taken to improve tsunami preparedness. One of the key developments was the establishment of the Indian Tsunami Early Warning Centre (ITEWC) in 2007, under the Ministry of Earth Sciences. This centre operates advanced systems to monitor earthquakes and tsunamis 24/7.
- ITEWC is a designated Tsunami Service Provider (TSP)for the Indian Ocean region under UNESCO’s Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission (IOC).
- The ITEWC uses seismological stations, pressure recorders, and tidal stations placed across the Indian Ocean.
- These devices can detect a tsunami-producing earthquake and issue warnings within about 10 minutes of detection. This system helps protect countries bordering the Indian Ocean from future tsunamis.
- The Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS), based in Hyderabad, has been at the forefront of ocean-related research and services in India. INCOIS provides tsunami alerts to 28 countries, showcasing its technological and scientific expertise.
- INCOIS operates a network of more than 300 seismic stations spread across the Indian Ocean, using advanced Global Seismic Network (GSN) technology.
- These stations can detect earthquakes as small as magnitudes are analysed to assess tsunami potential.
- Scientific Advancements: The 2004 tsunami spurred research into tsunami geology and earthquake monitoring. This research uncovered important historical evidence of past tsunamis in the region, including evidence of a tsunami from a thousand years ago found in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
- Tsunami Geology: Scientists found ancient evidence, like dead roots of trees exposed by rising and falling tides, which helped date past tsunami events.
- GPS and Seismology: Research institutions have strengthened seismic observations and geodetic studies along coastal regions, including the Andaman Islands. These advances improve our understanding of tsunami risks.
- Deep-ocean Assessment and Reporting of Tsunamis (DART): A network of DART is strategically deployed to monitor minute changes in sea level caused by underwater seismic activity. These buoys relay real-time data to ITEWC via satellite communication. The latest versions of DART buoys are more durable and equipped with advanced sensors for greater accuracy. Besides, supporting systems such as bottom pressure recorders and tide gauges, help track tsunami propagation.
- Numerical modelling: Numerical Modelling recreates tsunami scenarios using equations in mathematics and physics. A tsunami or tsunamigenic earthquake can happen due to several different permutations and combinations of seismic parameters. These are simulated as pre-run scenarios and stored in electronic formats.
- Future Tsunami Risks: Although the 2004 earthquake was a huge event, researchers warn that other regions, like the Makran Coast (off the coast of Iran and Pakistan), still pose risks. These regions could generate tsunamis that might affect India’s west coast, including cities like Mumbai, which has nuclear power plants.
What measures are required?
The world has witnessed a tenfold increase in the number of natural disasters since the 1960s. Data captured between 1900 and 2019 by the Institute for Economics and Peace reveal an increase from 39 incidents in 1960 to 396 in 2019. Given the increasing number of such events, following measures can be adopted:
- Nature-based solutions: These solutions involve protecting, restoring, and sustainably managing ecosystems in ways that increase their resiliency and ability to address those societal challenges, while also safeguarding biodiversity and improving human wellbeing.
- For example: Mangrove forests along coastlines are not only important for sustaining fisheries but also for providing protective natural barriers against erosion and strong storms.
- Better disaster response: The Wayanad landslide has exposed significant lapses in intergovernmental coordination and communication. The lack of timely warnings and efficient evacuation plans contributed to the high death toll and widespread destruction. This points to a critical need for robust and streamlined communication channels between different government agencies and with the public to ensure timely and effective disaster response.
- Investment: There is need to invest in disaster risk reduction, improve communication and preparedness strategies, and hold accountable those responsible for insufficient safeguards.
Fact Box: Tsunami
|
PYQQ: The 2004 Tsunami made people realize that mangroves can serve as a reliable safety hedge against coastal calamities. How do mangroves function as a safety hedge? (UPSC 2011)
Solution: (d) |


Mains Issues
Context
India and Saudi Arabia are strengthening their defense and industrial cooperation, with a focus on technology transfer, joint ventures, and localized production. This aligns with Saudi Arabia's Vision 2030 and India’s Make in India initiative, both of which emphasize reducing dependency on defense imports.
Defence-industrial cooperation between India and Saudi Arabia
- Mutual Trust in Defense Collaboration: Defense cooperation is built on a foundation of trust and shared goals, underscored by recent statements emphasizing Saudi Arabia as a top ally for India in defense technology sharing. Both nations aim to reduce their reliance on imports by strengthening domestic production capabilities.
- Investment and Localization: Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030 aims to localize 50% of its defense spending, complementing India’s push for self-reliance through its Make in India initiative.
