8th August 2024 (7 Topics)
Mains Issues
Context
Union Road Transport Minister Nitin Gadkari has mentioned that the government will allow the mixing of lignin up to 35% in petroleum-based bitumen for road construction as a large part of it is imported from other countries.
About Bio-Bitumen:
- Bitumen is a black substance produced through the distillation of crude oil and is widely used for making roads and roofs.
- Bio-bitumen is a bio-based binder derived from renewable sources such as vegetable oils, crop stubble, algae, lignin (a component of wood) or animal manure.
- Bio-bitumen production has been developed as a local alternative to petroleum bitumen, thereby reducing environmental impact.
- It is used in the construction of roads and roofs. It is used as a direct replacement, modifier, and rejuvenator.
- Straw will be used in making roads with bio-bitumen technology, which can reduce pollution.
Properties and Uses:
- The main uses of bio-bitumen are in airtight structures, such as a waterproof binder for road construction (asphalt floors), buildings, and marine structures.
- Due to its high adhesive and waterproof quality, it has been developed as a replacement medium for impermeable and traditional binders in structures.
- Uses of bio-bitumen as an alternative to petroleum bitumen : Bio-bitumen in India can be used as a viable alternative to petroleum bitumen in construction of structures that are natural and environmentally safe. Construction of national highways is expected to be around 12,300 km in the financial year 2023-24, Which is equal to approximately 34 kilometers per day.
Need for Bio-bitumen in India:
- Reducing import dependence:Its primary objective is to replace imported bitumen with domestically produced bio-bitumen in the coming decade, thereby reducing foreign exchange expenditure.
- Addressing environmental concerns: Bio-bitumen production aims to reduce environmental issues associated with stubble burning by using biomass and agricultural waste as feedstock.
- Promoting sustainable practices:By using bio-based materials, this initiative supports sustainable road construction practices and is in line with global environmental standards.
- Technical development and experimental studies:The Central Road Research Institute (CRRI) is collaborating with the Indian Petroleum Institute to conduct a pilot study on a 1 km road using bio-bitumen.
Major challenges of bio-bitumen production in India:
- Cost Effectiveness: Currently bio-bitumen production can be more expensive than conventional methods.
- Long term Performance: More extensive field trials are needed to assess the long-term performance and sustainability of bio-asphalt.
- Standardization: For bio-bitumen to be widely adopted, it is necessary to establish clear standards and specifications for it.
- Other available alternatives:
- Steel slag road technology:
- Steel slag is a new method of using waste generated during steel production to create stronger and more durable roads.
- Companies in Hamburg, Germany developed 100% recycled asphalt pavement (RAP) to reduce costs, save energy, and reduce carbon emissions.
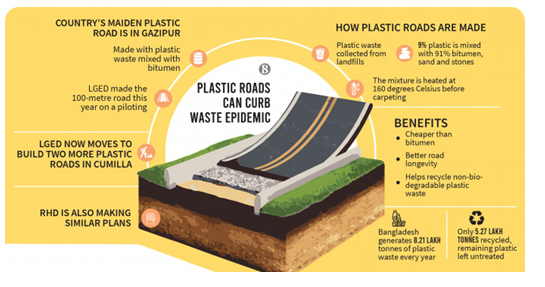
- Plastic Road:
- India has constructed a total of more than 2,500 kilometers of wide plastic roads.
- Even at the global level, plastic roads are being constructed in more than 15 countries.
- For example, in Ladakh it is mandatory to use at least 10% plastic waste for road construction.
- Steel slag road technology:


