Fact Box:
Buddhism in India:
- Siddhartha Gautam, born in 563 BC, was part of the Sakya royal family that ruled from Kapilvastu, Lumbini. At the age of 29, Gautama left home and led a life of self-denial.
- After 49 days of meditation, Gautama received enlightenment under a pipal tree at Bodhgaya in Bihar.
- Buddha made his first sermon in the village of Sarnath, near the town of Benares in the UP. The event is known as the Dharma-Chakra-Pravartana (legal wheel revolution).
- He died at the age of 80 in Kushinagara, a city in the UP. The event is known as Mahaparinibban.
- The rules of Buddhism:
- Middle Path: Avoid both extremes of worldly pleasure and the practice of extreme self-The Buddha instead called the 'Madhyam Marg' or the intermediate method to be followed.
- Four good truths:
- Suffering exists (Dukkha)
- Suffering has a cause (Samud?ya)
- Suffering has an end (Nirodha)
- There is a path that leads to the end of suffering(Magga)
- Eight-Way Ways: Positive Views, Proper Objective, Proper Speech, Proper Action, Proper Health, Positive Thinking, Positive Effort, Positive Concentration
- Five Principles or Pancasil- Violence, theft, sexual misconduct, lying or gossip, drunkenness
Major Buddhist texts:
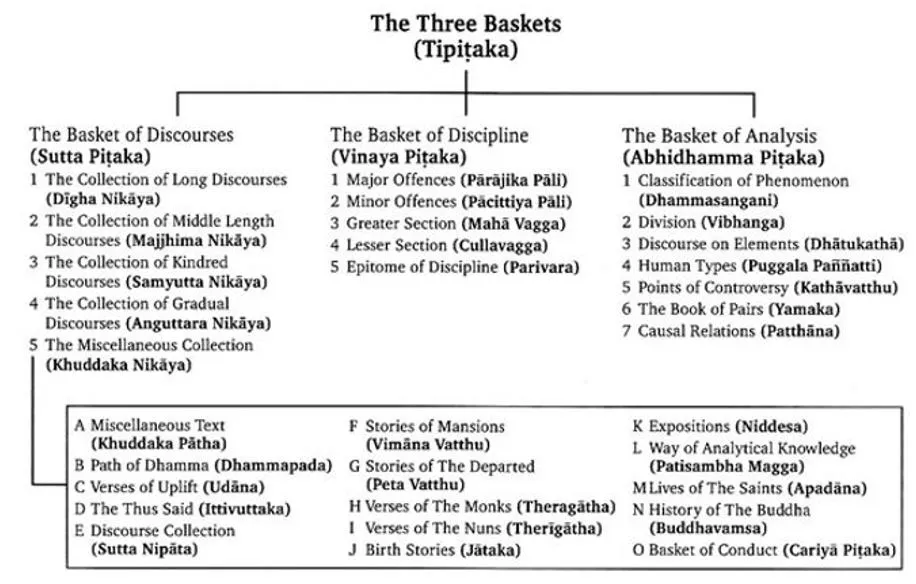
- The Buddhist scriptures are known as the Tipitaka which means 'three baskets'. Tripitaka is made up of three main sections:
- VinayaPitaka (moral code)
- SuttaPitaka (Dhamma Buddha): Divided into five Nicayas: Digha, Majjhima, Samyutta, Anguttara, AnguttaraKhuddaka
- AbhidammaPitaka (philosophical analysis)
- Other important Buddhist texts include Divyavadana, Dipavamsa, Mahavamsa, Milind Panha etc.
Buddhist Schools:
- Mahayana believes in the heaven of the Buddha and the idolatrous worship of the Buddha and the Bodhisattvas including the Buddha Nature.
- Hinayana believes in the original teachings of the Buddha or the Doctrine of the Elders. He does not believe in idolatry and seeks to gain personal salvation through self-discipline and meditation.
- Theravada is a Hinayana sect, founded in Sri Lanka and later spread throughout Southeast Asia.
- Vajrayan means "Car of Thunder", also known as tantric Buddhism.
- Zen is a school of Mahayana Buddhism founded in China.
|





