7th February 2025 (13 Topics)
Mains Issues
Context
The private diagnostics sector in India is facing significant scrutiny after a series of cases highlighted concerns over the accuracy and reliability of medical tests. Reports of incorrect test results leading to improper treatments have raised alarms about the lack of qualified professionals in diagnostic labs, pointing to systemic issues in the sector.
Current Status of the Sector
- The diagnostics industry in India consists of around 300,000 labs, with the sector contributing 9% to India’s healthcare industry, valued at Rs 860 billion in 2024 and expected to grow to Rs 1,275 billion by 2028.
- Main segments of the sector:
- Pathology involves diagnosis of diseases through the examination of tissues, cells, and body fluids
- Radiology involves use of medical imaging techniques to diagnose and treat diseases and injuries. Radiology is split into
- Soft (x-ray and ultrasound)
- Advanced radiology (CT-scan, MRI, nuclear imaging, and interventional radiology)
- Reason behind growth: Rising prevalence of chronic diseases, growth in geriatric population, demand for preventive tests, and higher penetration of government insurance schemes.
- Despite rapid growth, the sector remains under-regulated and fragmented, with many small, unorganised labs operating with varying standards.
- Regulations:
- The Clinical Establishments (Registration and Regulation) Act 2010 aims to bring all diagnostic centres and labs under its ambit, with their registration with respective State councils as clinical establishments.
- The National Commission for Allied and Healthcare Professions (NCAHP) Act 2021 do not permit laboratory technicians to practice independently and issue reports without certification by a pathologist.
- Diagnostic centres in India can obtain accreditation voluntarily from organisations such as the National Accreditation Board for Testing and Calibration Laboratories (NABL).
Issues Faced by the Sector
- Lack of Skilled Personnel: There is a significant shortage of qualified lab technicians, pathologists, and microbiologists. This leads to many diagnostic centers operating with untrained staff, which affects the quality and reliability of test results.
- Fragmentation and Under-Regulation: The sector is highly fragmented due to low entry barriers and the absence of stringent regulations. While some states have adopted regulations like the Clinical Establishments Act, implementation is inconsistent, and many labs remain unaccredited.
- Regulatory Gaps: There are gaps in the enforcement of laws in several states. For instance, states like Karnataka and Tamil Nadu struggle with inadequate regulation of the diagnostics sector, particularly regarding lab quality assurance, staff qualifications, and transparency.
- Urban-Rural Divide: There is a significant disparity in diagnostic services between urban and rural areas. While most diagnostic labs are concentrated in urban areas, rural regions, home to 70% of India’s population, account for only 24% of diagnostics revenue.
- Pricing and Affordability: Pricing in the diagnostics sector varies widely, with some patients being charged exorbitant fees for routine tests. Government initiatives like T-Diagnostics in Telangana aim to provide affordable diagnostic services, but issues with supply and resource allocation have hindered their effectiveness.
- Quality Assurance Issues: Many diagnostic centers lack standard operating procedures (SOPs) for sample collection, testing, and reporting. Inadequate attention to quality control, including proper biomedical waste management, has led to concerns about the reliability of lab results.
Space and Infrastructure Constraints: Several states have stringent space requirements for labs, which are often unfeasible for small-scale diagnostics providers. In Kerala, for example, only a fraction of the 6,500 small labs would be able to comply with existing space standards under the State Clinical Establishments Act.


Mains Issues
Context
India’s electric vehicle (EV) market is at a pivotal point, with significant investments already made in the sector, yet substantial growth in charging infrastructure is still required. Despite over USD 450 million (Rs 30,000 crores) having been invested in startups focused on charging networks and battery-swapping models, the country still faces a major gap in its public charging infrastructure.
What is the state of EV’s charging market?
- There is currently only one public charging station for every 135 EVs in India.
- This ratio is drastically lower than the global average of one station per 6 to 20 EVs.