Mains Issues
Context
A new report from the Centre for Science and Environment (CSE) revealed that the scheme PM KUSUM has achieved only 30 percent of its targets, raising concerns about its ability to meet the 2026 deadline.
About PM KUSUM:
- The Pradhan Mantri Kisan Urja Suraksha Evam UtthaanMahabhiyan (PM-KUSUM) scheme, launched in 2019 with the ambitious goal of solarising agriculture in India.
- The PM-KUSUM scheme is divided into three components:
- Component A: Installation of mini-grids on barren lands.
- Component B: Replacement of diesel water pumps with off-grid solar water pumps.
- Component C: Replacement of electric water pumps with on-grid solar water pumps and installation of mini-grids for agriculture feeder solarisation.
- The PM-KUSUM Scheme was launched in 2019 for de-dieselisation of the farm sector and enhancing the income of farmers.
- It is aimed at ensuring energy security for farmers in India, along with honouring India’s commitment to increase the share of installed capacity of electric power from non-fossil-fuel sources to 40% by 2030 as part of Intended Nationally Determined Contributions (INDCs).
- The scheme aims to add Solar capacity of about 34,800 MW by March 2026 with the total Central Financial support of Rs 34,422 crore.
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE)
- Under the Scheme, a central government subsidy upto 30% or 50% of the total cost is given for the installation of standalone solar pumps and also for the solarization of existing grid-connected agricultural pumps.
- Further, farmers can also install grid-connected solar power plants up to 2MW, under the Scheme on their barren/fallow land.
- This scheme is being implemented by the designated departments of the State Government.
Who are the beneficiaries?
- The eligible categoriesfor KUSUM Scheme are:
- An individual farmer.
- A group of farmers.
- FPO or Farmer producer organization.
- Panchayat.
- Co-operatives.
- Water User Associations.
Challenges:
- One of the principal challenges that the scheme has faced in its implementation has been the availability of cheap electricity for farmers. However, this cheap electricity has its flip side – it leads to increases in a state’s subsidy burden. This access to cheap electricity leads to a lack of incentive for farmers to shift from electric water pumps to solar water pumps.
- Another challenge is the centralization of the implementation model in some states.
- In Punjab, the report notes,the scheme’s implementation is overseen by the Punjab Renewable Energy Development Agency, as opposed to Rajasthan, where each component of the scheme has a different implementing agency.
Recommendations for improvement
To accelerate the scheme's progress and ensure it meets its 2026 targets, the CSE report recommends several measures:
- Decentralisation: Local implementing agencies with on-ground knowledge should manage the scheme to better cater to farmers’ needs.
- Financial viability: Offering farmers the option to pay upfront costs in installments could make the scheme more accessible.
- Increased central assistance: Boosting financial assistance from the Centre, tailored to state-specific needs and fluctuating prices of solar modules, would alleviate the financial burden on farmers.
Conclusion:
The PM-KUSUM scheme holds the potential to reduce carbon emissions by 5.2 million tonnes, making its successful implementation crucial for India's climate action efforts. With targeted recalibrations, the scheme can not only meet its 2026 targets but also play a significant role in promoting sustainable agricultural practices across the country.


Prelims Articles
Context
In a reply in Rajya Sabha, the Union health minister has mentioned that a total of 3.85 crore people in 17 identified States have been screened for sickle cell anaemia as of July 31, 2024.
- The National Sickle Cell Anaemia Elimination Mission (NSCAEM) was launched by Prime Minister Narendra Modi from Madhya Pradesh on July 1, 2023.
What is Sickle Cell Disease?
- It is an inherited blood disorder.
- It affects hemoglobin, the molecule in red blood cells that delivers oxygen to cells throughout the body.
- People with this disease have atypical hemoglobin molecules called hemoglobin S, which can distort red blood cells into a sickle, or crescent, shape.
- These sickle cells also become rigid and sticky, which can slow or block blood flow.
What causes it?
- The cause of Sickle cell disease is a defective gene, called a sickle cell gene.
- A person will be born with sickle cell disease only if two genes are inherited—one from the mother and one from the father.
- Symptoms:
- Early stage: Extreme tiredness or fussiness from anemia, painfully swollen hands and feet, and jaundice.
- Later stage: Severe pain, anemia, organ damage, and infections.
- Treatments:
- The only cure for this disease is bone marrow or stem cell transplantation.
- However, some treatments can help relieve symptoms, lessen complications, and prolong life.
National Sickle Cell Anaemia Elimination Mission:
- It was announced as part of the Union Budget 2023.
- Vision: Eliminate sickle cell disease (SCD) as a public health problem in India before 2047.
- The overall aim is to enable access to affordable and quality health care to all SCD patients and to lower the prevalence through awareness, change of practices and screening interventions.
- The mission will entail awareness creation, universal screening of seven crore people in the 0-40 years age group in affected tribal areas and counseling through collaborative efforts of central ministries and state governments.
- Initially, the focus shall be on 17 states with higher prevalence of SCD viz., Gujarat, Maharashtra, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, West Bengal, Odisha, Tamil Nadu, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Assam, Uttar Pradesh, Kerala, Bihar and Uttarakhand.


Prelims Articles
Context
The government has announced the first set of Rashtriya Vigyan Puraskar, or national awards for scientists.
About the Award:
- Vigyan Ratna Awards: These awards will recognise lifetime achievements & contributions made in any field of science and technology.
- Vigyan Shri Awards:These awards will recognise distinguished contributions to any field of science and technology.
- Vigyan Team Awards:These awards are to be given to a team comprising of three or more scientists/researchers/innovators who have made an exceptional contribution working in a team in any field of science and technology.
- Vigyan Yuva-Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar (VY-SSB):
- These awards are the highest multidisciplinary science awards in India for the young scientists (maximum 45 years).
- They are named after Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar, the founder and director of the Council of Scientific & Industrial Research (CSIR), who was also a renowned chemist and visionary.
- Awards Open to PIOs:
- Persons of Indian origin (PIOs) will now be eligible for the new awards, but only one PIO may receive the Vigyan Ratna.
- Three PIOs each can be selected for the Vigyan Shri and the VY-SSB.
- However, PIOs will not be eligible for the Vigyan Team awards.


