

1st November 2023 (9 Topics)
Context
An Annual Survey of India’s City-Systems (ASICS) 2023 of Indian cities shows that a majority of local governments are financially dependent on their State governments.
About the survey -
- The report, Annual Survey of India’s City-Systems (ASICS) 2023, was published by the Janaagraha Centre for Citizenship and Democracy, a non-profit institution.
- The Survey has highlighted various limitations and challenges faced by Indian cities in terms of financial autonomy, governance structures, and transparency.
Key Highlights –
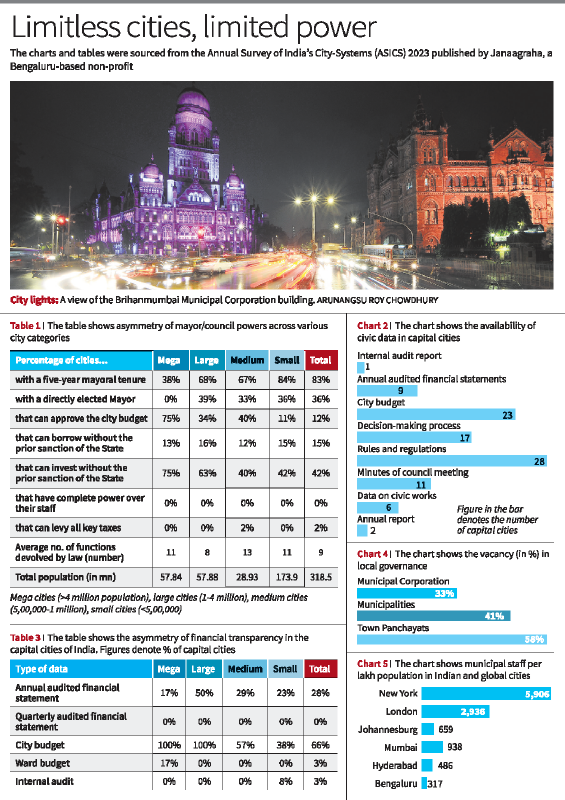
- Asymmetry of power across four city categories — megacities (>4 million (mn) population), large cities (1-4 mn), medium cities (0.5 mn-1 mn), small cities (<0.5 mn).
- It shows that while megacities have more say over their finances, their mayors do not have a five-year tenure and are not directly elected.
- On the other hand, more mayors in smaller cities have a five-year tenure and are directly elected, but lack a say on the city’s finances.
- The report also shows that mayors and councils have limited power in staff appointments and promotions.
- Cities especially lack control over their senior management teams who are deputed directly by State governments, which makes it tough to initiate disciplinary proceedings against them if needed.
- The report also mentions the lack of transparency in publishing cities’ civic information which citizens can access easily.
- Only 11 of the 35 States/Union Territories have enacted the Public Disclosure Law that mandates publishing of key civic data.
- Due to poor control over appointment of staff, the local governments suffer from high levels of unfilled posts.
- Data show that 35% of posts in India’s municipal corporations are vacant.
- The vacancy progressively worsens with 41% posts being vacant among municipalities and 58% being vacant in town panchayats.
- A comparison with other metropolises such as New York, London and Johannesburg shows that such a crippling shortage of staff is limited to Indian cities.
- Data shows the number of city staff per one lakh population.
- There are 5,906 city workers in New York and 2,936 in London for every one lakh population compared to just 317 in Bengaluru, 586 in Hyderabad, and 938 in Mumbai.
- Cities such as New York also been empowered to impose taxes, approve their own budget, invest and borrow without approval.
Impacts of limitations and challenges faced by Indian cities -
- Service Delivery: Limited financial autonomy hampers local bodies' ability to allocate funds effectively for essential services, hindering infrastructure development, healthcare, education, and other civic amenities.
- Accountability and Corruption: Lack of transparency may lead to corruption and misuse of funds, eroding public trust and reducing accountability in local governance.
- Citizen Participation: Weak governance structures can restrict citizen involvement in decision-making processes, impeding the representation and consideration of local community needs and concerns.
- Economic Development: Insufficient financial autonomy constrains the ability to invest in local economic development, thereby limiting job creation and overall growth.
- Service Quality: Weak governance structures and financial constraints could result in substandard service quality and inefficient resource utilization, impacting citizens' quality of life.
- Efficiency and Effectiveness: Transparency issues in governance might limit the efficacy of local bodies in executing projects, leading to delays, cost overruns, and inefficiencies.
- Sustainable Development: Financial limitations may hinder investments in sustainable development projects, impeding the adoption of eco-friendly initiatives and smart city practices.


