12th June 2024 (12 Topics)
Mains Issues
Context
In a recent development, an international tribunal composed of former judges from the region expressed shock at the harsh realities faced by Malaiyaha Tamil community, Sri Lanka's tea and rubber plantation workers.
Who are Malaiyaha Tamil community?
- The community originally brought from India to work in Sri Lanka's plantation sector over 200 years ago.
- The Malaiyaha Tamils live in upcountry Sri Lanka.
- The community is a distinct ethnic group, constituting the fourth largest population on the island nation — following the Sinhalese, the ‘Sri Lankan’ Tamils, and the Muslim community.
- They’re one of thepoorest communities in the country — underpaid and overworked.
- Economic Contribution: Despite their significant contribution to Sri Lanka's tea industry, with tea exports fetching approximately $1.3 billion annually, these workers receive meagre wages that barely meet their basic needs.
Discrimination faced by the Malaiyaha Tamil community
- Ethnic discrimination: They continue to face discrimination based on their ethnic origin.
- No land rights: The community continues to be denied land rights, further exacerbating their socio-economic marginalization and perpetuating cycles of poverty.
- Labour Exploitation: The workers, primarily women, are subjected to exploitative working conditions, including low wages tied to demanding daily targets of tea leaf plucking, regardless of weather conditions or safety concerns.
- Living Conditions: These workers endure inhumane and degrading living conditions in colonial-era line room accommodations, where multiple individuals often share cramped spaces with poor sanitation facilities.
There is urgent need for comprehensive measures to address the systemic discrimination and socio-economic injustices faced by the Malaiyaha Tamil community. This includes ensuring fair wages, improving living conditions, protecting land rights, and addressing exploitative labour practices across industries.
Fact Box: Important Pacts
|


Mains Issues
Context
A recent survey sheds light on the significant financial challenges faced by TB patients in India. The survey, encompassing 1,482 TB patients across four states, reveals alarming levels of economic hardship resulting from delays in diagnosis and the long course of TB treatment.
Key-findings of the Study
- Financial Strain: TB patients experience the severe financial strain, with delays in diagnosis and loss of income during treatment contributing to substantial economic burdens.
- Catastrophic Costs: Between 30% to 61% of study participants faced catastrophic costs, defined as out-of-pocket expenses exceeding 20% of pre-TB annual household income. These costs pose a significant threat to the financial stability of TB-affected households.
- Pre-Diagnosis Delay: Over half of the participants faced catastrophic costs even before commencing TB treatment due to delays in diagnosis. The average delay of seven to nine weeks from symptom onset to treatment initiation significantly contributed to financial burdens.
- Recommendations: The survey recommends
- intensifying private sector engagement
- improving rapid diagnosis
- implementing community awareness campaigns
- expanding health insurance coverage for pre-treatment expenses
- safeguarding TB patients from income loss
How ‘cost’ is a determining factor in TB treatment?
- TB treatment in India often imposes a significant financial burden on patients and their families due to various factors, including medical expenses, loss of income, and associated costs.
- Patients face a range of other recurring costs including the costs of accommodation, transport to healthcare facilities and consultations, multivitamins, and loss of income due to missed work
- Other Challenges:
- Delays in Diagnosis: Widespread delays in diagnosing TB persist due to various factors, including delayed testing and reliance on older diagnostic methods like smear microscopy.
- Diagnostic Gaps in Rural Areas: The availability of tools to diagnose extra-pulmonary TB, especially in rural areas, remains a significant gap in healthcare infrastructure.
- Barriers to Treatment Adherence: Poverty, lack of awareness about TB, and shortages of medication contribute to patients discontinuing treatment prematurely.
Case Study
|
What measures are required?
- The findings of the survey underscore the urgent need for both policy and public interventions to alleviate the economic burden of TB on patients and the nation.
- Addressing delays in diagnosis, ensuring uninterrupted livelihood during treatment, and expanding health insurance coverage are essential steps towards mitigating catastrophic costs for TB-affected households.
