11th June 2024 (13 Topics)
Context
ISRO's Aditya-L1 spacecraft, equipped with two remote sensing instruments - Solar Ultra Violet Imaging Telescope (SUIT) and Visible Emission Line Coronagraph (VELC), has captured recent solar activity.
Key-highlights:
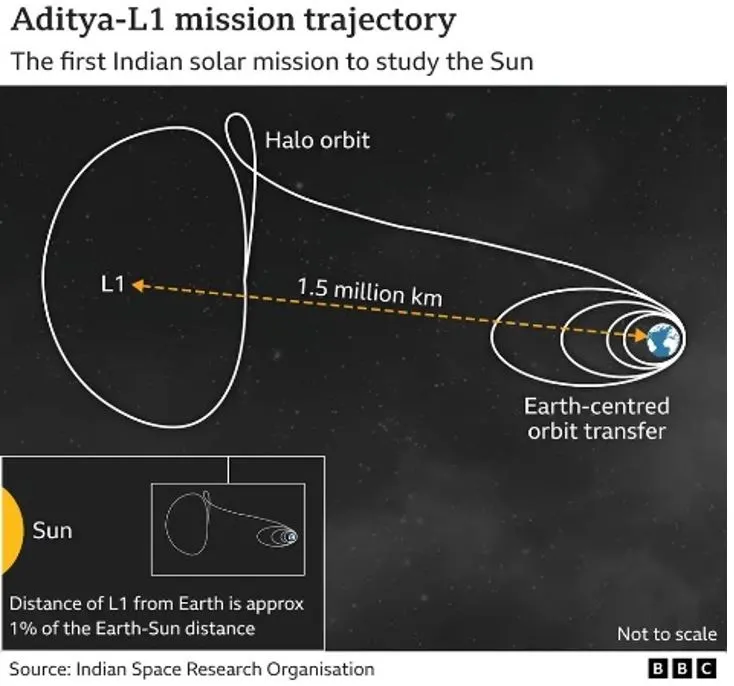
- Aditya-L1 reached the Lagrangian point (L1) in January 2024, 127 days after its launch on in September 2023. L1 is approximately 1.5 million km from Earth, allowing continuous observation of the Sun.
- Remote Sensing Instruments: SUIT and VELC onboard Aditya-L1 have recorded dynamic activities of the Sun during May 2024.
- SUIT captures solar ultraviolet images, while VELC observes visible emission lines from the Sun.
- Solar Events Recorded: Several X-class and M-class flares, accompanied by Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs), were detected during May 2024, leading to significant geomagnetic storms.
- The active region AR13664 on the Sun erupted multiple X-class and M-class flares during May. These events caused major geomagnetic disturbances.
|
Fact Box: About Aditya-L1
Basic Concepts:
|
More Articles