26th June 2024 (15 Topics)
Mains Issues
Context
Maharashtra, particularly the Marathwada region, is facing a severe water crisis due to deficient monsoons, exacerbated by geographical, agricultural, and policy factors.
Key Highlights
- Location: Marathwada lies in the rain-shadow region of the Western Ghats.
- Rainfall: While the western side of the Ghats receives heavy rainfall (2,000-4,000 mm), Marathwada gets much less (600-800 mm).
- Agricultural Practices: The region’s water crisis is intensified by the cultivation of water-intensive crops like sugarcane.
- Government Policies: Support for sugarcane cultivation has led to water mismanagement.
Reason Behind the Situation
- Rain-shadow Effect: Marathwada receives limited rainfall due to its position in the rain-shadow region of the Western Ghats. Moist winds lose most of their moisture after crossing the Ghats, leaving the area much drier.
- Climate Change: Studies indicate an increasing trend in drought severity and frequency in central Maharashtra, worsening the water crisis.
- Water-intensive Agriculture: Sugarcane cultivation, requiring 1,500-2,500 mm of water, is a major contributor to the water scarcity. Despite recommendations to ban sugarcane in low-rainfall areas, its cultivation has increased due to government support.
- Soil and Topography: The predominantly clayey black soil in Marathwada has a low infiltration rate, leading to poor groundwater recharge and high surface runoff.
Impact of the Water Crisis
- Drinking Water Shortage: Wells have run dry, and officials have had to provide drinking water through tankers.
- Agricultural Losses: Crop failure due to water scarcity affects farmers' livelihoods, leading to economic instability.
- Regional Disparities: Water scarcity is not uniform across Marathwada, with upland areas experiencing acute shortages compared to valleys with perennial groundwater.
Required Measures
- Supply-side Solutions: Implementing watershed management practices like building water-conserving structures (contour trenches, earthen bunds) and desilting water bodies can help manage available resources.
- Demand-side Solutions: Promoting water-efficient irrigation techniques, cultivating drought-resistant crops, and diversifying livelihoods can reduce water demand.
- Policy Shifts: Encouraging the cultivation of high-value, low-water-using crops and relocating sugarcane production to water-rich states can alleviate the water crisis.
- Government Intervention: Strengthening policies and providing targeted support to the most affected regions can enhance water resilience.
Mains Practice Question
Q. Analyze the multifaceted causes of Maharashtra's water crisis, with particular focus on Marathwada region. Suggest sustainable solutions that balance agricultural needs with water conservation.


Mains Issues
Context
The Indian government plans to set up the Mediation Council of India (MCI) by the end of this year to improve out-of-court dispute resolution and enhance ease of doing business.
1: Dimension- Structure and Functions of MCI
- Composition: The council will have three members, including a chairperson, who are experts in mediation.
- Appointments: Council members may be directly appointed by the Centre or on the advice of a special search-cum-selection committee.
- Regulatory role: MCI will lay down standards for the conduct of mediators and oversee their training and certification.
2: Dimension- Impact on Dispute Resolution
- Faster resolution: Mandated 180-day timeline for mediation proceedings to encourage quicker settlements.
- Business-friendly approach: Enhancing ease of doing business by providing an alternative to lengthy court processes.
- Standardization: Issuing guidelines for the mediation process to ensure consistency and quality.
3: Dimension- Potential Benefits and Challenges
- Corporate preference: Mediation may become a preferred method for dispute resolution, especially for businesses.
- Online mediation growth: Formation of MCI expected to boost the momentum of online dispute resolution (ODR) services.
- Implementation challenges: Success will depend on effective execution and acceptance by stakeholders.
Types of alternative dispute resolution in india :
|
PYQ
|
Mains Practice Question
Q. Evaluate the potential impact of the Mediation Council of India on the Indian judicial system and business environment. How can it contribute to improving the ease of doing business in the country?