- Government Targets and Infrastructure Requirements: The Indian government has set an ambitious target for EV adoption, with the goal for EVs to account for 30% of all new private vehicle registrations by 2030.
- This would result in approximately 80 million EVs on Indian roads by that year.
- In order to accommodate this massive increase, India will require a total of 9 million charging stations by 2030, according to the report titled Charging Ahead II.
- This would ensure that there is one charging station for every 20 vehicles, a crucial metric for facilitating widespread EV adoption.
Challenges and Roadblocks
- Capital-intensive nature: Building charging stations requires considerable investment, and securing funding remains a challenge.
- Land acquisition hurdles: Securing land for charging stations, especially in urban areas, continues to be a major bottleneck.
- Grid reliability: Ensuring the stability and reliability of the power grid to support large-scale EV charging infrastructure is another pressing concern.
- Low EV penetration in rural areas: While urban areas are seeing significant growth, rural areas still face challenges in terms of EV adoption, limiting the overall demand for charging stations.
Fact Box:Government Interventions:
Electric Vehicle (EV)
|


Prelims Articles
Context
In the latest step toward eliminating colonial practices and mindsets within the armed forces, Fort William in Kolkata, the headquarters of the Eastern Army Command, has been renamed Vijay Durg.
About Fort William
- Fort William was built in 1696 by the British East India Company in Kolkata.
- It is located on the eastern banks of the River Hooghly.
- It was named after King William III of England and served as a stronghold for the British in India.
- The fort was used to control Bengal and served as a base for British military operations, including the Battle of Plassey (1757), which allowed the British to dominate India.
- It was also central to British activities during the Revolt of 1857 (First War of Independence).
- The fort has six gates - Chowringhee, Plassey, Calcutta, Water Gate, St George's and Treasury.
- Post-Independence Role: After independence, Fort William became the Eastern Army Command's headquarters in 1963 following the Sino-India war of 1962.
- New Name – Vijay Durg: The proposed new name, Vijay Durg, translates to "Fort of Victory."
- The name is inspired by Vijaydurg Fort in Maharashtra, which is linked to Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj, a key figure in India's resistance to colonial powers. The name symbolizes India's victory over foreign rule and celebrates its own military history.
India’s Eastern Command
|


Prelims Articles
Context
The Trump administration has issued a directive that may potentially remove the sanctions waiver granted to India, which allowed the country to continue its work on Iran’s Chabahar port. This move is part of the U.S.'s broader "maximum pressure" campaign against Iran.
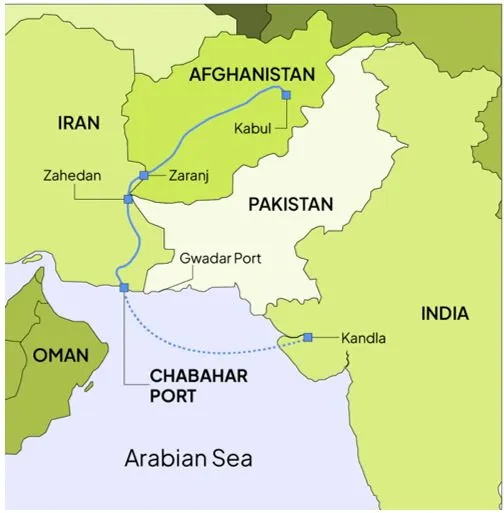
About Chabahar Port
- Located in Iran, Chabahar port provides India access to Afghanistan and Central Asia, bypassing Pakistan.
- India signed a 10-year deal in 2024, investing USD 120 million in port development and a USD 250 million credit facility for related projects.
- India Ports Global Limited (IPGL) has managed the port since 2018.
- The deep water port is located on the Makran Coast of Iran's Sistan-Baluchistan province.
- Moreover, Chabahar is the only Iranian portwith direct access to the Indian Ocean.