- Indian defense companies have actively sought partnerships in critical sectors like shipbuilding, electronics, AI, and cybersecurity, with Saudi firms showing strong interest.
- Bilateral Engagements: Recent high-level visits and defense exhibitions have facilitated discussions on joint training exercises, technology exchange, and co-development of military platforms.
- Military exercises such as ‘Sada Tanseeq’ and ‘Al Mohed Al Hindi’ exemplify the growing operational synergy between the two nations.
- Trade in Defense Equipment: Saudi Arabia has signed contracts for Indian defense equipment demonstrating the potential for deeper industrial ties.
- Saudi Arabia is reported to have procured the 155mm Advanced Towed Artillery Gun System (ATAGS) from Bharat Forge.
- Saudi Arabia has in the past evaluated two types of artillery guns manufactured from Bharat Forge.
Significance of Saudi Arabia for India
- Strategic Importance: Saudi Arabia is a key partner in West Asia, contributing to regional stability and India’s energy security. This partnership is critical for India’s Look West Policy.
- Economic Significance: Saudi Arabia is a significant source of investments in India. There is potential for growth in trade and manufacturing collaboration, particularly in high-tech industries.
- Geopolitical Relevance: Strong relationship strengthens India’s influence in the Gulf region. Furthermore, it promotes strategic autonomy by diversifying defense partnerships.
- Energy Security: Saudi Arabia is a major supplier of crude oil to India, playing a pivotal role in India’s energy needs.
Fact Box:India-Saudi Arabia Relations:
Current State of India’s Defence Sector
|


Mains Issues
Context
The Agreement on Science and Technology Cooperation between the United States and China, which has been a cornerstone of their bilateral engagements since 1979, was renewed for another five years, effective August 2024. This extension, accompanied by amendments, reflects both the enduring significance of the partnership and the complexities that have come to define it in recent years.
Background
- Signed initially in 1979 during a pivotal moment in U.S.-China relations, the Agreement symbolized mutual intent to collaborate on areas like agriculture and technology.
- Over the decades, it expanded its scope, incorporating themes like nuclear fusion, earthquake studies, and health research.
- Administered by the S.-PRC Joint Commission on Scientific and Technological Cooperation, it laid the groundwork for collaborative research, researcher exchanges, and the establishment of bilateral research centers.
However, recent geopolitical shifts and technological advancements have brought the Agreement under closer scrutiny, prompting debates about its future utility.
Key Features of the Renewal
- Restricted Focus Areas: The renewed Agreement narrows its scope to basic research and intergovernmental collaboration in specific pre-identified areas, such as earthquake studies and basic health research.
- Sensitive and emerging technologies have been explicitly excluded to mitigate concerns over their potential misuse.
- Enhanced Safeguards: The amendments incorporate measures to address long-standing U.S. concerns regarding researcher safety, data sharing, and intellectual property rights.
- Geopolitical Underpinnings: The renewal reflects an effort to strike a balance—preserving cooperation where possible while imposing guardrails to protect national interests.
Challenges and Controversies
- The Agreement has been credited with catalyzing China’s scientific transformation, but this success has also fueled concerns:
- Reports have highlighted instances where China commercialized U.S.-funded research outputs without equitable returns.
- China’s R&D spending surged from $375 million in 1979 to $442 billion in 2021, positioning it as a formidable scientific rival to the U.S.
- The rising number of Chinese students and researchers in the U.S. has significantly boosted collaborations but also raised questions about knowledge transfer and its implications.
These developments prompted debates in the U.S., with stakeholders divided on whether the Agreement continued to serve American interests.
Why the Renewal Matters
- For the U.S.: Opting for a renewal with conditions allows the U.S. to maintain oversight over China’s scientific trajectory while continuing selective engagement.
- The Agreement serves as a diplomatic instrument, keeping dialogue open amid broader strategic competition.
- For China: Retaining the Agreement ensures avenues for scientific mobility, collaborative research, and limited engagement with the U.S., even as geopolitical tensions persist.


Mains Issues
Context
Australia’s Online Safety Amendment (Social Media Minimum Age) Bill, 2024, seeks to address concerns surrounding the online safety of minors by setting the minimum age for creating social media accounts at 16 years. The legislation amends existing laws, including the Age Discrimination Act, 2024, to facilitate its implementation. Once passed, it will mark a significant step in regulating social media use by minors, aligning with global discussions on online safety.
Key Features of the Proposed Law
- Applicability: The law targets Age-Restricted Social Media Platforms (ARSMPs), which facilitate online interaction and content sharing among users. Platforms such as TikTok, Instagram, Facebook, Snapchat, and others are likely to be included under its purview.
