5th July 2024 (9 Topics)
Mains Issues
In a significant development, a woman who formerly worked at the Raj Bhawan has moved the Supreme Court challenging the immunity granted to West Bengal Governor CV Ananda Bose under Article 361 of the Indian Constitution. She has accused the Governor of sexually assaulting her and argues that Article 361 should not prevent police investigation and criminal proceedings in such cases.
What is Article 361?
- Article 361 of the Constitution of India provides immunity to the President of India and Governors of states from certain legal actions during their term in office.
- This constitutional provision aims to safeguard the independence and functioning of these high offices without undue interference from legal proceedings.
- Key Provisions of Article 361
- According to Article 361(2), no criminal proceedings can be initiated or continued against the President or Governor of a State in any court during their term of office. This immunity extends to actions taken in the course of their official duties.
- The intent is to shield these officials from potential harassment or disruption caused by legal challenges during their tenure.
- Limitations of Immunity: While immunity prevents criminal proceedings and arrest warrants during their term, it does not provide absolute impunity for all actions.
- The immunity clause primarily covers acts done in the exercise of their official powers and duties. It does not shield them from prosecution once they leave office, nor does it extend to actions clearly outside the scope of their constitutional responsibilities.
Supreme Court’s Stance
|
Subject of legal scrutiny
- Article 361 of the Indian Constitution serves as a crucial safeguard for the President and Governors, shielding them from certain legal actions during their term in office.
- However, the extent of this immunity remains a subject of legal scrutiny and interpretation, especially in cases where allegations of serious wrongdoing arise
Role of the Governor
|


Mains Issues
Context
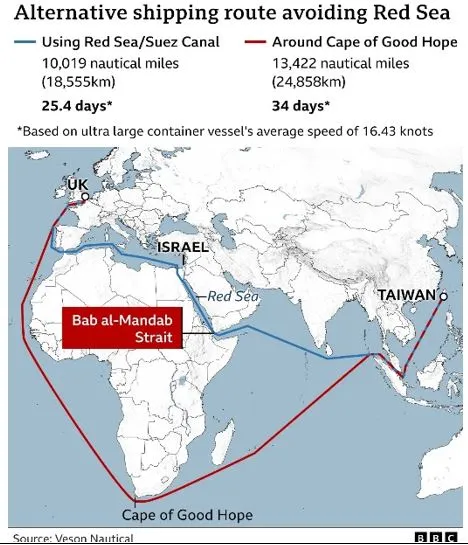
Recent months have brought significant challenges to the global shipping industry. While there is no respite in the Middle East for the shipping industry that continues to face hardship due to the Red Sea route suspension, there is now tension in the South East due to severe congestion at Singapore port and China’s Shanghai/Ningbo ports has only aggravated the disruptions.
What is Red Sea crisis?
- The Red Sea crisis involves increased attacks by Iran-backed Houthi rebels in Yemen on commercial ships in the Bab-el-Mandeb strait, a narrow passage connecting the Arabian Peninsula and the Horn of Africa.
- These attacks have intensified since late November and are seen as a response to Israel's actions in Gaza.
- The Bab-el-Mandeb strait is crucial because it serves as a gateway for ships traveling from Asia to the Suez Canal, which handles about 12% of global trade. This route is vital for transporting goods like oil from the Persian Gulf to Europe and North America.
- Due to the attacks, ships may need to take a longer route around the Cape of Good Hope in southern Africa, adding about 10 days and 6,000 kilometers to their journey between Europe and Asia.
Impact of Red Sea Attacks on Shipping
- The shipping industry, responsible for approximately 80% of global trade, continues to grapple with the repercussions of frequent attacks on vessels navigating the Red Sea.
- This sustained threat has forced the suspension of routes critical for maritime trade, exacerbating logistical bottlenecks and delays.
- Congestion Crisis in Southeast Asia: The ports of Singapore, Shanghai, and Ningbo—key hubs connecting Asia to Europe and beyond—are experiencing unprecedented congestion.
- Delay: The bunching of vessels outside these ports has disrupted ship rotations and significantly delayed cargo handling processes. Indian exporters, reliant on Singapore and Port Klang for transshipment, are particularly affected.
- Increasing cost: This delay has compelled many vessels to bypass Singapore altogether, complicating logistics planning and increasing costs for exporters, as evidenced by rising container prices from $950 to over $1,200 since September 2023.
- Affected movements: The congestion crisis in Singapore and neighboring ports like Port Klang is disrupting global trade flows, affecting the movement of goods between Asia, Europe, and the Americas.
How a new route can change things for India?
- A multimodal route that includes a railway, roadway network and seaports, the INSTC spans 7,200km (4,500 miles) from St. Petersburg to the port of Mumbai in India.
- INSTC connects Russia to India through Iran's Chabahar port.
- INSTC is being seen as an alternative to the Suez Canal trade route.
The INSTC corridor can be a critical geostrategic tool India needs to enhance its trade footprints in Central Asia.
Maritime Routes:
|