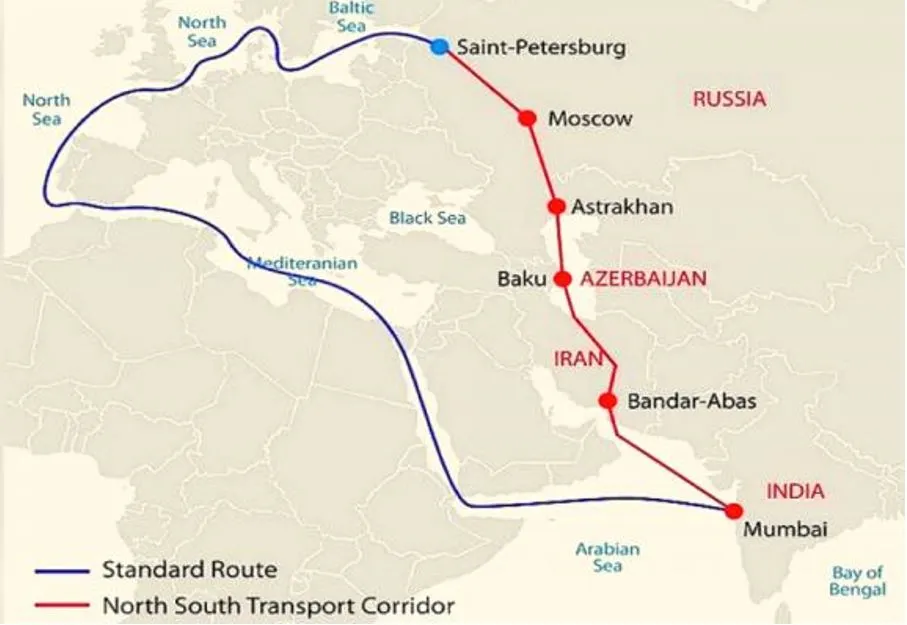
- Chabahar connects Mumbai to the International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC), reducing transport costs and improving trade.
- The port has handled over 90,000 TEUs of container traffic and 8.4 million metric tons of cargo since 2018.
- Impact of removal on waiver on India
- Development Work at Risk: Revocation of the sanctions waiver could hinder India’s development efforts at Chabahar.
- Trade Growth: Chabahar saw a 43% increase in vessel traffic and 34% rise in container traffic in FY 2024, proving its growing significance for India’s trade.
- Geopolitical Impact: India’s ties with Iran are key to its presence in Central Asia and Afghanistan. The sanctions could disrupt these strategic interests.
International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC)
|


Prelims Articles
Context
The Supreme Court of India addressed the delay by Tamil Nadu Governor R.N. Ravi in assenting to 12 Bills sent by the State government. These Bills, primarily related to higher education and the appointment process of Vice-Chancellors in State Universities, had been pending for over three years.
What is the process of granting assent?
- Assent of the Governor or the President is necessary for a Bill passed by the legislature to become law. After a Bill is passed by both Houses of the State Legislature, it is presented to the Governor for assent.
- Governor’s Options (Article 200): The Governor has the power to:
- Grant Assent: The Bill becomes law.
- Withhold Assent: The Governor can withhold assent, but it must be returned to the Legislative Assembly for reconsideration.
- Return for Reconsideration (except Money Bills): If the Governor returns the Bill, the Legislature can amend it. If re-passed, the Governor must assent.
- Money Bills are automatically deemed assented to by the Governor.
Key Constitutional Provisions
|
- Reserve for President’s Consideration (Article 201): If the Governor believes the Bill affects the Constitution or has national importance, it can be reserved for the President’s consideration.
- Discretionary Powers: The Governor can withhold assent if the Bill is against national interests, violates the Constitution, or conflicts with Union laws, though this power is not absolute.
- Article 167: The Governor may require the Chief Minister to communicate decisions of the Council of Ministers, including Bills pending for assent.
- No Timeline for Decision: There is no specified timeline within which the Governor must act, often leading to delays or a "pocket veto."
