

21st April 2025 (15 Topics)
Context
The Ramban tehsil of Jammu and Kashmir witnessed torrential rainfall and hailstorms. According to the India Meteorological Department (IMD), the region received 16.9 mm of rainfall in just 24 hours, which is a 575% increase over the normal of 2.5 mm. Government authorities and meteorological experts flagged the situation using terms like “flash flood,” “landslide,” and “cloudburst” — all of which are natural disaster events commonly witnessed in Himalayan and other hilly regions.
What is a Cloudburst?
- A cloudburst is a very intense and sudden rainfall event — defined as 10 cm (100 mm) or more rainfall in an hour over a small area, typically 10 km × 10 km.
- Cloudbursts are most common in mountainous regions such as the Himalayas due to a process called orographic lifting:
- Warm, moist air from plains moves towards the mountains.
- As it rises along the slopes, the air cools due to lower atmospheric pressure.
- The cooling air condenses rapidly, forming dense clouds.
- When saturation is reached and the water cannot be held any longer, the entire mass of water “bursts” out as a violent downpour.
- Challenges
- The phenomenon is highly localized – makes them hard to predict with current radar or satellite technologies.
- It can result in sudden and devastating impacts in very short time spans.
- It leads to flash floods, landslides, and infrastructure destruction.

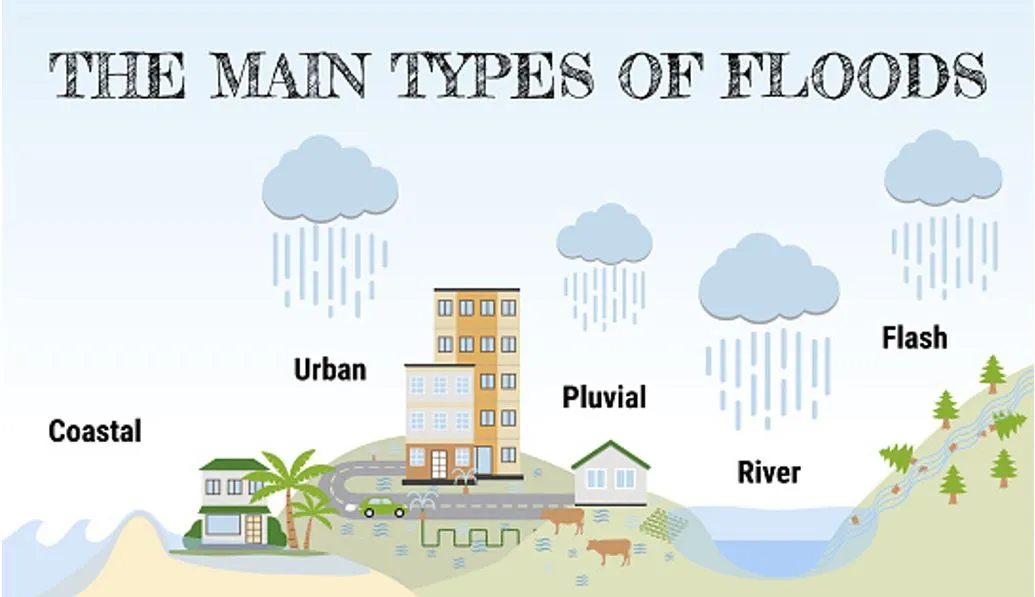
What is a Flash Flood?
- A flash flood is a rapid flooding of low-lying areas, often caused by intense rainfall over a short duration. In hills, they occur because:
- Rocky terrain doesn’t absorb water
- Water rapidly flows down slopes, entering streams, nullahs, and rivers suddenly.
| Differences from River Floods | ||
|
Feature |
Flash Flood |
River Flood |
|
Onset |
Sudden (within hours) |
Gradual (over days or weeks) |
|
Duration |
Short (a few hours) |
Long-lasting |
|
Common terrain |
Hilly or semi-urban |
Plains and floodplains |
|
Risk focus |
Loss of life due to surprise |
Infrastructure and crop damage |
- When these water bodies can’t carry the load, water spills over, flooding roads, homes, and fields.
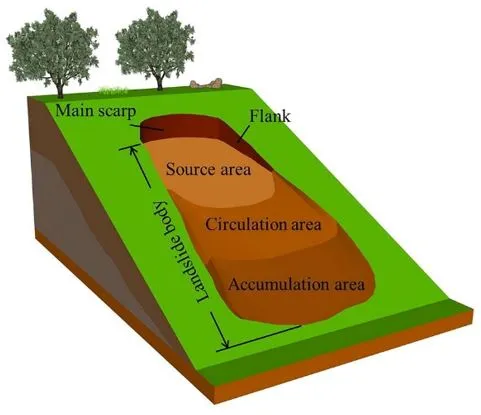
What is a Landslide?
- A landslide is the downward movement of rock, earth, or debris on a slope. It occurs when the force of gravity becomes greater than the material's ability to resist sliding. This can be caused by:
- Heavy rain (like cloudbursts or flash floods)
- Earthquakes
- Human activities such as road-cutting, deforestation, and unplanned construction
- Water is a critical trigger. It adds weight to soil and rocks. It reduces internal friction, making it easier for the material to slides.
Why Are These Events Common in Jammu & Kashmir?
- Mountainous Terrain: The region lies in the Himalayan fold belt, with steep slopes, fragile rocks, and unstable geology — all of which are conducive to landslides and flash floods.
- Changing Rainfall Patterns: With climate change, the region is seeing more frequent extreme weather events and short, intense spells of rain instead of steady, moderate rainfall
- Unplanned Urbanization and Deforestation: Construction in ecologically sensitive areas, deforestation, and improper land use contribute to soil erosion and destabilization of slopes.
- Inadequate Drainage Infrastructure: Many towns and villages in the region lack stormwater drainage systems, making them vulnerable to waterlogging and flooding.
Policy and Preparedness Dimensions
- Early Warning Systems (EWS): IMD and local meteorological stations need to improve real-time alerts, radar coverage, and forecasting models, especially in hilly and remote areas.
- Disaster Preparedness Plans: District administrations must regularly update and conduct mock drills, prepare evacuation plans, and stock emergency materials.
- Infrastructure Resilience: Roads, power lines, and houses must be designed to withstand floods and landslides, following eco-sensitive building codes.
- Climate Adaptation Strategies: There’s a need to shift focus from just relief to climate-resilient development, which includes:
- Afforestation
- Watershed management
- Risk zonation maps
More Articles