- The Minister of Communication retains the discretion to exempt specific platforms from the definition of ARSMPs.
- Compliance Obligations: Platforms must take reasonable steps to ensure individuals under 16 years do not create accounts. Failure to comply may attract civil penalties of up to USD 49.5 million.
- Guidelines for compliance will be developed by Australia’s eSafety Commissioner, ensuring clarity on what constitutes “reasonable steps.”
- Timeline and Implementation: The law’s enforcement is set to begin no earlier than 12 months after approval, allowing time for stakeholder consultations and age-verification trials.
- Platforms will be required to implement age-verification mechanisms for all account holders, ensuring adherence to the minimum age requirement.
- Data Privacy and Security: Platforms must destroy personal data collected during age verification after its intended use, with penalties under the Privacy Act, 1988 for misuse or unauthorized disclosure.
- Privacy obligations aim to mitigate risks associated with sensitive data collection and its potential misuse.
Underlying Concerns and Criticism
- Challenges of Implementation: The lack of a universally accepted age-verification technology has been highlighted as a hurdle, with Australia’s Age Verification Roadmap acknowledging the evolving nature of this field.
- Privacy Risks: Critics have raised concerns about the extent and type of data required for age verification, noting potential trade-offs between ensuring safety and protecting user privacy.
- Effectiveness of the Ban: Research underscores the dual nature of social media—while it can offer connectivity and support, it also exposes minors to risks like bullying, self-harm, and disordered eating.
- Academics and stakeholders argue that blanket bans may oversimplify complex issues, advocating for nuanced solutions that balance risks and benefits.
- Criticisms from Political Groups: Critics have described the legislation as “rushed” and questioned its alignment with existing evidence, calling for a more measured approach.
- Age limits for social media aren’t the most effective way to protect teens from its potential harms. Young people have shown remarkable prowess for finding workarounds — even those under the age of 13 whom most platforms already prohibit. Using social media is not inherently beneficial or harmful to teens, but strict age limits ignore individual differences in adolescents’ maturity levels.
- In other words, turning 16 doesn’t instantly make you more competent at navigating the digital world than a mature 14-year-old.
|
Pros |
Cons |
|
|
Global Comparisons
- United States: Previous efforts to impose age restrictions through laws like the Communication Decency Act, 1996, and the Children’s Online Protection Act, 1998, were struck down due to constitutional challenges related to free speech.
- Current U.S. laws, such as the Children’s Internet Protection Act, 2000, focus on ensuring online safety in schools and libraries through filtering technology.
- India: While Indian laws address online child pornography and require platforms to exercise due diligence, there are no restrictions on minors creating accounts on social media platforms.


Mains Issues
Context
Prime Minister Narendra Modi laid the foundation stone for the Ken-Betwa River Linking Project (KBLP) on December 25, 2024, marking the 100th birth anniversary of former PM Atal Bihari Vajpayee. The project has been criticized for its potential environmental impact, especially on the Panna Tiger Reserve.
About the Project
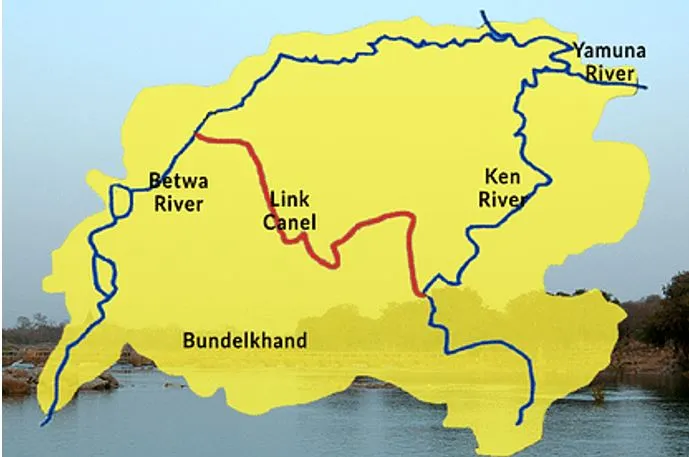
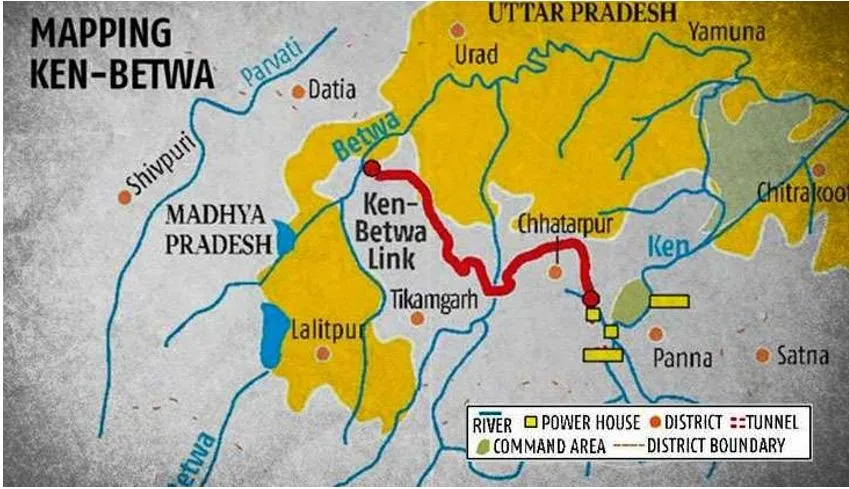
- The KBLP envisages transferring water from the Ken river to the Betwa river, both tributaries of the Yamuna, to address water scarcity in the Bundelkhand region.