- Furthermore, enhancing private sector engagement and community awareness campaigns can facilitate timely diagnosis and treatment initiation, reducing financial hardships associated with TB.
Fact Box: About Tuberculosis (TB)
|


Mains Issues
Context
The University Grants Commission (UGC) has made a big change in policy: now, colleges can admit students twice a year, starting next year. This move brings Indian universities in line with global norms, which could lead to better connections with other countries and more student exchanges. To achieve the goals of Vision 2047, India needs to start with strong short-term plans right away.
Current State of India’s Higher Education System:
- Student Population: India has 25% of the world's students.
- Institution Numbers: With over 58,000 higher education institutions, India has the world's second-largest higher education system. In 2021-22 alone, nearly 2,400 new institutions were added.
- Enrollment: There's been a 4.5% increase in student enrollment compared to the previous year, totaling 4.33 crores.
- Gender Enrollment: The Gross Enrollment Ratio (GER) for females has been higher than males since 2018-19, thanks to various government schemes empowering women. The National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 aims to raise the GER to 50% by 2035, a 40% increase from current levels.
- Teacher Ratio: The pupil-teacher ratio (PTR) in universities and colleges remains at 24:1.
- National Education Policy (NEP) 2020: The government launched NEP 2020 to address various educational challenges. However, its implementation faces hurdles due to existing complexities and institutional hesitancy.
Issues in Education System and Remedial Measures:
- Limited Funds and Redistribution:
- Issue: Lack of adequate resources like manpower, infrastructure, and funds hampers educational quality and accessibility.
- Remedy: Government needs to allocate sufficient resources at both provincial and national levels to address educational needs. Redistribution of resources to ensure equitable access to education is vital.
- Autonomy for Education Institutions:
- Issue: Excessive administrative control restricts the autonomy of educational institutions, hindering innovation and quality.
- Remedy: High-performing institutions should be granted autonomy in operations, including syllabus revision and reforms. Collaboration between state and central governments is crucial for implementing measures to reduce control over top-ranked institutions.
- Expensive Higher Education:
- Issue: Privatization and profit-driven models have led to high costs of professional and technical education, limiting accessibility.
- Remedy: Government can establish entities offering education loans at lower interest rates or with longer repayment tenures. Private institutions should offer more scholarships to economically and socially weaker sections to enhance affordability.
- Obsolete Curriculum:
- Issue: Current curriculum focuses on general education, failing to prepare students adequately for real-life challenges.
- Remedy: Align curriculum with international standards, introduce multidisciplinary institutions with flexible credit systems, and allow students to choose courses freely.
- Archaic Academic Structure:
- Issue: Assessment methods and evaluation criteria are outdated and not in line with international standards.
- Remedy: Embrace continuous evaluation and formative assessment models, prioritize practical and vocational courses, and streamline education areas for better assessment.
- Inferior Primary Education Infrastructure:
- Issue: Inadequate infrastructure leads to high dropout rates, wasting potential human resources and causing financial strain.
- Remedy: Focus on skill development and vocational education at the middle school level, preparing students for the job market. Early vocation-based courses can instill the importance of education in families and alleviate financial burdens.
Government Initiatives for Higher Education in India:
- National Education Policy (NEP) 2020: Launched in 2020, NEP aims to revamp the education system, focusing on holistic development, flexibility, and multidisciplinary learning.
- Swayam: An online platform offering free courses from school to postgraduate level, launched to promote digital learning and increase access to quality education.
- SWAYAM PRABHA: A group of 32 DTH channels transmitting high-quality educational content, aimed at reaching remote areas and disadvantaged groups.
- Education Quality Upgradation and Inclusion Program (EQUIP): Aims to enhance access, inclusion, quality, excellence, and employability in higher education.
- Technical Education Quality Improvement Programme (TEQIP): Aims to improve the quality of technical education through long-term projects implemented in phases.
- Institute of Eminence (IoE) Scheme: Empowers higher educational institutions to become world-class teaching and research institutions.
- Rashtriya Uchchatar Shiksha Abhiyan (RUSA): A Centrally Sponsored Scheme aimed at providing strategic funding to eligible state higher educational institutions.
