

21st December 2024 (10 Topics)
Context
The United States sanctioned four Pakistani entities on charges of contributing to nuclear-armed Islamabad's long-range ballistic missile program. A senior White House official recently stated that Pakistan's developing long-range ballistic missile capabilities could eventually allow it to strike targets beyond South Asia, including the United States, making it an “emerging threat” to U.S. national security.
Pakistan’s Ballistic Missile Program
- Pakistan, which conducted its first nuclear test in 1998, now possesses an estimated 170 nuclear warheads.
- The country has developed a wide array of ballistic missiles capable of carrying nuclear payloads, which increases the stakes in the region and raises concerns about missile proliferation.
- Missile Development: Pakistan is increasingly developing long-range ballistic missile systems with the ability to strike targets much farther than just South Asia. These missiles are being equipped with larger rocket motors, indicating an advancement towards missiles that could potentially reach the U.S.
Impact on U.S.-Pakistan Relations
- Deteriorating Relations: The U.S.-Pakistan relationship has worsened significantly after the U.S. withdrawal from Afghanistan. Pakistan's growing ties with China, coupled with the U.S. rapprochement with India, have further strained ties. Pakistan sees the S.-India strategic partnership as a challenge to its own regional security interests.
- S. Concerns: U.S. officials are questioning why Pakistan would seek to develop missile systems that could be used to target countries outside the region, such as the U.S. Pakistan’s growing missile capabilities could also undermine global security by contributing to nuclear arms proliferation.
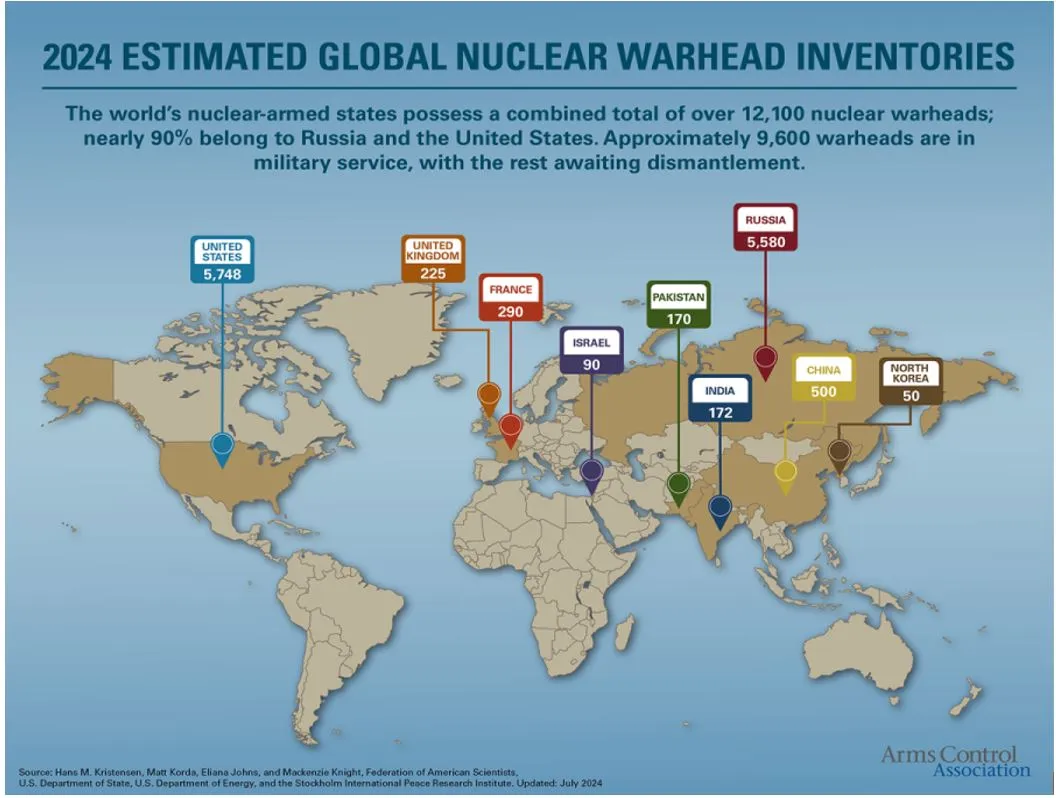
Fact Box:Current State of Nuclear Warheads (As of 2024)
Estimates of Nuclear Stockpiles:
Non-NPT Nuclear Weapons Possessors These states have developed nuclear weapons outside the NPT framework:
|