Mains Issues
After two decades, Nagaland is set to vote in civic polls with 33% reservation for women, marking a significant step towards gender representation in the state's urban local bodies (ULBs).
Key Highlights of the Event
- Reservation for Women: This is the first time Nagaland's civic polls will implement a 33% reservation for women.
- Affected Areas: Elections will be conducted in 10 out of 16 districts. Six eastern districts are not participating due to the influence of the Eastern Nagaland People’s Organisation (ENPO).
- Municipal and Town Councils: Nagaland has three municipal councils—Dimapur, Kohima, and Mokokchung—and 36 town councils. Specific wards in these councils are reserved for women.
Background:
- Legal Battle: Nagaland resisted implementing 33% reservation for women in municipalities and town councils, mandated by Article 243 T (3)of the Constitution.
- Naga Mothers Association and People’s Union for Civil Liberties (PUCL) fought a 15-year legal battle to enforce the constitutional provision.
- Obstacles: Nagaland's government and prominent sections of Naga societyopposed reservation, citing cultural customs and constitutional provisions.
- The tribal bodies argued that women have traditionally not been part of decision-making bodies in Naga customs.
- According to them, allowing reservation for women would violate special provisions granted to the state under Article 371A of the Constitution.
Intervention of Supreme Court:
- In 2016, Supreme Court intervened, stayed the High Court's order, and revived the directive to hold elections within one month.
- State government, along with civil society groups, initiated violent protests against the reservation.
- SC bench, led by Justice Kaul, expedited the case in 2023, finally mandating elections to be held by June 2024.
PYQ
|
Fact Box: Article 371A of the ConstitutionThe provision states that “no Act of Parliament would apply under the Legislative Assembly of Nagaland by a resolution decides in respect of Naga customary laws and procedures, administration of civil and criminal justice, ownership and transfer of land, land and social practices”. |
Mains Practice Question
Q: Discuss the significance of introducing 33% reservation for women in Nagaland's urban local body elections and the challenges faced in its implementation.


Mains Issues
The recent railway accident in Darjeeling, West Bengal, has once again highlighted the absence of 'Kavach', India's Automatic Train Protection (ATP) system. Despite available funds, the implementation of Kavach has been slow, raising concerns about railway safety.
Key Highlights
- Kavach can warn loco pilots of potential signal overshooting and apply brakes automatically
- Cost of installing Kavach: ?50 lakh per kilometre for tracks, ?70 lakh per engine
- Total estimated cost for full implementation: ?45,000 crore
- Current deployment: 1,465 km of tracks (2% of total) and 139 engines (less than 1% of total)
1: Dimension- Financial Aspects of Kavach Deployment
- Budget allocation: The yearly cost of deploying Kavach (?4,500 crore) is less than 2% of the Railways' capital expenditure budget (?2,52,000 crore in FY25).
- Cost breakdown: Equipping 68,000 km of tracks would cost ?34,000 crore, while fitting 15,200 engines would require ?10,640 crore.
- Affordable implementation: Covering the entire Railways network with Kavach would require only a small fraction of the Railways' budget over a 10-year period.
2: Dimension- Current Progress and Challenges
- Slow deployment: Since field trials began in 2016, only 2% of total route length and less than 1% of engines have been equipped with Kavach.
- Time projection: At the current pace, it would take 46 years to deploy Kavach across all route kilometers and over 100 years for all engines.
- Approval delays: Three firms were approved to supply equipment in 2018-19, but Kavach was only adopted as the national ATP system in July 2020.
3: Dimension- Required Measures for Acceleration
- Increased pace: To complete installation in 10 years, the pace needs to increase to 6,800 route km/year for tracks and 1,500 locos/year for engines.
- Mission mode implementation: Railways Minister has directed the installation to be taken up in "mission mode" following recent accidents.
- Focus on critical routes: Prioritizing high-traffic and accident-prone routes for initial deployment could maximize safety impact.
PYQ
|
Mains Practice Question
Q. Despite adequate financial resources, the implementation of the Kavach system in Indian Railways has been slow. Analyze the reasons for this sluggish progress and suggest measures to accelerate its deployment.


