

23th September 2025 (13 Topics)
Context:
The Government has undertaken a major GST rate rejig to simplify classification, rationalise slabs, and reduce the inverted duty structure (IDS), with the aim of boosting consumption and investments.
Background of GST Rationalisation
- Introduction of GST (2017): GST subsumed 17 indirect taxes and 13 cesses into a unified framework, initially with four slabs – 5%, 12%, 18%, and 28%.
- Problem of Complexity: Multiple slabs and exceptions created confusion for taxpayers and businesses.
- Objective of GST 2.0: To streamline rates, reduce disputes, and spur consumption by placing items in a simplified two-slab structure.
Key Changes in Rate Structure
- Standardisation of Rates:
- Four main slabs (5%, 12%, 18%, 28%) further rationalised; exemptions removed for items like bread, food additives, and health insurance.
- Precious stones taxed at 1.5%; diamonds at 0.25%; gold and silver at 3%.
- Medical devices, bio-fuel, and hydrogen vehicles rationalised under lower slabs.
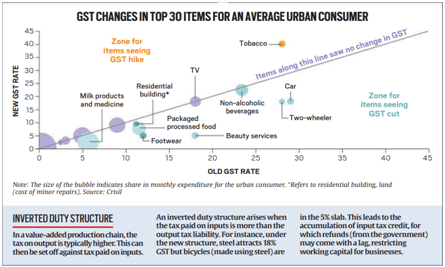
- Consumer Impact:
- Household expenditure expected to decline due to reduction in rates of essential goods like milk products, footwear, and packaged food.
- Some items such as tobacco continue to be taxed at higher rates for revenue and health concerns.
Inverted Duty Structure (IDS): A Persistent Issue
- Definition: IDS arises when input tax is higher than output tax, leading to accumulation of Input Tax Credit (ITC).
- Examples: Steel taxed at 18% but bicycles made using steel at 12%.
- Concerns: Refunds are often delayed, locking working capital for businesses, especially SMEs.
Expected Benefits
- For Consumers:
- Increased disposable income, enhancing demand for goods and services.
- Reduced litigation due to simplified classification.
- For Businesses:
- Lower compliance burden, promoting ease of doing business.
- Potential rise in investment due to predictable tax environment.
- For Government:
- Streamlined revenue inflow through reduced evasion.
- Enhanced efficiency in tax collection via harmonised slabs.
Challenges and Concerns
- Incomplete IDS Resolution: Certain sectors (fertilisers, textiles, bicycles) continue to suffer from blocked credit.
- Revenue Concerns: Excessive rate cuts could limit fiscal capacity of the government.
- Frequent Changes: Continuous modifications in slab rates may cause uncertainty for businesses.
More Articles