- Prime Minister's Research Fellows (PMRF) Scheme: Designed to improve research quality in higher educational institutions by attracting top talent into research.
- Scheme for Promotion of Academic and Research Collaboration (SPARC): Facilitates academic and research collaborations between Indian institutions and top institutions worldwide.
- e-PG Pathshala: Provides high-quality, interactive e-content across various subjects under the National Mission on Education through ICT (NME-ICT).
- Surveys and Rankings:
- National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF)
- All India Survey on Higher Education (AISHE)
- Vocational Education:
- National Apprenticeship Training Scheme (NATS)
- Scheme for Higher Education Youth in Apprenticeship and Skills (SHREYAS)
Fact BoxRegulation of Higher Education
India Rankings 2023 of higher education institutions
|


Mains Issues
Context
In a breakthrough effort to tackle the pressing issue of arsenic contamination in groundwater, researchers at the Indian Institute of Science (IISc) have devised a pioneering three-step process. This method not only effectively removes heavy metal pollutants like arsenic but also ensures their safe disposal, preventing them from re-entering the environment.
Key-highlights
- Scientists have developed a patent-pending technique aimed at addressing the critical aspect of sustainable waste management in water purification.
- The three-step method effectively eliminates heavy metal contaminants like arsenic from groundwater, ensuring the production of safe drinking water.
- The innovative process not only eliminates arsenic efficiently but also ensures environmentally friendly disposal of the removed pollutants.
- The Problem: Arsenic and fluoride contamination in groundwater is a significant concern across India, with numerous districts exceeding permissible limits set by regulatory bodies like the Bureau of Indian Standards and the World Health Organization.
- These contaminants pose severe health risks to both humans and animals.
- Traditional methods of water purification often neglect the crucial step of disposing of removed contaminants safely, leading to potential recontamination.
Factors contributing to contamination:
- Naturally Occurring Contaminants: Fluoride, arsenic, nitrate, iron, and heavy metals naturally exist in certain geological formations, affecting water quality.
- Industrial Activities: Untreated or poorly treated industrial effluents discharged into water bodies contaminate surface and groundwater sources.
- Agricultural Activities: Excessive use of pesticides, fertilizers, and agrochemicals in agriculture leads to water contamination over time.
- Sanitation Practices: Inadequate sanitation facilities and open defecation, especially in rural areas, contribute to water source contamination.
- Geogenic Processes: Geogenic processes, such as those causing uranium contamination, can occur naturally, exacerbated by groundwater overexploitation.
- Improper Waste Disposal: Improper disposal of biowaste contaminates groundwater and surface water, increasing the risk of waterborne diseases.
Impact of Groundwater Contamination
- Public Health Risks: Consumption of contaminated groundwater can lead to various health issues, including gastrointestinal disorders, neurological problems, skeletal deformities, and even cancer.
- Common Contaminants and Health Impacts:
- Arsenic: Chronic exposure can lead to black foot disease and poses significant health risks.
- Fluoride: High fluoride intake causes neuromuscular disorders, dental deformities, and skeletal fluorosis.
- Nitrates: Excessive nitrate levels in water can result in methemoglobinemia and blue baby syndrome.
- Uranium: Elevated uranium levels in drinking water can cause kidney toxicity.
- Radon: Presence of radioactive radon in groundwater poses risks of lung cancer.
- Economic Burden: Treating water-related illnesses imposes significant healthcare costs on individuals and communities. Productivity losses due to sickness also impact economic development.
- Environmental Degradation: Contaminated groundwater affects ecosystems, harming aquatic life and disrupting biodiversity. It can also degrade soil quality and impair agricultural productivity.
- Social Inequities: Communities reliant on contaminated groundwater often face socio-economic challenges, including limited access to safe drinking water, reduced educational opportunities, and compromised livelihoods.
- Long-Term Consequences: Groundwater contamination can persist for decades or even centuries, posing ongoing risks to human health and the environment. Remediation efforts may require substantial time, resources, and technological interventions.