Mains Issues
Context
The Defence Ministry has signed its 350th contract under the Innovations for Defence Excellence (iDEX) initiative with SpacePixxel Technologies for developing a miniaturised satellite.
What is a miniaturized satellite?
- A miniaturized satellite, often referred to as a "CubeSat," is a type of small satellite characterized by its compact size and standardized design.
- These satellites are typically built using cubic units known as "U" which measure 10x10x10 centimeters (1U).
- CubeSats can be scaled up to larger sizes such as 2U, 3U, 6U, or even 12U, depending on mission requirements.
- Strategic Advantages
- Faster deployment: Miniaturised satellites allow for quicker and more economical deployment of space assets.
- Scalability and adaptability: The modular design enables easy customization and scaling of capabilities as per mission requirements.
- Reduced environmental impact: Smaller satellites generally have a lower environmental footprint compared to larger counterparts.
iDEX
|
Defence Innovation Organization (DIO)
|
Mains Practice Question
Q. Evaluate the role of initiatives like iDEX in promoting indigenous defence technology development. How can such programs contribute to India's strategic autonomy and defence preparedness?


Mains Issues
Context
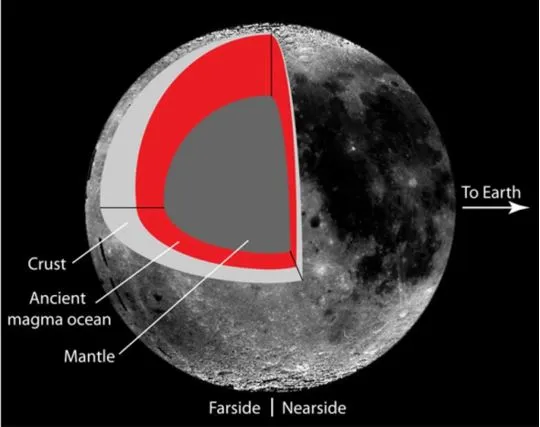
China has become the first country to successfully collect and return samples from the far side of the Moon, marking a significant milestone in lunar exploration and space technology.
Key Highlights
- Chang'e-6 mission landed on the Moon's far side and collected from the South Pole-Aitken Basin.
- The samples include 2.5-million-year-old volcanic rock and other material that scientists hope will answer questions about differences between the moon’s two sides.
- The samples are expected to answer one of the most fundamental scientific questions in lunar science research:
- What geologic activity is responsible for the differences between the two sides?
Why Far Side of the Moon is difficult to catch?
|
PYQ
|
Mains Practice Question
Q. Analyze the scientific and geopolitical implications of China's successful retrieval of lunar samples from the far side of the Moon. How might this achievement influence the future of international space exploration and cooperation?


Mains Issues
Context
The recent Lok Sabha elections in India, held amid record-breaking heatwaves, highlighted the growing impact of climate change on daily life and governance, yet the issue remained largely unaddressed by political parties.
1: Dimension- Electoral Impact of Climate Change
- Voter turnout: Rising temperatures in 43 of 93 constituencies during Phase 3 corresponded with lower voter participation compared to 2019.
- Health hazards: 18 polling staff died in Uttar Pradesh and Bihar on the final voting day due to extreme heat.
- Future implications: Prolonged heatwaves may necessitate rethinking the timing and structure of future elections.
2: Dimension- Global Climate Crisis Acceleration
- Persistent heating: The past 12 months have seen average global temperatures exceed the 1.5°C threshold above pre-industrial levels.
- Marine impacts: Massive marine heatwaves are causing widespread coral bleaching and stronger storms.
- Himalayan changes: Significantly less snowfall in winter, with 2024 labeled an "extraordinary below normal snow year" by ICIMOD.
3: Dimension- Urgent Need for Action
- Emissions reduction: Despite warnings, global CO2 emissions from fossil fuels continue to rise instead of decreasing.
- Critical timeframe: Decisions made in the next 24 months will be crucial to avoid climate breakdown.
- Adaptation strategies: Need for increased focus on heat shelters, green areas, and community-level climate resilience measures.
India’s Measures to combat climate change
India's Role in International Climate Diplomacy:
|
Mains Practice Question
Q. "The recent heatwaves and their impact on the Indian general elections provide a glimpse into the future challenges posed by climate change." Discuss the implications of this statement for governance and policy-making in India.