- The project lies in Bundelkhand, which spreads across 13 districts of Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh.
- Under the project, a 77-metre high and 2.13 km long Daudhan dam and two tunnels (upper level 1.9 km and lower level 1.1 km) will be constructed on the Ken river in the Panna Tiger Reserve
- It is the country's first river-linking initiative, under the National Perspective Plan for interlinking of rivers, which was prepared in 1980.
- Key Features:
- Total canal length: The Ken-Betwa Link Canal will be 221 km in length, including a 2-km tunnel.
- Envisioned to provide:
- 62 lakh hectares of irrigation (8.11 lakh ha in Madhya Pradesh and 2.51 lakh ha in Uttar Pradesh).
- Drinking water for 62 lakh people.
- Generation of 103 MW of hydropower and 27 MW of solar power.
- Phases: The Ken-Betwa Link Project has two phases.
- Phase-I will involve building the Daudhan Dam complex and its subsidiary units such as the Low Level Tunnel, High Level Tunnel, Ken-Betwa Link Canal and power houses.
- Phase-II will involve three components — Lower Orr Dam, Bina Complex Project and Kotha Barrage.
- States Involved (Regions benefitting): Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh.
- Madhya Pradesh: Panna, Tikamgarh, Chhatarpur, Sagar, Damoh, Datia, Vidisha, Shivpuri, Raisen.
- Uttar Pradesh: Banda, Mahoba, Jhansi, Lalitpur.
- Critical Locations:
- Daudhan Dam: Situated inside the Panna Tiger Reserve, Daudhan dam is 2,031 m long, out of which 1,233 metre will be earthen and the rest 798 m will be of concrete. The height of the dam will be 77 m. The dam will submerge about 9,000 hectares of land, affecting 10 villages.
- Ken Gharial Sanctuary: Downstream, likely affected by changes in water flow.
- Timeline: The project is expected to be completed in eight years.
Challenges/Concerns
- Environmental:
- Deforestation: Submergence of 98 sq km of the Panna Tiger Reserve, leading to the loss of 2-3 million trees.
- Wildlife Threats: Tigers, gharials, vultures, and other species are said to be displaced.
- Ecological Disruption: There are concerns over hydrological balance and rainfall patterns, with studies indicating potential rainfall deficits.
- Social: Approximately 5,228 families in Chhatarpur and 1,400 families in Panna will be displaced due to submergence and land acquisition.
- Economic: Questions over the economic viability raised by the Supreme Court’s Central Empowered Committee (CEC).
Significance
- Water Scarcity Solution: It will address acute water shortages in Bundelkhand, a drought-prone region.
- Agricultural Boost: It will ensure year-round irrigation for a large area of arable land, promoting agricultural productivity.
- Energy Generation: Renewable energy will be provided through hydropower and solar power installations.
- National Water Strategy: Paves the way for future river interlinking projects under India’s National Perspective Plan (1980), which envisions 16 peninsular and 14 Himalayan river links.
What is Inter-linking of rivers?
- River Linking is a project of linking two or more rivers by creating a network of manually created reservoirs and canals, and providing land areas that otherwise does not have river water access and reducing the flow of water to sea using this means.
- It is based on the assumptions that surplus water in some rivers can be diverted to deficit-river by creating a network of canals to interconnect the rivers.
- Uses:
- For Irrigation purposes
- flood control in the region
- for Livelihood needs of locals
- Building Dams for water conservation
- The initial plan to interlink India’s rivers came in 1858 from a British irrigation engineer, Sir Arthur Thomas Cotton.