Prelims Articles
Context
The Army is set to initiate the trials of the US-made Stryker armoured infantry combat vehicles here in both deserts and high-altitude Ladakh soon. India and the US selected the Stryker under the US-India Initiative on Critical and Emerging Technologies (iCET) for joint production trials.
What is Stryker armoured infantry combat vehicles?
- The Stryker armored infantry combat vehicle is a family of eight-wheel-drive vehicles developed jointly by General Dynamics Land Systems Canada and the United States.
- It originated from the GDLS Canada LAV III 8×8 vehicle, which itself evolved from Switzerland's Mowag Piranha III.
- Named after American soldiers Stuart S. Stryker and Robert F. Stryker, the vehicle entered US Army service as the first new military vehicle since the 1980s Abrams tank.
- Features of the Stryker:
- Design: V-hull armored infantry vehicle.
- Armament: Equipped with a 30 mm cannon and a 105 mm mobile gun.
- Protection: Made from high-hardness steel with basic protection against 14.5mm rounds on the front and 7.62mm ball ammunition from all directions. Features bolt-on ceramic armor for added protection.
- Mobility: Can be transported by Chinook helicopters, which are used by the Indian Air Force.
- Variants:
- Infantry Carrier Vehicle (ICV): Main variant for transporting infantry.
- Mobile Gun System (MGS): Variant equipped with a 105 mm gun for direct fire support.
- Purpose in India:
- India and the US selected the Stryker under the US-India Initiative on Critical and Emerging Technologies (iCET) for joint production trials.
- The Indian Army aims to replace its fleet of over 2,000 BMP-II vehicles with modern wheeled and tracked infantry combat vehicles.
Fact Box:
What are Infantry Combat Vehicles (ICVs)
|


Prelims Articles
Context
>In a concerted effort to achieve comprehensive development across India's aspirational districts, NITI Aayog has launched the ambitious Sampoornata Abhiyan. This nationwide campaign aims to address key social sector indicators through targeted interventions in 500 aspirational blocks and 112 aspirational districts.
About Sampoornata Abhiyan
- Sampoornata Abhiyan is a focused initiative aimed at achieving saturation in 12 critical social sector indicators.
- These indicators encompass areas crucial for holistic development, including health, nutrition, agriculture, social development, and education.
- The campaign is designed to run for three months, from June to September, engaging district and block officials alongside elected representatives to organize a series of awareness and developmental activities.
- It targets 12 key social sector indicators:
- Health and Nutrition: Health camps and Paushtik Aahar Melas for better healthcare and nutrition outcomes.
- Agriculture and Rural Development: Agricultural exhibitions and sustainable farming practices promotion.
- Social Development: Gram Sabhas, Nukkad Nataks, and cultural events to foster community engagement.
- Education and Skill Development: Workshops and competitions to enhance educational and vocational skills.
Fact Box: About Aspirational Districts Programme
|


Prelims Articles
Context
A lone female has been spotted for more than three years in a stretch of the river within the Kaziranga National Park and Tiger Reserve.
About the Reptile Species
- Indian Gharial (Gavialis gangeticus) is the only surviving member of an ancient family of crocodiles
- Indian gharial is one of the largest river-dwelling crocodile species of the world.
- Adult gharials exhibit a strong association with river systems, often displaying seasonal migratory patterns.
- India’s largest gharial population resides in the National Chambal Sanctuary (77% of the global adult population). The remaining gharial populations in India are found in Katarniaghat Wildlife Sanctuary, the Gandak River (Indo-Nepal border), Corbett National Park, the Son River, Mahanadi River, and Hastinapur Sanctuary.
- Conservation Status:
- International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List: Critically endangered
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: Schedule 1
- In 2009, a gharial reintroduction programme has been launched for saving the gharials in India.