Prelims Articles
Context
Julian Assange pleaded guilty in a court in Saipan, the capital of the US territory, before flying home to Australia.
About
- Saipan is the largest island and capital of the Northern Mariana Islands, a Territory of the United States in the western Pacific Ocean.
- Like territories such as Guam or Puerto Rico, the Northern Marian Islands are part of the US without the full status of a state.
- The US took control of Saipan during World War II.
- It is only part of the US that Chinese citizens can enter without a visa.


Prelims Articles
Context
The International Criminal Court issued arrest warrants for Sergei Shoigu, the former Russian defence minister, and leading Russian general Valery Gerasimov on Tuesday for alleged crimes committed during Russia's invasion of Ukraine.
About:
- ICC is the world’s first permanent international criminal court.
- It is governed by an international treaty called 'The Rome Statute'.
- ICC is not a UN organization but is has a cooperation agreement with the United Nations.
- Headquarters:The Hague, the Netherlands.
- Jurisdiction:The Rome Statute, grants the ICC jurisdiction over four main crimes:
- The crime of Genocide
- Crimes against Humanity
- War crimes
- Crime of Aggression
- Membership:Most countries on Earth – 123 of them – are parties to the treaty, but there are very large and notable exceptions, including Russia, India and the US. And, for that matter, Ukraine.
- Ukraine also is not a member of the international court, but it has granted it jurisdiction over its territory
Rome Statute
|


Prelims Articles
Context
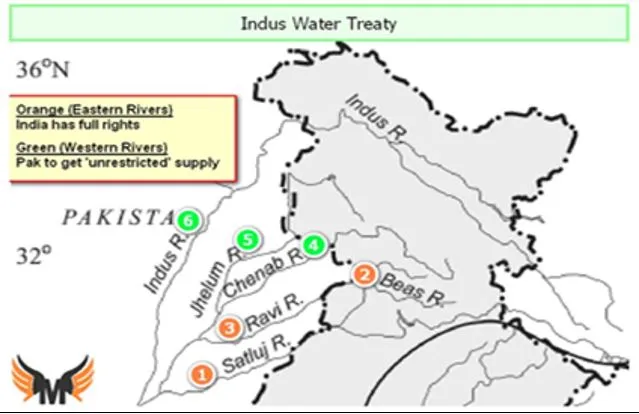
A large delegation of Indo-Pakistan teams on Monday flew to Jammu and Kashmir's Kishtwar district with neutral experts and started inspection of two power projects under the Indus Water Treaty (IWT).
About
- The six-decade-old treaty governs the sharing of waters of six rivers in the Indus system between the two countries.
- Main Rivers:Indus River, Jhelum, Chenab, Ravi, Beas, and Sutlej.
- The basin is mainly shared by India and Pakistanwith a small share of China and Afghanistan.
- Under the treaty signed between India and Pakistan in 1960, all the waters of
- Eastern rivers, namely Ravi, Sutlej, and Beas (Eastern Rivers) were allocated to India for exclusive use
- Western rivers- Indus, Jhelum, and Chenabwere allocated to Pakistan except for specified domestic, non-consumptive, and agricultural use permitted to India as provided in the Treaty.
- India has also been given the right to generate hydroelectricitythrough run-of-the-river (RoR)projects on the Western Rivers which, subject to specific criteria for design and operation is unrestricted.
River Indus: Geographic Location
Significance:
|