Fact Box:Panna Tiger Reserve (PTR)
Ken River
Betwa river
|


Mains Issues
Context
Weighing in on India’s slowing growth and high inflation conundrum, senior Reserve Bank of India (RBI) officials asserted that the “time to act is now to excoriate inflation and revive investment strongly”, even as they believed the growth trajectory is poised to lift in the second half of the year.
Key Observations
Economic Growth Trajectory
- Current Challenges: India’s GDP growth in Q2 2024-25 slipped to 5.4%, driven primarily by private consumption and fixed investment. The momentum, however, was weighed down by inflation-induced pressures.
- Signs of Recovery:
- Early indicators for Q3 2024-25 suggest an upswing:
- Festival-related economic activity.
- A noticeable revival in rural demand.
- Growth is projected to rebound to 6.8% in Q3 and 6.5% in Q4.
- Future Outlook: GDP growth is forecast to average 6.7% in 2025-26, underpinned by resilient private consumption.
Inflation Dynamics
- Recent Trends: Retail inflation eased from 6.2% in October to 5.5% in November, aided by declining food prices. However, the relief is uneven:
- Rice prices have fallen, but wheat and atta prices remain firm.
- Edible oil continues to face upward price pressures.
- Prices of onions and tomatoes have dropped, while potatoes remain steady.
- Input Cost Pressures: Across both manufacturing and services sectors, input costs hardened in November, leading to the steepest price increases in over a decade. Firms, facing rising costs, are increasingly inclined to pass these on to consumers.
Key Challenges
- Weakening Consumer Demand: The repeated inflation shocks have significantly eroded purchasing power, reflecting in subdued sales growth for corporations and sluggish demand conditions.
- Private Investment Hesitation: A lack of robust private investment is evident, as firms rely on existing capacity rather than committing to capacity expansion amid uncertain demand.
- Fiscal Constraints: A slowing nominal GDP growth rate threatens to constrain fiscal spending, including capital expenditure, complicating efforts to meet deficit and debt targets.
- Global Risks: Geopolitical tensions, rising protectionism, and debt overhangs present risks to emerging market economies (EMEs).
- Currencies and equity markets in EMEs remain vulnerable to volatility in global trade and capital flows.
Policy Recommendations
- Target Inflation Aggressively: Timely interventions are necessary to prevent inflation from undermining industrial and export growth, especially as seasonal relief from food prices sets in.
- Focus on Investment Revival: Creating conditions for capacity expansion and fixed asset investment is critical to stimulate economic activity and enhance long-term growth prospects.
- Support Private Consumption and Exports: Measures to accelerate private consumption and bolster exports could reinforce economic resilience.
Fact Box:Economic Concepts
Global Economic Trends
|


Prelims Articles
Context
Four years after launching the Svamitva scheme to digitize property records in rural India, Prime Minister Narendra Modi is set to hand over 5.8 million property cards to their owners in over 50,000 villages across 12 states.
What is the Svamitva scheme?
- SVAMITVA (Survey of Villages and Mapping with Improvised Technology in Village Areas) is a Central Sector Scheme launched by the Ministry of Panchayati Raj.
- It was launched in 2020 to provide rural property owners with official "Records of Rights," granting them access to bank loans, reducing disputes, and improving village-level planning.
- Progress so far:
- Currently, it has been implemented across 31 states and Union territories.
- A total of 20.19 million property cards have been issued under the Panchayati Raj scheme so far.
- 92 per cent of drone mapping has been completed in 317,000 villages. The scheme is on track to meet its targets by 2026.
- Significance of the initiative
- Banks are increasingly accepting these property cards, which have helped many women establish legal rights over land.
- In essence, the scheme has facilitated the identification of open spaces and contributed to enhanced community development.
Ministry of Tourism has sanctioned a total of 76 projects for an amount of Rs.5287.90 Crore under the Swadesh Darshan Scheme, out of which 75 projects are physically complete


Prelims Articles
Context
The Ministry of Tourism in 2024 focused on infrastructure development, sustainable tourism, global promotion, and skill development, with initiatives under schemes like Swadesh Darshan 2.0, PRASHAD, and SASCI.
Major Initiatives and Achievements of the Ministry of Tourism in 2024
- Swadesh Darshan Scheme: Ministry of Tourism has sanctioned a total of 76 projects for an amount of Rs.5287.90 Crore under the Swadesh Darshan Scheme, out of which 75 projects are physically complete.
- The scheme has been revamped as Swadesh Darshan 2.0 (SD2.0) to focus on sustainable and responsible tourism.
- 34 projects sanctioned under SD2.0 worth ?793.20 crore.