Fact Box:Water Governance
Government Initiatives related to water management and conservation:
|
PYQPrelims Question Q. Which of the following can be found as pollutants in the drinking water in some parts of India? (2013)
Select the correct answer using the codes given below.
Solution: (c) Mains Question Q: The effective management of land and water resources will drastically reduce the human miseries. Explain. [2016] |


Prelims Articles
Context
Last year, the Geological Survey of India (GSI), announced that it had established lithium reserve of 5.9 MT in Jammu & Kashmir’s Reasi district, putting India among the top 10 countries with such reserves. However, private companies have been reluctant to bid.
About Lithium:
- Lithium (Li) is a non-ferrous metaland is one of the key components in EV batteries.
- It's a silvery-white metal with a delicate texture.
- It is the lightest metal and the lightest solid element under normal circumstances.
- It must be kept in mineral oil since it is very reactive and combustible.
- It is both an alkali and a rare metal.
- Application: Rechargeable batteries for mobile phones, laptops, digital cameras and electric vehicles. Lithium is also used in some non-rechargeable batteries for things like heart pacemakers, toys and clocks.
Why Lithium is a Significant Material?
- Increased Applicability: Growing demand for bulk energy storage in renewable energy applications, notably in electric vehicles (EVs) and backup electric storage systems.
- Advantages of Lithium-ion Batteries: Good rate of charging and longer lifespan compared to other battery types. Higher energy density, enhancing battery performance.
- Wide Usage: Apart from batteries, used in various industries including glass, ceramics, rocket fuel, and lasers.
How Critical is Lithium for India?
- Importance in Electric Mobility: Crucial for India's focus on electric mobility in major cities like New Delhi, Mumbai, Bangalore, Kolkata, and Chennai.
- Strategic Significance: Considered strategically important due to its applications in nuclear and high-tech industries, including electronics, telecommunications, information technology, space, and defense.


Prelims Articles
Context
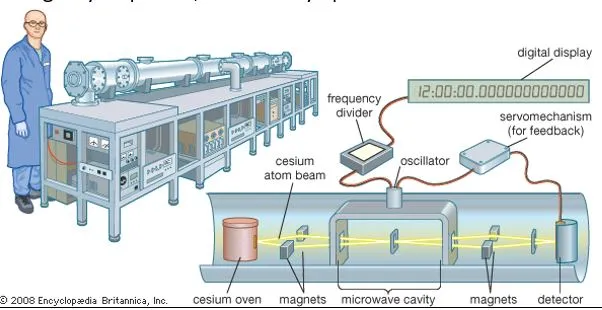
A recent study introduced a portable optical atomic clock suitable for onboard ships. This innovation, utilizing molecular iodine as a frequency standard, represents a significant advancement in optical timekeeping. Miniaturization of components like the spectrometer, laser system, and frequency comb enables compact designs suitable for various applications.
Key-highlights:
- Testing: Initial tests demonstrated the stability and accuracy of these portable optical atomic clocks.
- The clocks exhibited resilience to environmental factors like temperature fluctuations and humidity changes.
- Features:
- Optical atomic clocks operate at optical frequencies, leveraging lasers to stimulate atomic transitions.
- The coherent light emitted by lasers ensures precise and stable measurements.
- Strontium (Sr) and ytterbium ions are commonly used in optical atomic clocks due to their narrow linewidths and stable optical transitions.
- Accuracy: While not as accurate as laboratory-based optical atomic clocks, these portable variants offer sufficient precision for real-world applications.
- Quality: accuracy, portability, and robustness
- Application: poised to revolutionize various industries, from maritime navigation to space exploration
Fact Box: About Atomic clock
|


Prelims Articles
Context
The United Nations has declared 2025 as the International Year of Quantum Science and Technology to increase public awareness of the importance of quantum science and to bolster support for using it to address current challenges.
What is Quantum Computing?
- Quantum computing is a revolutionary field at the intersection of computer science, physics, and mathematics.
- It harnesses the principles of quantum mechanics to solve complex problems faster than classical computers.
- This advantage stems from leveraging quantum phenomena like superposition and entanglement.