- The Sarkaria Commission (1988) and the National Commission to Review the Working of the Constitution (2000) recommended time limits for granting assent (e.g., 6 months for assent, 3 months for President’s decision). There are ongoing debates on enforcing such timelines.
- Judicial Review: The Supreme Court has held that if the Governor’s decision to withhold assent is found to be mala fide (in bad faith), it can be subject to judicial scrutiny and struck down. Courts can review such actions for constitutionality (Rameshwar Prasad, 2006).
Fact Box:About Governor
|
PYQQ. Which of the following are the discretionary powers given to the Governor of a State? (2014)
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Solution: (b) |


Prelims Articles
Context
The Supreme Court of India made a landmark decision allowing High Courts to appoint retired judges on an ad-hoc basis to address the mounting backlog of criminal cases. The decision came in the wake of a growing pendency of cases, particularly in criminal appeals, across the country’s High Courts.
About Ad-hoc Judges Appointment
- Article 224-A allows the appointment of retired judges to High Courts on an ad-hoc basis. This provision was introduced by the Constitution (Fifteenth Amendment) Act, 1963.
- The appointment requires the consent of the retired judge and the President of India. Such judges enjoy the same jurisdiction, powers, and privileges as sitting judges.
- Appointment Procedure:
- Once a retired judge consents to the appointment, the Chief Justice of the High Court submits the name and proposed tenure to the Chief Minister.
- The Chief Minister forwards the recommendation to the Governor, who then sends it to the Union Minister of Law and Justice.
- The Union Law Minister consults the Chief Justice of India (CJI), after which the recommendation is sent to the Prime Minister.
- Finally, the President of India approves the appointment, and the Chief Minister issues the formal notification.
- When Can Ad-hoc Judges be Appointed? Ad-hoc judges are appointed under specific circumstances, particularly when:
- Judicial vacancies exceed 20% of the sanctioned strength.
- Cases in a specific category have been pending for more than five years.
- More than 10% of cases are pending for over five years.
- The case disposal rate is lower than the rate of incoming cases.
- Conditions for Appointment in January 2025 Order:
- The Supreme Court's January 2025 order allows High Courts to appoint retired judges on an ad-hoc basis, even when vacancies are less than 20% of the sanctioned strength.
- Ad-hoc judges will only hear criminal appeals and must be part of a Bench led by a sitting judge.
- The number of ad-hoc judges should not exceed 10% of the High Court’s sanctioned judicial strength.
- Appointment Duration and Number: Ad-hoc judges should typically be appointed for 2 to 3 years. Each High Court can have 2 to 5 ad-hoc judges.
- Allowances and Benefits:
- Ad-hoc judges will receive the same pay and allowances as permanent judges, excluding pension.
- They will either be provided with rent-free accommodation or a housing allowance.


Prelims Articles
Context
The Rajasthan government dissolved nine districts and three divisions during a cabinet meeting. The number of districts in the state now stands at 41 and divisions at seven. The districts that have been done away with include Dudu, Kekri, Shahpura, Neemkathana, Gangapur City, Jaipur Rural, Jodhpur Rural, Anupgarh, and Sanchore. The divisions of Pali, Sikar, and Banswara have also been dissolved.
What is the Procedure to form a new District?
- The power to create new districts or alter existing ones lies with the State Government. This process is entirely within the purview of the state and does not require intervention or approval from the Central Government.
- The State Government can either create a new district or modify existing districts through an executive order or by passing a legislative bill in the State Assembly.
- Method of Formation or Alteration of Districts: To form a new district or modify an existing one, the State Government may follow these steps:
- Executive Order: The state can issue an executive order to create, abolish, or modify districts. This is the most common method for administrative convenience.
- Legislative Process: Alternatively, the State Assembly may pass a law to create a new district or alter boundaries, if needed. This could involve a formal procedure in the legislative body, including debates, voting, and passing a bill.