- Introduced a Challenge-Based Destination Development initiative with four thematic categories:
- Spiritual Tourism, Culture & Heritage, Vibrant Villages, and Ecotourism.
- 42 destinations identified for development under these themes.
- PRASHAD Scheme (Pilgrimage Rejuvenation and Spiritual Augmentation Drive): 48 projects sanctioned worth ?1646.99 crore; 23 projects completed.
- Assistance to Central Agencies Scheme: 65 projects sanctioned worth ?937.56 crore; 38 projects completed.
- Special Assistance to States for Capital Investment (SASCI): 40 projects sanctioned across 23 states for ?3295.76 crore to develop iconic tourist centers with interest-free loans for 50 years.
- Tourism Statistics (2023)
- International Tourist Arrivals (ITAs): 18.89 million.
- Foreign Tourist Arrivals (FTAs): 9.52 million.
- Domestic Tourist Visits (DTVs): 2509 million.
- Foreign Exchange Earnings (FEEs): ?231,927 crore.
Swadesh Darshan Scheme
PRASHAD Scheme
|


Prelims Articles
Context
The 55th meeting of India’s Goods and Services Tax (GST) Council, was held in Jaisalmer, Rajasthan, significant attention was given to addressing pressing economic issues such as food inflation, unemployment, rural job creation, and maintaining capital expenditure momentum.
Key takeaways from the 55th GST Council meeting:
- Increase in GST for used electric vehicles (EVs):The Council approved raising the GST rate on old and used electric vehicles from 12 per cent to 18 per cent.
- This move aims to align the tax structure of used EVs with that of new EVs, which are currently taxed at 5 per cent.
- Hike in GST for small petrol and diesel cars:A decision was made to increase the GST rate on small petrol and diesel cars from 12 per cent to 18 per cent. This adjustment is intended to standardise tax rates across different vehicle categories.
- Tax relief on health and life insurance premiums:The Council granted full GST exemptions on term life insurance premiums and health insurance premiums for senior citizens. Additionally, health insurance policies with coverage up to Rs 5 lakh for other individuals will also enjoy tax relief. This measure is expected to make insurance more affordable and accessible.
- GST rate adjustments on luxury goods: To boost revenue, the Council decided to increase GST rates on luxury items such as high-end wristwatches and shoes. This change is projected to generate an additional Rs 22,000 crore annually.
- Reduction in GST on essential items:In an effort to reduce household expenses, the Council lowered GST rates on essential goods, including bicycles, exercise books, and large packs of packaged drinking water. This move is aimed at providing relief to consumers.
- GST Rate Changes
- GST Rate Reduction on Fortified Rice Kernel (FRK): The GST rate on Fortified Rice Kernel (FRK), classifiable under HSN 1904, reduced to 5% from existing GST rate of 18%.
- GST Exemption on Gene Therapy: To exempt GST on gene therapy.
- IGST Exemption on Long Range Surface to Air Missile System (LRSAM): To extend IGST exemption to systems, sub-systems, equipment, parts, sub-parts, tools, test equipment, and software meant for the assembly/manufacture of LRSAM system under Notification 19/2019- Customs.
- Compensation Cess Reduction for Merchant Exporters: Rate of compensation cess to be reduced to 0.1% on supplies to merchant exporters. Reduction recommended to bring the compensation cess rate at par with the GST rate.
- IGST Exemption for International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) Imports: IGST to be exempted on import of all equipment and consumable samples by the inspection team of the IAEA subject to specified conditions.
- Concessional GST on Food Preparations for Government Programs: Concessional 5% GST rate to be extended to food inputs of food preparation for free distribution to economically weaker sections under government programmes subject to the existing conditions.
- Increase in GST Rate on sale of old and used vehicles: GST rate on the margin on the sale of all old and used vehicles, including electric vehicles, to be increased from 12% to 18%.
- No GST applicable on ‘penal charges’ levied by banks and s (NBFCs) for non-compliance with loan terms.
- Pepper and raisins supplied by agriculturists not to be liable to GST.
- Specific Commodity Clarifications:
- Autoclaved Aerated Concrete Blocks (ACC):Blocks with over 50% fly ash content will attract 12% GST under HSN 6815.
- Pepper and Raisins:Fresh or dried pepper and raisins supplied by agriculturists will not attract GST.
- Ready-to-Eat Popcorn: Popcorn mixed with salt and spices attracts 5% GST if not pre-packaged and labelled, and 12% GST if it is pre-packaged. Popcorn mixed with sugar (e.g., caramel popcorn) falls under confectionery (HSN 1704) and attracts 18% GST.
- Pre-Packaged and Labelled Goods: The definition has been revised to include all commodities intended for retail sale, containing up to 25 kg or 25 litres, and bearing labels under the Legal Metrology Act.