- Types of Quantum Technologies Various qubit technologies are being explored, including gate-based ion trap processors, gate-based superconducting processors, photonic processors, neutral atom processors, Rydberg atom processors, and quantum annealers.
- In 2023, India became the seventh country to have a National Quantum Mission, after the US, Austria, Finland, France, Canada and China, dedicated to the development of quantum technologies.
Quantum Mechanics Basics
- Quantum mechanics explores the behavior of particles at a microscopic scale. In this realm, particles behave differently from what we observe in the macroscopic world. Key to quantum computing is the concept of qubits, which can exist in superposition states, unlike classical bits.
- A qubit (or quantum bit) is the quantum mechanical analogue of a classical bit.
Principles of Quantum Computing
- Superposition: Qubits can exist in multiple states simultaneously, providing inherent parallelism for quantum computers.
- Entanglement: When qubits become entangled, the state of one qubit instantly correlates with another, regardless of distance.
- Decoherence: Environmental factors can disrupt the quantum state of qubits, leading to decoherence. Overcoming this challenge is crucial for building stable quantum computers.
Applications of Quantum Computing
Quantum computing holds immense potential across industries:
- Machine Learning: Quantum computing can enhance data analysis and prediction capabilities.
- Optimization: Quantum algorithms can optimize complex processes, leading to cost reduction and efficiency improvements.
- Simulation: Quantum computers can tackle simulations that are currently intractable for classical computers, particularly in chemistry and materials science.
Use Cases in Various Industries
Industries are exploring quantum computing for diverse applications:
- Machine Learning: Predicting market movements and improving manufacturing operations.
- Optimization: Optimizing loan portfolios, supply chains, and production processes.
- Simulation: Conducting accurate simulations in chemistry and materials science, enabling breakthroughs in drug discovery and materials research.
PYQQ: Which one of the following is the context in which the term “Qubit” is mentioned? (2022)
Solution: (b) |


Prelims Articles
Context
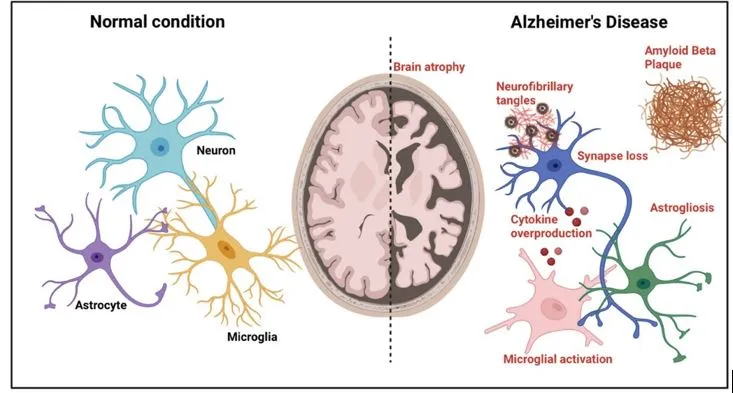
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has unanimously voted in favor of administering Donanemab, a new Alzheimer's drug.
What is Donanemab?
- Donanemab is a monoclonal antibody, much like its predecessor Lecanemab, designed to target amyloid beta protein plaques in the brain, a characteristic feature of Alzheimer's disease that can be observed through imaging techniques.
- Other amyloid-fighting drugs, such as Leqembi and Biogen, were approved by the FDA last year.
- Donanemab can significantly slow down cognitive decline in early Alzheimer's patients by 35.1% over a span of 76 weeks.
- It is currently the only one of its class available to Alzheimer’s patients, outside clinical trials.
Side Effects and Risks
- Studies indicate that it may result in slightly higher adverse events compared to Lecanemab.
- Apart from infusion-related reactions, the main concern lies in amyloid-related imaging abnormalities (ARIA), including brain swelling and bleeding.
- The study revealed that 24% of participants experienced ARIA involving brain swelling, and 19.7% had ARIA involving brain bleeds. However, it's worth noting that most of these cases were asymptomatic.