Prelims Articles
Context
In a recent development, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) has unveiled its Artificial Intelligence Preparedness Index (AIPI) Dashboard, ranking 174 economies worldwide based on their readiness to adopt and integrate artificial intelligence (AI) technologies.
Key Highlights of the AIPI
- Global Rankings and Categories: The index categorizes countries into Advanced Economies (AE), Emerging Market Economies (EM), and Low-Income Countries (LIC).
- Singapore, Denmark, and the United States lead as top-ranked Advanced Economies with scores of 0.80, 0.78, and 0.77 respectively.
- India is classified as an Emerging Market with a score of 0.49, positioned at the 72nd rank globally.
- Factors Influencing Rankings
- Digital Infrastructure: India scored 0.11, lagging behind China (0.19), the US (0.18), and Singapore (0.21).
- Human Capital and Labor Market Policies: India scored 0.12, slightly lower than China (0.15) and Singapore (0.20).
- Innovation: India's score was 0.11, similar to Indonesia, but less than China, Singapore, the UK, and the US.
- Regulation and Ethics: India and China both scored 0.15, with Singapore leading at 0.22, followed closely by the US and the UK.
About the AIPI Index
|


Editorials
Context
The article challenges the notion of irreconcilable differences between 'Hinduism' and 'Islam' in medieval India, highlighting the complex interplay and synthesis of religious and cultural traditions, particularly in the Hindi heartland.
Sufi Epics and Hindu Influences:
- Chandayan's Synthesis: The 14th-century Sufi epic 'Chandayan' by Maulana Daud exemplifies the blending of Hindu mythology with Sufi philosophy.
- Popular Narrative Adoption: Sufis incorporated local legends and popular ballads into their works, following a tradition similar to Hindu, Buddhist, and Jain epics.
- Multilayered Meanings: Texts like the Chandayan contained both popular narratives and esoteric Sufi teachings, appealing to a wide audience.
Interactions Between Sufism and Yoga:
- Shared Practices: Both Sufis and Yogis employed breathing exercises and chanting for spiritual experiences, and rejected caste distinctions.
- Tantric Influences: Bengali Sufi literature adapted tantric yogic concepts, equating chakras with mystical stations and replacing gods with angels.
- Cross-Cultural Claims: Some yogis claimed Prophet Muhammad as a Nath Yogi, while Sufi master Muhammad Ghawth Gwaliyari identified Gorakhnath with the Islamic prophet Khizr.
Regional Variations in Indian Islam:
- Diverse Approaches: Different Sufi orders had varying attitudes towards local traditions, from peaceful integration to occasional violent conversions.
- Literary Adaptations: Works like the 16th-century 'Padmavat' used local legends to convey Sufi metaphysical concepts.
- Cultural Rootedness: Regional language traditions reveal an Indian Muslim world deeply rooted in local myths and traditions.
Challenges to Historical Narratives:
- Courtly vs. Popular Perspectives: The article contrasts the hostile rhetoric of Persian court chroniclers with the more syncretic practices of the general population.
- Misrepresentation in Modern Times: It criticizes both the romanticization of Mughal kings by liberals and the far-Right portrayal of all Indian Muslims as invaders.
- Nuanced Understanding: The author advocates for recognizing the complex, multifaceted nature of Indian Muslim history, rooted in Indian traditions.
Impact on Indian Cultural Landscape:
- Religious Fluidity: The intermingling of Sufi and Hindu traditions demonstrates the fluid nature of religious boundaries in medieval India.
- Linguistic Contributions: Sufi works in regional languages enriched Indian literature and fostered cultural exchange.
- Shared Spiritual Heritage: The synthesis of yogic and Sufi practices created a unique spiritual landscape in regions like Bengal and Punjab.
UPSC Mains Questions:
Q. "Medieval Indian Sufi literature reflects a complex synthesis of Islamic and indigenous traditions." Discuss this statement with reference to specific texts and their cultural significance.