Fact Box:GST Council
|
PYQQuestion 1. What is/are the most likely advantages of implementing ‘Goods and Services Tax (GST)’? (UPSC 2017)
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Solution: (a) Question 2. Consider the following items: (UPSC 2018)
Which of the above items is/are exempted under GST (Good and Services Tax)?
Solution: (c) |


Prelims Articles
Context
A recent study highlights the growing threats to the critically endangered lion-tailed macaque, endemic to the Western Ghats of India, due to increasing human-wildlife interactions.
About the Lion-Tailed Macaque
- The Lion Tailed Macaque(Macaca silenus) is an old world monkey.
- It is a relatively small-sized macaque with a furless black face and a white ‘mane’.
- Covered in a thick coat of black fur, its short tail ends in a tuft, which is why it is known as the Lion-tailed Macaque.
- Conservation Status:
- IUCN Red List:
- CITES: Listed under Appendix I, providing the highest level of protection.
- Habitat: They are found exclusively in the Western Ghats, across fragmented forests in areas such as Anamalai Hills, Nelliyampathy, Nilambur Ghats, Sholayar, Sabarimala, Agumbe, and others.
- Population: Approximately 4,200 individuals remain in the wild.
PYQQuestion 1. Consider the following fauna: (UPSC 2023)
How many of the above are generally nocturnal or most active after sunset?
Solution: (c) |


Editorials
Context
The Disaster Management (Amendment) Bill, 2024, has sparked concerns regarding its impact on participatory governance and accountability. Critics argue that the Bill fails to address key gaps in the Disaster Management Act (DMA), 2005, and weakens provisions meant to ensure a holistic, inclusive, and efficient disaster management system.
Lapses in the Bill’s Provisions
- Top-Down Approach in Terminology: The Bill uses terms like ‘monitor’ and ‘guidelines’, which may undermine local communities' role as ‘first responders’, as emphasized in global frameworks such as the Sendai Framework. A more collaborative approach using terms like ‘supervision’ would have fostered greater trust with local entities.
- Lack of Acknowledgment for Local Communities: While the Bill defines concepts like 'hazard' and 'resilience', it ignores the critical role of local communities, panchayats, and NGOs in disaster management, evident in past disasters like Cyclone Aila and the 2013 Kedarnath floods.
- Absence of Intersectional Vulnerability Considerations: The Bill neglects to address intersectional vulnerabilities, failing to recognize the compounded discrimination faced by women, disabled individuals, and marginalized communities during disasters, thus limiting the Bill's inclusivity.
Concerns Regarding Accountability and Governance
- Omission of Relief Standards: Sections 12, 13, and 19, which set minimum standards of relief for disaster victims and special provisions for vulnerable groups, are omitted in the Bill. This omission weakens accountability in disaster relief and hampers the holistic recovery process.
- Performance Evaluation Gaps: The Bill lacks provisions for evaluating district authorities' performance, potentially allowing for political exploitation of disaster recovery efforts and undermining accountability in disaster management operations.
- Absence of Animal Welfare Measures: The Bill overlooks the death of animals in disasters, neglecting the responsibilities of Disaster Management Authorities (DMAs) in implementing the Animal Birth Control (ABC) Rules, 2023, and addressing the impact of disasters on wildlife.
Gaps in Regional and Urban Disaster Management
- Urban Disaster Management Authority (UDMA): The Bill proposes an Urban Disaster Management Authority (UDMA), but its need remains unclear. Municipal Corporations, which control urban land use, often contribute to urban flooding, and the Bill fails to address the role of these bodies in disaster management.
- Lack of Regional Collaboration: The Bill fails to mention regional collaboration frameworks like SAARC, BIMSTEC, or BRICS, missing an opportunity to strengthen cross-border disaster response strategies in South Asia, especially in light of increasing zoonotic and epizootic diseases.
- Limited International Cooperation: The Bill does not encourage international collaboration or decentralization of responsibilities within the National Disaster Management Authority. A regional approach, as outlined in the 2011 SAARC Agreement on Rapid Response, could have improved disaster resilience across neighboring countries.
Practice Question
Q. Critically analyze the provisions of the Disaster Management (Amendment) Bill, 2024, and discuss how its limitations may impact India’s disaster management framework. What are the implications for regional and international collaboration in disaster response?


Editorials
Context
The issue of guaranteeing Minimum Support Price (MSP) for crops has gained significant attention, especially amidst growing concerns over farmer distress, groundwater depletion, and the rising cost of food imports. Experts argue that guaranteeing MSP would benefit farmers, address environmental issues, and reduce India’s dependency on foreign imports.