Fact Box: Alzheimer's Disease
|


Prelims Articles
|
S.No. |
Term |
About |
|
1. |
Dementia |
Dementia is a general term that represents a group of diseases and illnesses that affect your thinking, memory, reasoning, personality, mood and behavior. T |
|
2. |
Gross enrollment ratio (GER) |
Gross enrollment ratio (GER) is an indicator of educational progress. It calculates by dividing enrollments by corresponding population in that age group. |
|
3. |
Geogenic processes |
Geogenic processes refer to natural processes that occur within the Earth's lithosphere, hydrosphere, atmosphere, and biosphere, leading to the formation and transformation of geological materials and landscapes. |
|
4. |
Qubit |
A qubit (or quantum bit) is the quantum mechanical analogue of a classical bit. |


Editorials
Context
The rapid credit growth in India has raised concerns about a potential financial crisis. The situation is exacerbated by an unregulated financial sector, unsustainable household debt, and a dangerous narrative of economic prosperity fueled by credit expansion.
A Lofty and Dangerous Narrative:
- Unhinged Hype: India is experiencing a credit boom driven by policymakers promoting the narrative of financial innovation and inclusion through digital infrastructure. This hype has led to a poorly regulated financial sector and increased consumer debt.
- Applauding Credit Surge: Both international and domestic analysts have praised India's financial sector growth, citing robust bank lending and low non-performing assets. For instance, the IMF and NCAER highlighted a 20% increase in bank lending in recent reviews.
- Debt-Fueled Prosperity: The surge in lending, particularly for personal loans, masks deeper issues such as job deficits and human capital deficiencies. When lending slows, the financial sector's apparent health is at risk, potentially leading to an economic crunch.
Household Debt and Economic Risks:
- Household Debt Boom: The expansion of household lending, growing at 25-30% annually, is considered a "bad" boom. It drives up domestic prices without enhancing productive capacity, making the economy less competitive.
- Unsecured Loans: A significant portion of household loans, about a quarter, is unsecured, with credit card debt being a major component. The number of credit cards in India rose from 20 million in 2011 to nearly 100 million in 2024, often extended to low-creditworthy individuals.
- Debt-Service Burden: Despite household debt being 40% of GDP, the debt-service-to-income ratio is 12%, one of the highest globally. This situation mirrors the pre-crisis conditions in the US and Spain before the 2008 financial crisis.
Challenges of Regulation and Preventive Measures:
- Chaotic Financial Services Industry: The financial sector in India is characterized by a large number of providers, including banks, NBFCs, and fintech companies, many with dubious practices. The pressure to generate profits has led to increased lending to households rather than productive sectors.
- Scams and Misuse: Since economic liberalization in 1991, financial scams have proliferated. Post-COVID-19, fintechs and NBFCs have targeted households with high-interest loans, leading to a cycle of debt and addiction to credit.
- Preventive Measures: To avert the crisis, the financial services industry needs to be downsized to align with productive borrowing needs. Policy changes should include weakening the rupee to boost exports and mitigate the downturn.
UPSC Mains Questions:
Q. Examine the impact of rapid credit growth on the financial stability of an economy. Discuss the potential risks associated with unregulated expansion of household debt


Editorials
Context
The Supreme Court's recent judgments significantly impact the rights of the accused and the practices of investigating agencies. These rulings address the necessity of custody before filing a charge sheet and the requirement to inform the accused of the grounds of arrest in writing.
Filing of Charge Sheet:
- Siddharth v. State of Uttar Pradesh (2021): The Supreme Court ruled that custody is not required for filing a charge sheet if the accused cooperates and the investigation can be completed without arrest. Section 170 of the CrPC does not mandate presenting the accused in custody when filing the charge sheet.
- Relief for Investigating Officers: This judgment provides relief to investigating officers (IOs), particularly in riot cases or when numerous accused are involved. It allows for filing charge sheets without needing all accused in custody, provided they are unlikely to abscond or disobey summons.
- Challenges in Implementation: Despite the ruling, IOs face practical difficulties in complying with this directive, such as courts not accepting charge sheets without the accused present or setting arbitrary limits on the number of charge sheets accepted per day.