Editorials
Context
The 2024 Indian Lok Sabha elections raised concerns about the potential impact of AI-generated deepfakes on voter behavior and democratic processes. However, post-election analysis suggests that these fears may have been overstated.
AI's Constructive Use in Elections:
- Authorized Content: Political parties spent an estimated $50 million on authorized AI-generated content for targeted communication.
- Personalized Videos: AI was used to create personalized videos of party workers, allowing for scalable distribution.
- Language Accessibility: The Bhashini AI platform enabled politicians to dub speeches in multiple languages, addressing India's linguistic diversity.
Positive Applications of AI in Electoral Process:
- Fraud Detection: AI helped detect fraud, optimize booth and voter management logistics, and improve resource efficiency.
- Voter Outreach: Generative AI allowed politicians to reach voters in a more personalized and scalable manner.
- Inclusive Voting: AI technologies made voting access easier for differently-abled voters.
Challenges and Concerns:
- Misinformation: Some instances of deepfakes impersonating candidates and spreading misinformation were reported.
- Information Overload: The widespread use of AI-generated content made it difficult for voters to distinguish between real and fake information.
- Democracy at Risk: There were initial fears about AI subverting democracy and influencing election outcomes.
Outcome and Lessons Learned:
- Technology vs. Tradition: The election results showed that less IT-savvy parties won in many places, indicating that technology alone doesn't determine outcomes.
- Voter Discernment: Indian voters demonstrated the ability to see through both political rhetoric and fake news.
- Public Awareness: The widespread use of AI tools may have increased public understanding of the technology, potentially inoculating people against deepfakes.
UPSC Mains Questions
Q. Examine the role of AI in enhancing voter engagement and participation in Indian elections. What are the challenges and opportunities presented by AI technologies in the electoral context?


Editorials
Context
Recent intense heatwaves in north India have highlighted the growing impact of climate change on public health. This situation calls for urgent action to address the emerging climate-induced health crisis through multi-stakeholder collaboration and technological innovation.
Climate Change and Health Impacts:
- Heat-Related Illnesses: Environmental epidemiologists have linked heat to heatstroke, kidney injury, malnutrition, and anaemia.
- Air Pollution Effects: Poor air quality is associated with lung disease, cardiovascular disease, and neonatal mortality.
- Extreme Weather Consequences: Over 80% of Indians are exposed to extreme weather events, with heavy rainfall linked to mosquito-borne and diarrhoeal illnesses.
Assessing Vulnerability and Needs:
- Real-Time Monitoring: Decision-makers need a real-time weather map for climate-related health vulnerability at a granular level.
- Comprehensive Index: A vulnerability index should consider exposure levels, population sensitivity, and adaptive capacity.
- Rural Focus: Particular attention is needed on data related to the health of India's rural residents.
Leveraging Technology for Health Surveillance:
- CHIP Platform: Rajasthan's Community Health Integrated Platform (CHIP) expanded from COVID-19 surveillance to tracking comprehensive primary care for 45 million people.
- CoWin Success: The central government's CoWin platform facilitated the world's largest vaccination drive, demonstrating India's capacity to manage complex health challenges through technology.
- Climate-related Health Vulnerability Index (CHVI): Rajasthan developed a CHVI incorporating multiple datasets, with ASHA workers acting as public health researchers using digital tools.
Building Resilient Healthcare Infrastructure:
- Upgrading Facilities: Invest in climate-resilient healthcare infrastructure to withstand climate shocks.
- Training Healthcare Workers: Equip healthcare professionals with skills to manage climate-related health issues.
- Ensuring Supplies: Maintain adequate supplies of essential medicines and equipment to respond to climate-induced health crises.
Public Awareness and Education:
- Empowering Individuals: Provide knowledge about climate-related health risks and preventive measures.
- Community-Driven Action: Support grassroots movements with resources and accurate information to drive behavioral changes.
- Reducing Vulnerability: Educate communities on adapting to and mitigating climate-related health risks.
UPSC Mains Questions:
Q. Examine the role of technology in managing climate-induced health crises. What are the challenges and opportunities in using technological solutions to enhance public health resilience in India?