Editorials
Context
The recent Supreme Court of India verdict affirmed that the Lieutenant Governor (L-G) of Delhi holds independent authority to appoint aldermen to the Delhi Municipal Corporation. This decision highlights the vulnerability of the elected Delhi government to central control, questioning the effectiveness of having an elected Assembly for Delhi given its Union Territory status.
Central Control Over Delhi's Governance
- Supreme Court Verdict: The Supreme Court upheld the L-G’s independent authority to appoint aldermen, relying on legal provisions governing Centre-Delhi relations and past judgments.
- L-G's Statutory Duty: The Court emphasized that the L-G’s power to appoint aldermen is a statutory duty, not requiring the advice of Delhi's Council of Ministers.
- Union Territory Status: The verdict underscores Delhi’s status as a Union Territory, allowing the Centre significant control over its administration despite having an elected Assembly.
Implications of the Verdict
- Balance of Power: The judgment reflects the delicate balance of power between the elected government and the appointed administrator in Delhi.
- Centre's Final Authority: The Centre retains ultimate authority, with the power to enact, amend, or supersede laws made by the Delhi Assembly, effectively undermining Delhi's government.
- Political Conflicts: Ongoing political conflicts between the BJP-led Centre and the AAP-led Delhi government drive multiple legal disputes, highlighting the friction in Centre-Delhi relations.
Mains Question:
Q1. Discuss the implications of the Supreme Court's verdict on the independent authority of the Lieutenant Governor of Delhi to appoint aldermen for the governance of the National Capital Territory. How does this decision impact the balance of power between the Centre and the elected Delhi government?


Editorials
Context
The recent change in regime in Bangladesh, highlights its potential negative impacts on India and the broader South Asian region. It delves into the implications for India-Bangladesh relations, the rise of Islamist movements, and the necessity of opposition in a functioning democracy.
Implications for India
- Deteriorating Relations: The departure of Sheikh Hasina, a pro-India leader, and the rise of anti-Indian elements, including Begum Khaleda Zia, threatens bilateral relations.
- Islamist Movements: The rise of Islamist movements in Bangladesh, which could target Hindus and destabilize the region, mirrors past conflicts and tensions.
- Strategic Concerns: Bangladesh's geographical position means changes in its political landscape have direct strategic implications for India's security and regional stability.
Lessons from History and Governance
- Value of Opposition: Sheikh Hasina's dominance without opposition highlights the importance of a functional opposition in democracy to address public grievances and prevent unrest.
- Economic Progress vs. Democracy: The situation in Bangladesh underscores that economic progress alone cannot satisfy the populace; political freedom and democratic governance are equally important.
- Regional Instability: The instability in Bangladesh adds to the complexities India faces with its neighbours, including China, Pakistan, and other South Asian countries, complicating regional diplomacy and security.
Mains Question:
Q. Discuss the impact of political instability in Bangladesh on India’s strategic interests and regional security. Evaluate the role of effective opposition in maintaining democratic stability in South Asian countries.


Editorials
Context
The concerning issue of inadequate job placements for students at the Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs), highlights the need for enhanced practical training through robust internship programs to improve employability and meet industry requirements.
Challenges in IIT Placements
- Employment Struggles: Around 8,000 IIT students face difficulties securing jobs, with many dissatisfied with offered packages due to economic challenges and cautious hiring by companies.
- Skill Deficiencies: The job market challenges question the quality of education at IITs, indicating a gap between academic training and required industry skills.
- Outdated Education System: The focus on classroom learning with insufficient hands-on training leaves students underprepared for real-world job demands, necessitating a shift towards practical education.
Importance of Robust Internships
- Enhancing Employability: Internships provide essential industry experience and networking opportunities, bridging the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application.
- Key Factors for Effective Internships: Ideal internships should last 4-6 months, include mentorship and financial support, and be well-structured to ensure meaningful learning and skill acquisition.
- Addressing Unemployment: With a significant rise in educated unemployed youth, creating a robust internship ecosystem can improve employability and contribute to economic growth.
Mains Question:
Q. Discuss the role of internships in enhancing employability among graduates. How can educational institutions, industry partners, and the government collaborate to create an effective internship ecosystem in India?