- The Centre does not have any role or jurisdiction in this matter, meaning that each state has the autonomy to decide how its districts should be organized.


Prelims Articles
Context
India is considering whether it should continue its participation in the OECD's global tax deal following the United States' decision to withdraw from the pact. US’s exit effectively nullified the progress made by the OECD in bringing together 140 countries to agree on a global minimum tax of 15% for profits made by multinational corporations.
About OECD Global Tax Deal
- The Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (“OECD”) Global Tax Deal is a groundbreaking international agreement to overhaul how multinational corporations are taxed.
- In 2021, nearly 140 countries signed the OECD's global tax deal.
- The deal emerged from the Base Erosion and Profit Shifting (“BEPS”) project, launched in 2013 to combat tax avoidance by multinational corporations
- Its purpose is to create a more unified international tax regime, with the U.S., home to several of the world’s largest multinational corporations like Google and Amazon, playing a pivotal role in pushing the negotiations forward.
- The deal introduces a two-pillar framework aimed to address the "race to the bottom" approach of global tax competition and discourage cross-border tax avoidance by firms.
- Pillar 1 aims to reallocate the residual profits of large multinationals from their home countries to jurisdictions where they generate revenue
- Pillar 2 establishes a 15 per cent global minimum corporate tax.
Implications of U.S. Pullout:
- Global Tax Coordination:With the U.S. withdrawing from the deal, it could lead to uncertainty in global tax coordination. The U.S. has historically been a key player in international economic agreements, and its absence may reduce the effectiveness of the Global Tax Deal.
- Impact on U.S. Multinationals:The withdrawal could benefit tech giants by ensuring that they do not face additional tax liabilities in other countries, especially those related to top-up taxes under the OECD agreement. These companies would continue to avoid the 15% minimum tax in foreign jurisdictions, potentially reducing their overall tax burden.
- Impact on India:India, like other countries, could face challenges in enforcing tax policies on global digital services. The U.S. withdrawal from the deal may limit India's ability to apply top-up taxes on U.S. multinational corporations operating in India. Additionally, India's proposed 2% equalization levy on foreign tech giants might come under pressure if other countries align their tax policies with the OECD framework. This could affect India’s ability to generate revenue from international tech firms.


Prelims Articles
Context
India's largest solar cell and module manufacturing unit has been recently inaugurated at the Gangaikondan SIPCOT Industrial Growth Centre in Tamil Nadu.
About the Plant
- The facility is set up by TATA Power's solar energy arm, TP Solar Limited
- Investment: Rs 3,800 crore.
- It is designed to produce 30-GW photovoltaic cells and modules annually, which will be used in solar power generation units across the country.
- The plant is equipped with advanced robotic automation, and will feature cutting-edge TOPCon and Mono Perc technology, which will ensure high efficiency and long-term reliability for solar projects, including rooftop solar installations.
- The unit will not only produce solar modules but also manufacture raw materials necessary for module production.
- Additionally, Vikram Solar is also setting up a 3-GW solar cell and 6-GW module manufacturing facility at the same site, further boosting the region’s solar energy manufacturing capabilities. This expansion is part of Tamil Nadu's ongoing efforts to create a robust clean energy infrastructure.
Fact Box:Solar Cells:
Solar Modules:
Important Government Schemes
|


Prelims Articles
Context
The Union Defence Ministry of India signed contracts worth Rs 10,147 crore for the procurement of advanced ammunition for the Army’s Pinaka Multiple Rocket Launch Systems (MRLS).
About Pinaka:
- The Pinaka Multiple Rocket Launch System (MRLS) is a key long-range artillery weapon used by the Indian Army, designed to provide rapid, high-volume firepower.
- The system has been developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
- It is named after Pinaka, the bow of the Hindu god Lord Shiva, symbolizing power and precision.
