

12th August 2022 (7 Topics)
Context
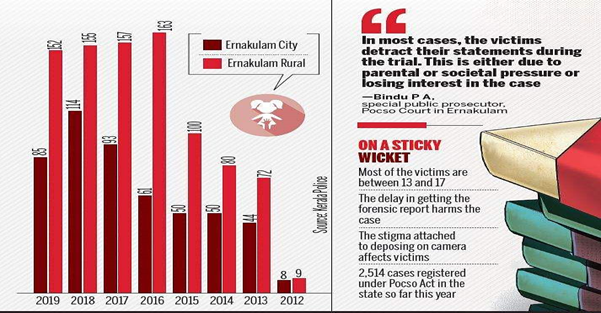
In the wake of increasing incidents of sexual assaults against children reported, the Kerala child rights panel is getting ready to organise awareness classes for teachers in government and aided schools in the state on the POCSO Act and its various aspects.
About
- The POCSO act was enacted in 2012, especially to protect children aged less than 18 from sexual assault sexual abuse, sexual harassment and pornography.
- The act mandates that investigation in the cases is to be completed in two months (from the date of registration of FIR) and trial in six months.
- The Act defines a child as any person below eighteen years of age.
- POCSO states a sexual assault is to be considered aggravated if- The abused child is mentally ill or When the abuse is committed by;
- A member of the armed forces or Security forces
- A public servant
- A person in a position of trust or authority of the child, like a family member, police officer, teacher, or doctor or a person-management or staff of a hospital – whether Government or private.
Kerala panel’s decision
- The objective of the Commission is to prevent POCSO atrocities in the state and also to ensure all necessary assistance to the survivors.
- The classes would be conducted under the aegis of the district Legal Services Authority.
India’s present situation
- Despite the existence of a strong legal framework, there has been a substantial increase in the number of crimes against children, according to the NCRB Report on Crimes against Children. As on 2019, this number stands close to a total of 1.5 lakh cases.
- Data presented by the NCRB in its Crime in India report 2017-2019 shows that even though in terms of absolute numbers, the number of cases with completed trial is increasing, the percentage of trials completed to the total cases for trials remains constant at 10%. As a result, 89% of the total cases for trials had their trials pending.
- Hence, to complete trials within the stipulated time, there is a dire need for the establishment of more fast-track courts in the country.
|
Constitutional Provisions
|
Role of National Commission for Child Rights
- The NCPCR is a body that works towards achieving a child rights-centric approach in all the laws, programmes, policies and administrative mechanisms in India.
- It functions under the Ministry of Women & Child Development of the central government.
- It strives to ensure that all laws and policies in the country are in consonance with the rights of children as emphasised by the Indian Constitution as well as with the UN Convention on the Rights of the Child.
- The Commission acknowledges the universality and inviolability of child rights.
- It focuses on children that form a part of the most vulnerable sections of society.
- The Commission sees every right of the child as equally important and hence, does not grade the rights according to importance.
Related Government Initiatives
- Child Abuse Prevention and Investigation Unit
- Beti Bachao, Beti Padhao
- Juvenile Justice Act/Care and Protection Act, 2000
- Child Marriage Prohibition Act (2006)
- Child Labour Prohibition and Regulation Act, 2016
More Articles