Prelims Articles
Context
Centre has notified the rates and guidelines for Remission of Duties and Taxes on Exported Products (RoDTEP) export incentive scheme.
About
- RoDTEP stands for Remission of Duties and Taxes on Export Products.
- It is formed to replace the existing MEIS (Merchandise Exports from India Scheme).
- The scheme will ensure that the exporters receive the refundson the embedded taxes and duties previously non-recoverable.
- The scheme was brought about with the intention to boost exportswhich were relatively poor in volume previously.
Key Features of the Scheme
- Refund of the previously non-refundable duties and taxes:Mandi tax, VAT, Coal cess, Central Excise duty on fuel etc. will now be refunded under this particular scheme. All the items under the MEIS and the RoSTCL (Rebate of State and Central Taxes and Levies) are now under the purview of the RoDTEP Scheme.
- Automated system of credit:The refund will be issued in the form of transferable electronic scrips. These duty credits will be maintained and tracked through an electronic ledger.
- Quick verification through digitisation:Through the introduction of the digital platform, the clearance happens at a much faster rate. Verification of the records of the exporters will be done with the help of an IT-based risk management system to ensure speed and accuracy of transaction processing.
- Multi-sector scheme:Under RoDTEP, all sectors, including the textiles sector, are covered, so as to ensure uniformity across all areas.


Prelims Articles
|
S.No. |
Term |
About |
|
1. |
K-shaped Recovery |
A K-shaped recovery is an economic trend where, following a recession, different parts of the economy recover at different rates. Some sectors experience strong growth while others continue to struggle, creating a diverging path resembling the arms of the letter "K." |
|
2. |
Valuation Effect |
Valuation effect refers to the change in a country's net foreign assets due to fluctuations in exchange rates or asset prices, rather than through traditional trade or financial flows. It can either increase or decrease a nation's external wealth depending on how its holdings are affected by market movements. |
|
3. |
User Development Fee |
User Development Fee (UDF) is a charge levied on passengers at airports to fund infrastructure development, maintenance, and expansion. The fee varies across airports and is collected by the airport operator. |
|
4. |
Extradition |
Extradition is the formal process by which one country surrenders an individual accused or convicted of a crime to another country seeking to prosecute or sentence them. It is based on a bilateral or multilateral treaty and aims to ensure justice is served regardless of borders. |
|
5. |
Butterfly effect |
The butterfly effect is the concept that a small change in one part of a complex system can have large and unpredictable effects elsewhere. It highlights the interconnectedness and sensitivity of systems to initial conditions, often used metaphorically to describe chain reactions and unintended consequences. |


Editorials
Context
India needs to adopt a comprehensive National Security Strategy (NSS) to effectively address its diverse security challenges. Without such a strategy, India's national security decisions remain fragmented and reactive.
Issues Surrounding the Lack of an NSS:
- Strategic Disarray: India's national security decisions are often made in a fragmented manner, with various military services competing for resources without a unified strategic vision.
- Reactive Policy Making: India’s current approach to national security is largely reactive, which is insufficient to address long-term strategic risks such as climate change, pandemics, and geopolitical tensions.
- Opaque Decision-Making: Strategic decisions are often concentrated among a few individuals at the highest levels of government, lacking transparency and broader input.
Benefits of a Comprehensive NSS:
- Holistic Threat Assessment: An NSS would require the government to conduct a thorough assessment of threats and opportunities, ensuring that long-term risks like China's naval expansion are systematically addressed.
- Strategic Planning and Resource Allocation: It would provide a framework for long-term strategic planning, helping to prioritize military and economic investments, and avoid wasteful expenditures on projects with limited strategic value.
- Enhanced Signaling and Diplomacy: An NSS would clarify India’s strategic intentions to both allies and adversaries, strengthening its position as a security provider in the Indian Ocean and improving diplomatic relations.
Implementation Challenges and Strategic Coordination:
- Inter-Governmental Synchronization: An NSS would necessitate better coordination among various arms of the government, including defense, foreign affairs, and intelligence agencies, to ensure unified efforts towards national security goals.
- Accountability and Transparency: Publishing an NSS would introduce accountability mechanisms, making the government’s strategic plans transparent to the public and ensuring bureaucratic adherence to political directives.
- Strategic Blueprint: An NSS would provide a coherent strategic blueprint, guiding decisions on critical issues like the development of military capabilities and international partnerships, ensuring rational long-term growth.
UPSC Mains Question
Q. Discuss the importance of a National Security Strategy (NSS) for India in the context of contemporary global and regional security challenges. How can an NSS improve India’s strategic decision-making process?


