9th February 2024 (11 Topics)
Context
The Reserve Bank of India’s Monetary Policy Committee (MPC), in its sixth meeting, maintained a status quo on the repo rate. In another significant step, it extended the Key Fact Statement (KFS) requirements to cover all retail and MSME loans.
Key-Takeaways:
- The Reserve Bank of India’s Monetary Policy Committee has decided to keep the policy repo rate unchanged at 6.5%.
- CPI for FY24 is projected at 5.4%, while its likely to be at 4.5% in FY25. RBI has pegged real GDP growth for FY25 at 7%.
- Retail inflation to average 5.4% this fiscal, to come down to 4.5% in FY25
- Monetary transmission by financial institutions still remains incomplete
- Current economic momentum to sustain in the next fiscal
- RBI to introduce an offline functionality in CBDC-Retail for transactions in areas with poor or limited internet connectivity.
- RBI will review regulatory framework for electronic trading platforms to enable market makers access offshore ETPs offering permitted Indian Rupee products
- RBI asked lenders to provide key fact statement (KFS) about the terms of the loan agreement, including all-inclusive interest cost, to borrowers for retail as well as MSME loans
What Is the Key Fact Statement (KFS)?
- The KFS is a concise document that provides borrowers with essential information about their loan agreements. It serves as a financial compass, guiding borrowers through the intricacies of borrowing.
- All-Inclusive Interest Rate: The KFS includes the actual annualized interest rate, which encompasses not only the base interest but also any additional charges, fees, and penalties associated with the loan.
- The change: The Key Fact Statement (KFS) requirements now cover all retail and MSME loans. Previously, this mandate was applicable only to specific categories of lenders, but now it applies across the board. Let’s break down what this means and why it matters:
Why Is the KFS Important?
- Transparency: Borrowers often skim through lengthy loan documents, missing critical details. The KFS ensures transparency by spotlighting the complete cost of borrowing. Whether it’s processing fees, documentation charges, or penalties, borrowers will know exactly what they’re paying for.
- Empowering Borrowers: Armed with this knowledge, borrowers can compare loan offers effectively. They’ll be better equipped to choose the most suitable loan for their needs.
|
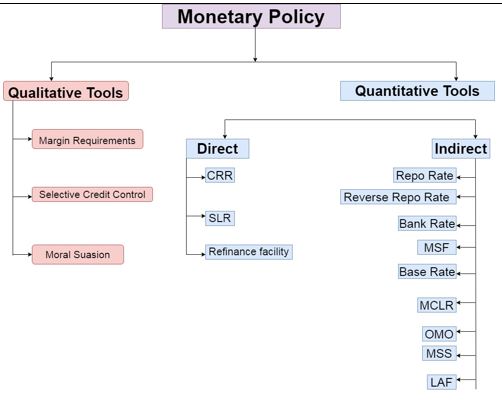
What Is the Monetary Policy?
What is Monetary Policy Committee(MPC):
|
More Articles