

28th September 2022 (9 Topics)
Context
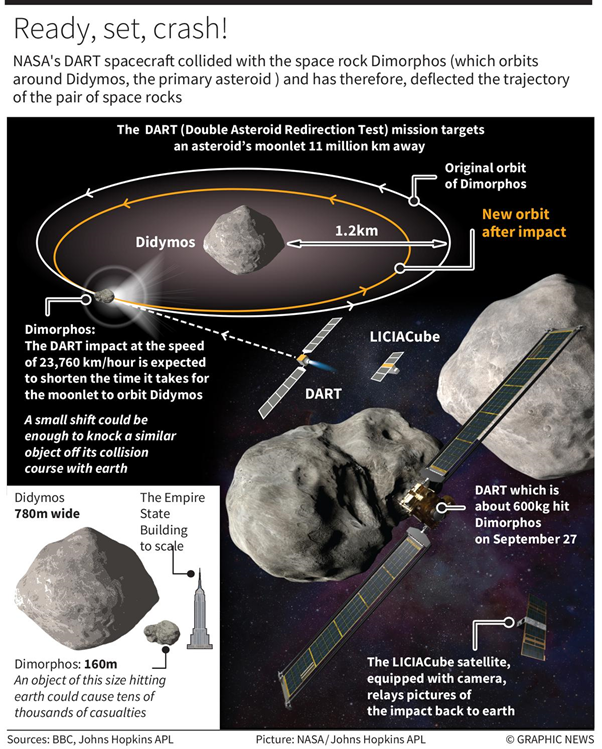
Recently, the DART (Double Asteroid Redirection Test) spacecraft collided with the space rock Dimorphos (just 160 metres wide).
About
Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART)
- DART is the first-ever mission dedicated to investigating and demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection by changing an asteroid’s motion in space through kinetic impact.
- This method will have DART deliberately collide with a target asteroid which poses no threat to Earth, in order to change its speed and path.
- DART’s target is the binary, near-Earth asteroid system Didymos, composed of the roughly 780-meter (2,560-foot) -diameter “Didymos” and the smaller, approximately 160-meter (530-foot)-size “Dimorphos,” which orbits Didymos.
- DART will impact Dimorphos to change its orbit within the binary system.
- DART is also carrying a cubesat that will film the larger spacecraft's impact and beam the footage back to researchers on Earth.
- At the time of DART's impact, Didymos will be visible enough to be a good candidate for study and distant enough to be no danger, at approximately 6.8 million miles (11 kilometers) away from Earth.
|
What is an Asteroid?
|
What are the other possibilities of this technique?
- At the heels of NASA, China is set to deflect a 40m diameter earth-crossing asteroid called 2020 PN1 sometime in 2026.
- While ostensibly the drive comes from the desire to protect earth from killer asteroids, perhaps the lure of space mining lurks behind.
- Mining rare earth elements comes with a high environmental cost. In the coming years, the penalty for polluting could make space mining economically viable.
- If one can tug a mineral-rich asteroid near the Moon or establish a space mining factory between the orbits of earth and Mars, precious mineral resources needed for decades could be easily sourced.
- The ‘kick’ technique that deflects asteroids can then be used to move a small asteroid into a convenient position for space mining.
- Now shelved, NASA’s Asteroid Redirect Mission (ARM) aimed at precisely this by bringing a 20-tonne space rock near earth to study and mine. In a way, the DART mission is also part of this frame.