- Key Features:
- Range and Firepower: The Pinaka MRLS is capable of firing multiple rockets in a single salvo. The upgraded system has an impressive range of 75 km, with plans to enhance it to 120 km and eventually 300 km. It can deliver a salvo of 72 rockets on target in just 44 seconds, allowing for a concentrated attack on enemy positions.
- Ammunition Types: The system uses various types of rockets, including high explosive, anti-tank, and area denial munitions. The new contracts aim to acquire ADM Type-1 (designed to deny areas to enemy forces) and HEPF-Mk-1 rockets (enhanced versions of existing rockets for greater range and precision).
- Fully Automated System: The Pinaka system is fully automated, enabling fast and efficient rocket launches. This automated system helps the army deliver concentrated strikes on targets within a short time frame, providing a significant tactical advantage.


Editorials
Context
The deportation of hundreds of Indian migrants from the United States is raising concerns. This wave of deportations coincides with Trump's focus on tightening immigration laws and has created potential diplomatic tensions between India and the U.S., especially with the U.S. using military flights for deportations.
Increased Deportations and Concerns for India:
- Rise in Deportations: Between June and October 2024, approximately 1,60,000 individuals were deported, with a significant number from India. This marks an intensification of S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) actions, raising concerns about the growing number of returning migrants to India.
- Use of Military Flights: The U.S. has started using military flights for deportations, signaling a tougher stance on illegal immigration. The use of such flights, particularly with reports of shackling migrants, has sparked protests, notably from Colombia, highlighting the severity of the deportation process.
- Bilateral Tensions: The timing of these deportations, just ahead of Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s visit to the U.S., has potential diplomatic implications. This move signals that U.S. immigration policies may not be easily influenced by diplomatic efforts, creating a potential flashpoint in India-U.S. relations.
India’s Role in Managing Illegal Immigration:
- Responsibility to Accept Citizens: India has a responsibility to accept its citizens who have been deported from other countries. However, this comes with the challenge of ensuring that only verifiably Indian nationals are allowed to return. This puts pressure on India to manage these deportations effectively.
- Stricter Controls on Migration: To prevent its citizens from resorting to dangerous illegal immigration routes, particularly through Mexico and Canada, India must implement stricter controls. Awareness campaigns need to educate citizens in states with high deportation rates about the risks associated with illegal immigration.
- Addressing Root Causes of Migration: The government must address the underlying factors driving illegal migration, including economic distress, agricultural crises, and employment shortages. By tackling these issues, India can reduce the push factors that lead to people seeking illegal migration opportunities.
Practice Question:
Q. Examine the challenges posed by the increasing deportation of Indian migrants from the United States. What measures can the Indian government take to address the root causes of illegal immigration and manage the situation effectively?


Editorials
Context
India’s Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) has extended the deadline for thermal power plants to comply with sulphur dioxide (SO2) emission norms by three years. The revised deadline is now December 31, 2027, despite the original target of December 31, 2024, and the reasons for this extension have not been provided. This extension marks the latest development in a long-running saga regarding India’s thermal power plants' compliance with air pollution norms.
Revised SO2 Emission Norms and Debate on Compliance:
- Initial Emission Norms: In December 2015, MoEFCC introduced stricter emission norms for thermal plants, focusing on SO2, particulate matter, and other emissions. The deadline for compliance was initially set for December 2017, with the norms aligning closely with international standards.
- Debate Over Implementation: The debate shifted from meeting emission norms to the feasibility of using Flue Gas Desulphurisation (FGD) technology for SO2 reduction, with discussions focused on long gestation periods and high installation costs for FGDs, even though FGDs were not mandatory in the norms.
- Conflicting Views on SO2 Emissions: Various bodies, including the Central Electricity Authority (CEA) and NITI Aayog, questioned the relevance of strict SO2 norms due to Indian coal’s lower sulphur content. Some studies argued that SO2 emissions might not significantly impact air quality and should not be prioritized over particulate emissions.