Grounds of Arrest:
- Pankaj Bansal v. Union of India (2023): The Supreme Court emphasized the constitutional right under Article 22 and statutory mandate of Section 19(1) of the PMLA, requiring the grounds of arrest to be provided in writing. This ensures the accused can seek legal counsel and bail based on clearly stated facts.
- Extension to UAPA: In Prabir Purkayastha v. State (NCT of Delhi), the Court reiterated that the provision for informing the grounds of arrest applies equally under the UAPA. The grounds must contain specific details justifying the arrest, beyond mere formal parameters.
- Criminal Procedure Code (CrPC): Section 50(1) of the CrPC requires informing the accused of the grounds of arrest. The arrest memo must include details of the offense, date, place, time of arrest, and be signed by both the IO and the accused. However, there is no requirement to provide a copy of the arrest memo to the accused.
Policy Implications and Enforcement:
- Strengthening Legal Rights: The Supreme Court's directives aim to strengthen the legal rights of the accused, ensuring transparency and fairness in the arrest process. Providing written grounds of arrest aligns with constitutional protections and helps the accused mount an effective defense.
- Challenges for Law Enforcement: Implementing these directives may pose challenges for law enforcement, particularly in ensuring compliance and training officers to adhere to the new requirements.
- Potential Legal Amendments: To fully realize these protections, amendments to the CrPC may be necessary to mandate providing a copy of the arrest memo to the accused, thus enhancing accountability and adherence to constitutional mandates.
UPSC Mains Questions:
Q. Analyse the challenges faced by investigating officers in filing charge sheets in criminal courts. What measures can be taken to address these challenges?


Editorials
Context
China's advancements in small modular reactors (SMRs) and the strategic implications for India highlight the urgent need for India to accelerate its own SMR program and collaborate with the United States to counterbalance China's growing influence.
China’s Advancements in Small Modular Reactors:
- Linglong One SMR: China reached a significant milestone by installing the core module of the Linglong One SMR in Hainan Province. This reactor exemplifies the advantages of SMRs, such as size, portability, safety, and cost-effectiveness.
- Expansion of Nuclear Capacity: China’s nuclear energy program is set to surpass the US in total nuclear power capacity within the next decade. Nearly two dozen reactors are under construction, with the Linglong One’s commissioning imminent.
- Strategic Exports: China is poised to export SMRs globally, especially in South Asia, thereby extending its influence. Past collaborations with Pakistan at the Chashma Complex exemplify this strategy.
Strategic Implications for India:
- Growing Chinese Influence: China’s nuclear exports could lead to long-term dependencies for recipient countries, potentially compromising their sovereignty through unsustainable financing models akin to the Hambantota Port scenario in Sri Lanka.
- US Concerns: US officials have expressed concerns over China’s plans for floating nuclear reactors in disputed areas like the South China Sea. These reactors could exacerbate regional tensions and impact India’s strategic interests.
- India’s Urgent Response: India needs to expedite its SMR program, leveraging international collaboration, particularly with the US, to counterbalance China’s advancements and maintain strategic stability in the region.
Policy Recommendations for India:
- Public-Private Partnerships with the US: India should forge a robust SMR partnership with the US, building on the nuclear cooperation agreed upon during Prime Minister Modi’s state visit to Washington in June 2023. Addressing policy and regulatory challenges, such as India’s nuclear liability law, is crucial.
- Access to Advanced Technologies: Collaboration with American companies like Holtec International can provide India with cutting-edge SMR technologies, facilitating deployment in diverse environments and utilizing existing infrastructure.
- Strengthening Domestic Ecosystem: An SMR partnership would enhance India’s manufacturing capabilities, create jobs, and align with Modi’s Atmanirbhar Bharat vision. Establishing a regional SMR grouping can advance India’s climate and foreign policy goals.
UPSC Mains Questions:
Q. Analyze the role of small modular reactors in India’s energy strategy. How can international collaborations enhance India’s capabilities and contribute to its climate and foreign policy objectives?