

- Unparalleled economic growth.
- The gaps between rich and poor countries, and rich and poor people within countries widened
- Income gap between rich and poor countries will rise is a concern
- Environmental impact as the industries and markets grow.
- Leaves many uneducated and less skilled unemployed forever as in ages of technology driven world it is essential to have a competitive education and skills.
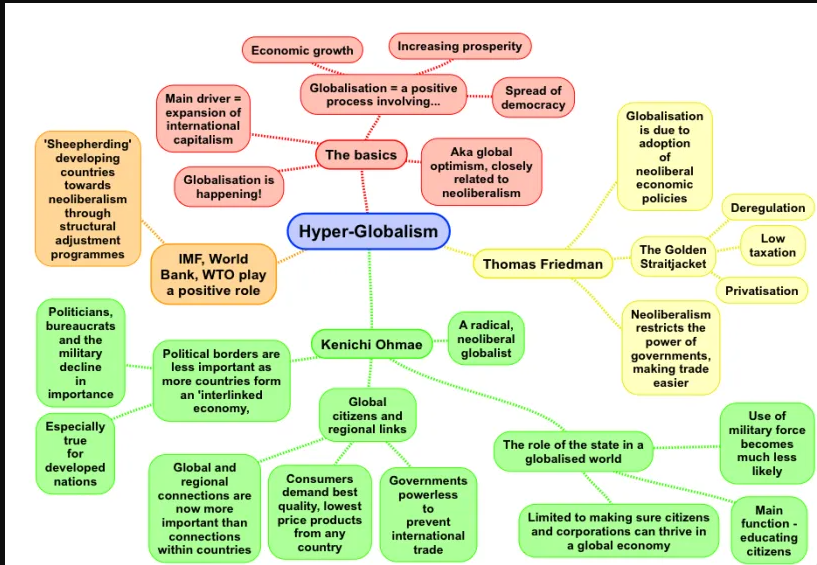
- Hyper globalisation simply means sudden shift in size, scope and velocity of globalisation begun in late 1900 and continues till date. It covers 3 dimensions such as; Economic Globalisation, Cultural Globalisation and Political Globalisation.
- The concept first arose in the 2011 work by Dani Roderick, an economist and professor of International Political Economy at the Kennedy School of Government at Harvard University, who described it in The Globalization Paradox.
- The latest Hyper globalisation started in later years after foundation of world trade organisation in 1995 and Dani Roderick sees hyper-globalization as a type of globalization that allows multinational companies to avoid the rules and regulations of nation states.
Major characteristics of hyper globalism are:
- The dematerialization of globalization (the importance of services is considered important than material)
- the democratic globalization (Growth of trade is because of output become more wide spread and democratic)
- Criss-crossing globalization (the similarity of goods and capital are criss-crossing across various borders).
- The rise of a mega-traders such as; China, Singapore, Malaysia who exports exceeds 50% of world GDP.
- The proliferation of regional trade agreements and the imminence of mega-regional ones is accompanied to swift growth of trade.
- The decline of barriers to trade in goods but the continued existence of high barriers to trade in services
A related feature of this era of hyper globalization is the rise of multinational corporations and the sharp surge in flows of foreign direct investment (FDI), which have both caused and been caused by cross-border and other flows of goods and services.
The main difference between globalisation and hyper globalisation is very narrow and can be best described as the rate of speed at which the process of globalisation takes place. period between 1870 and 1914 the Golden Age of globalization in which world trade in terms of gross domestic product went from a 9 percent to 16 percent share. However, in the current age of hyper-globalization, which includes both goods and services, the gross domestic product share has reached 33 percent.
- Takashi Inoue describes three forces of hyper-globalization:
-
- Economic force in which extensive growth in global trade creates cross-border economic integration,
- Human communications force via the Internet in which instant and global communication of social media and the Internet are changing norms of human communication blurring social barriers, and
- Technological disruption force coming from new innovations in technology driven by Internet-of-Things (IoT), big data, and Artificial Intelligence (AI) bringing massive economic and rapid social changes leading to a world of Singularity.
- A related feature of this era of hyper globalization is the rise of multinational corporations and the sharp surge in flows of foreign direct investment (FDI), which have both caused and been caused by cross-border and other flows of goods and services.
- Rapid population growth, where need for goods rise with population resulting demand for more interconnected markets
- Thrive for economic expansionary policies by various country’s
- More international trade, especially since the 1950s had led to increasing wealth, health, education for most countries. For instance, China which has benefitted from increasing is just one of four nations known as theBRIC Nations (Brazil, Russia, India and China) that are considered the upcoming economies predicted to be wealthier than Britain by 2050.
- Bring investment and jobs to developing countries.
- Patterns of consumption are becoming globalised – more people around the world are consumers rather than living subsistence lifestyles.
- The spread of democracy and respect for human rights – for example, the end of colonial rule in Africa, the collapse of communism and the Arab Spring. This is also evidenced in the establishment of the United Nations and the growth of global social movements such as green peace.
The period of hyper globalization has been associated with the most dramatic turnaround in the economic fortunes of developing countries. Hyper globalism is making the movement of goods, services (including technology) and human not only easier but also necessary. Hence it is providing a way to spread liberal ideas. This can be the cause for increasing democratic movement’s world over. Increasing demand for sustainable development in many places is result of awareness of such protests elsewhere in the world. Women empowerment, increasing accessibility of quality educational and health benefits etc. can also be attributed to evolution of hyper globalism. All this help make the world a better prosperous world. Hyper Globalization may be pursued at current or even higher speeds in later, but need to be proceeded gradually where Sustainable development, culture, happiness are involved. All the nations need to discuss and agree upon terms regarding the same. Finally Hyper Globalization has to be pursued at a pace where positives fat outweighs negatives. The major reason behind threatening human prosperity is increasing inequality, amassing of wealth by few individuals. This needs to be taken care for truly enjoying the benefits of Hyper Globalism.
Related Articles