Delays and Financial Implications:
- Repeated Extension of Deadlines: The MoEFCC has repeatedly delayed the compliance deadlines, with the latest extension pushing the deadline for SO2 norms to December 31, 2027. This marks the fourth revision of the deadlines, creating inconsistency in the enforcement of pollution control standards.
- Cost of Compliance Passed to Consumers: To alleviate the financial burden on thermal plants, electricity regulators allowed the costs of FGD installation to be passed on to consumers, irrespective of whether the emission norms were met. This approach ensures that electricity consumers bear the cost of unutilized FGD equipment.
- Unused Equipment and Environmental Impact: As a result of the delayed compliance timeline, many plants with FGDs may not operate them, leading to consumers paying for equipment that remains unused. This delay in using pollution control equipment will prevent local communities from experiencing the benefits of cleaner air in the near future.
Practice Question:
Q. Critically analyze the reasons behind the repeated extension of the deadline for thermal plants to meet sulphur dioxide emission norms in India, and discuss its environmental, health, and financial implications.


Editorials
Context
The Trump administration’s decision to withdraw from the OECD global tax deal undermines over a decade of global efforts aimed at curbing tax evasion and ensuring that countries can tax profits generated within their jurisdiction. The move threatens the progress made in taxing digital multinational companies and enforcing minimum corporate tax rates.
The Global Tax Deal and Its Objectives:
- OECD Global Tax Deal: In 2021, the OECD global tax deal aimed to curb tax evasion by digital multinational corporations (MNCs). The treaty had two key pillars: the right for countries to tax digital MNC profits generated within their jurisdiction and a 15% global minimum corporate tax rate for MNCs earning over €750 million.
- Global Consensus: Around 130 countries, including major economies like the US, Germany, and France, supported this treaty, and 55 countries had already implemented laws to comply with the new tax framework. India was one of the signatories, hoping to reduce tax avoidance by large corporations operating globally.
- Trump Administration’s Withdrawal: In January 2024, the Trump administration issued a memorandum withdrawing the US from the OECD global tax deal. It declared that any commitments made by the Biden administration regarding the deal lacked authority unless approved by Congress, endangering the treaty's future and threatening global tax reforms.
The Potential Impact of US Withdrawal on Global Tax Efforts:
- Protection of Digital MNCs: The withdrawal reflects the Trump administration’s support for US-based digital MNCs, such as Apple, Microsoft, Alphabet, and Amazon, which often use low-tax jurisdictions to avoid paying taxes. The administration has also indicated potential retaliatory actions against countries taxing US companies under this treaty.
- Global Setback for Tax Reforms: The US, which initially led the global tax reform movement, now jeopardizes the success of this deal. Countries that had reluctantly agreed to the tax treaty may reconsider their participation, as the absence of US support undermines the deal's global consensus.
- Rise of Tax Havens and Money Laundering: With the US stepping back, tax havens and low-tax jurisdictions that facilitate tax evasion could see a resurgence. This could encourage illegal practices like money laundering and round-tripping, and undermine global cooperation on tax transparency and information sharing.
India’s Role and Future Path:
- Continued Efforts to Combat Tax Evasion: India must persist in its efforts to combat tax evasion by digital MNCs despite the setback from the US withdrawal. Maintaining strong tax enforcement and compliance with global standards is crucial for India’s economic growth and fairness in global taxation.
- Form Alliances for Information Sharing: India should continue forging alliances with other countries to enhance information sharing on tax-related matters. Collaborating with like-minded nations will ensure that global tax evasion practices are kept in check, despite challenges posed by US policies.
- Advocate for Equitable Taxation Policies: India must also advocate for equitable tax policies that ensure large corporations pay their fair share of taxes, especially in developing countries. Fostering international dialogue on taxation will be key to ensuring a level playing field and counteracting the return of tax avoidance practices.
Practice Question:
Q. Evaluate the potential global economic and diplomatic implications of the Trump administration’s decision to withdraw from the OECD global tax deal. How can India continue its efforts to combat tax evasion in light of this development?