Necessity of MSP Guarantee
- Farmer Distress and Suicides: The lack of fair MSP has contributed to immense financial distress among farmers, leading to a troubling rise in farmer suicides. Reports indicate nearly 7,00,000 farmer suicides in the past three decades, with many farmers unable to recover costs due to low market prices for their crops.
- Impact on Groundwater and Crop Diversification: In states like Punjab, where rice and wheat farming is predominant, MSP guarantees for 23 crops could encourage diversification, which would help conserve vital groundwater resources. Diversified farming would also allow farmers to grow more profitable crops, reducing reliance on water-intensive rice.
- Economic and Health Benefits: Guaranteeing MSP would also help reduce India’s dependency on oil and pulses imports, saving nearly Rs 2 lakh crore annually. Additionally, reducing reliance on imported oils like palm oil, which has health concerns, would improve public health and strengthen the nation’s agricultural sector.
Issues with Current MSP Implementation
- Discrepancy Between MSP and Market Prices: In many states, despite MSP being set for crops, farmers are forced to sell their produce at significantly lower prices due to insufficient government procurement. For example, in states like Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, and Rajasthan, farmers often sell their paddy below the MSP, leading to massive financial losses.
- OECD Report on Farmers’ Losses: An OECD report highlights that farmers have incurred nearly Rs 60 lakh crore in losses due to the government's failure to enforce proper MSP. In 2023 alone, the country lost Rs 14.72 lakh crore due to inadequate MSP support, exacerbating the debt crisis among farmers.
- Unfair Financial Burden on Farmers: The gap between the MSP and the actual market price results in increasing farmer indebtedness, with many farmers falling deeper into debt each year. The government’s failure to ensure fair MSP contributes directly to this worsening financial situation.
Potential of Guaranteed MSP for National Development
- Boosting National Agricultural Resilience: Guaranteeing MSP would strengthen India's agricultural sector, helping it become self-sufficient in oilseeds and pulses. Punjab, for instance, has the potential to diversify and produce a variety of crops, reducing the need for imports and contributing to food security.
- Low Cost of Guaranteeing MSP: The cost of guaranteeing MSP for crops is significantly lower than the amount spent on oil and pulses imports, estimated to be around Rs 20,000 to Rs 50,000 crore. This cost is a small price to pay for stabilizing the agricultural sector and ensuring long-term food security for India.
- Environmental and Social Benefits: A guaranteed MSP would also reduce electricity consumption in agriculture by promoting crop diversification, contributing to lower electricity costs for households. Additionally, it would protect groundwater resources, benefiting both agricultural and non-agricultural sectors in the long run.
Practice Question
Q. Discuss the importance of guaranteeing Minimum Support Price (MSP) for crops in India. How would its implementation help in addressing farmer distress, environmental concerns, and national economic stability?


Editorials
Context
The 2004 Indian Ocean tsunami, which devastated Nagapattinam, Tamil Nadu, catalyzed major reforms in disaster management in India. Two decades later, while significant progress has been made, evolving risks continue to demand enhanced preparedness and resilience strategies.
Progress in Disaster Management
- Institutional Reforms Post-Tsunami: The 2004 tsunami prompted the Disaster Management Act of 2005, establishing the National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) and empowering local authorities to implement tailored disaster plans.
- Technological Advancements: India developed the Indian Tsunami Early Warning Centre (ITEWC) in 2007, using GIS, AI-driven risk assessments, and mobile apps to improve real-time monitoring and preparedness for natural disasters.
- Focus on Long-Term Resilience: Nagapattinam's recovery involved building multi-hazard-resistant homes and critical infrastructure, alongside integrating disaster risk insurance for homes, marking a shift toward long-term disaster resilience.
Lessons from Nagapattinam and Global Comparisons
- Community Empowerment in Recovery: Over 400 NGOs were crucial in Nagapattinam’s recovery, involving local communities in medical aid, sanitation, and livelihood restoration, which enhanced the efficiency of disaster response.
- Global Comparisons: Global examples like Chile’s efficient recovery and Haiti’s slow recovery highlight the importance of robust disaster management systems, insurance, and preemptive measures in reducing post-disaster losses.
- Addressing Vulnerabilities: Despite improvements, vulnerable coastal and urban populations remain at risk. Integrating disaster risk reduction into development plans and continuous community education is essential for building resilience.
Practice Question
Q. Analyze the lessons learned from the 2004 Indian Ocean tsunami in shaping India’s disaster management framework. How do India’s strategies compare with global practices in disaster preparedness and recovery?