Editorials
Context
The issues faced during the National Eligibility cum Entrance Test (NEET) this year have highlighted significant problems such as the inflation of scores and ranks, and the subsequent difficulties this caused for candidates. There is a pressing need for comprehensive Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) to ensure the integrity and fairness of the examination process.
Issues with NEET:
- Score Inflation and Rank Discrepancies: The inflation of scores and ranks led to many candidates not securing admission to their desired colleges despite expectations based on previous years’ scores.
- Irregularities and Allegations: Allegations of cheating, paper leakage, and other irregularities have persisted, undermining the credibility of the NEET exam.
- Impact on Aspirants: The discrepancies have significantly affected the 23 lakh NEET aspirants, causing distress and confusion among candidates and their families.
Need for Robust Governance and SOPs:
- High Stakes and Vulnerability: NEET’s high stakes make it vulnerable to both accidental and intentional irregularities. Strong governance is essential to maintain the integrity of the examination process.
- Distribution Errors: Incidents like the distribution of incorrect question papers highlight critical weaknesses in the current SOPs. Such errors lead to panic among candidates and require substantial corrective measures.
- Comprehensive SOPs: A thorough and foolproof set of SOPs covering all aspects of the exam process—from question paper setting to admissions—is necessary to prevent malpractices and ensure smooth operations.
Steps Towards Transparency and Improvement:
- NTA’s Voluntary Disclosures: Despite the issues, the National Testing Agency (NTA) has made commendable efforts in voluntarily disclosing information related to the examination process under the Right to Information (RTI) Act, 2005.
- Legal Precedents for SOP Development: The need for well-defined SOPs has been established through legal battles and judgments, particularly concerning the admission processes for the Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs).
- Continuous Upgradation: The importance of continuously upgrading and fine-tuning the selection process to maintain its relevance and integrity is essential, as highlighted by the Supreme Court’s observations.
UPSC Mains Questions
Q. Evaluate the role of transparency and voluntary disclosures by examination authorities like the NTA in maintaining the integrity of entrance exams. How does the Right to Information (RTI) Act contribute to this process?


Editorials
Context
The future of developing countries lies in the services sector, as traditional industrialization faces challenges due to the increasing skill and capital intensity of manufacturing. Enhancing productivity in labour-absorbing services has become crucial for sustainable growth and equity.
Challenges in Manufacturing:
- Skill-Biased Innovation: New technologies like automation and 3D printing reduce demand for low-skilled labor, making it difficult for developing countries to compete globally using labor-intensive techniques.
- Limited Labour Absorption: Competitive manufacturing sectors in developing countries have become like 'enclave sectors', unable to absorb significant amounts of labor, similar to the mining industry.
- Global Standards and Competition: High-quality standards in global value chains limit the extent to which unskilled labor can substitute for physical capital and skilled labor.
Importance of Labour-Absorbing Services:
- Productivity and Growth: With the majority of jobs in services, productivity in these sectors is essential to support income growth and overall economic development.
- Skill-Intensive Services: Sectors like banking, infotech, and BPOs are productive and tradable but do not absorb much labor due to their skill-intensive nature.
- Focus on Service Sector: Increasing productivity in labor-absorbing services such as retail, care, and personal and public services is crucial for job creation and economic equity.
Strategies for Expanding Productive Employment:
- Incentivizing Large Firms: Encourage established large firms, including retailers and ride-sharing platforms, to expand employment either directly or through local supply chains.
- Supporting Small Enterprises: Enhance the productive capabilities of small enterprises through public inputs like management training, loans, customized worker skills, and specific infrastructure or technology assistance.
- Leveraging Digital Tools: Provide digital tools or new technologies that complement low-skill labor, enabling less educated workers to perform tasks traditionally reserved for more skilled professionals.
- Vocational Training and Wrap-Around Services: Combine vocational training with additional support programs to enhance employability, retention, and promotion of less-educated workers, modeled after successful initiatives like Project Quest.
UPSC Mains Questions
Q. Analyze the role of vocational training and digital tools in improving the employability and productivity of low-skilled workers in the services sector. Provide examples of successful initiatives in this context.